| Previous | Next | Contents | Index | Navigation | Glossary | Library |
Required and available capacity are stated in hours per week per resource.

Routing-based CRP treats repetitive schedules as if they were planned orders for each day in the period spanned by the schedule start and end dates. Thus, for the repetitive schedules, order quantity is the suggested daily rate.
For planned orders for items that use Lot basis resources, routing-based CRP calculates required hours using the following formula. Notice that for Lot basis resources, the order quantity has no impact on required hours.

The following table shows four plan entries for C, and illustrates how, for each entry, routing-based CRP calculates required hours and dates for D1, R2. Remember that from the resource requirements loaded from Oracle Bills of Material, Oracle Capacity determined that 8 hours of D1, R2 are required to build one unit of C, and that the resource offset for D1, R2 is 0.5. Assume a lead time of 2 days for building C. In this example, 18 units of C are required on 03-FEB. These 18 units represent derived demand from the discrete job for 6 units of A due on 07-FEB. Routing-based CRP calculates the required hours for D1, R2 as 18 x 8 = 144 hours. Routing-based CRP calculates the required date as 03-FEB - (2 x (1 - 0.5)) = 03-FEB - 1 = 02-FEB. 05-FEB and 06-FEB are non workdays.
| Item | Plan Date | Plan Qty | Required Hours | Required Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 03-FEB | 18 | 144 | 02-FEB |
| A | 03-FEB | 12 | 96 | 02-FEB |
| A | 08-FEB | 30 | 240 | 07-FEB |
| A | 11-FEB | 30 | 240 | 10-FEB |
| Table 1 - 20. Required Hours and Required Dates for D1, R2 (Page 1 of 1) | ||||
The following table illustrates how routing-based CRP uses required dates to bucket the required hours for D1, R2 into weekly buckets. The example assumes that the first bucket starts on 31-JAN.
| Week Start Date | Department | Resource | Required Hours |
|---|---|---|---|
| 31-JAN | D1 | R2 | 240 |
| 07-FEB | D1 | R2 | 480 |
| Table 1 - 21. Bucketed Required Hours and Required Dates for D1, R1 (Page 1 of 1) | |||
Routing-based CRP treats suggested repetitive schedules as if they were planned orders for each workday between the schedule start date and the schedule end date, and calculates required hours and required dates using the same calculations illustrated in the previous example.

Since the Snapshot loads operation start dates directly from Oracle Work in Process, required dates are already known and there is no need for routing-based CRP to calculate them.
Oracle Capacity calculates required hours and dates for all discrete and non-standard jobs, and adds them to the required hours and dates calculated for planned orders and repetitive schedules for each resource.
You can define resources, departments, shifts, and shift calendars in Oracle Bills of Material. Having defined your departments, resources, and shifts, you can assign shifts to resources and resources to departments.
Routing-based CRP calculates available hours for a resource by summing the available hours for each shift that uses the resource using the following formula:
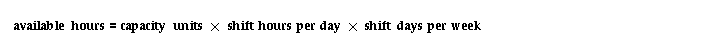
For 24-hour resources, routing-based CRP modifies the formula as follows:

Capacity units represents the number of resource units available to a department. Shift hours per day and shift days per week reflect the availability times you specify for each shift in Oracle Bills of Material. Workdays per week reflect the number of workdays in the week based on the workday calendar you define in Oracle Bills of Material.
The following table illustrates how routing-based CRP would calculate available hours for D1, R2, assuming that you have assigned it to two shifts, Shift 1 and Shift 2. In this example, the available hours for D1, R2 on Shift 1 is 2 x 6 x 5 = 60 hours. Routing-based CRP would calculate the total hours available for D1, R2 as 60 + 80 = 140 hours per week.
| Shift | Capacity Units | Shift Hours/Day | Shift Days/Week | Available Hours |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shift 1 | 2 | 6 | 5 | 60 |
| Shift 2 | 2 | 8 | 5 | 80 |
| Table 1 - 22. Available Hours for D1, R2 (Page 1 of 1) | ||||

The following table illustrates how routing-based CRP would calculate capacity utilization for D1, R2 for the weeks starting 31-JAN and 07-FEB. In the Resource Requirements Snapshot Example, the capacity utilization for D1, R2, for the week starting 31-JAN, is 240/140 x 100% = 71%.
| Week Start Date | Required Hours | Available Hours | Capacity Utilization |
|---|---|---|---|
| 31-JAN | 240 | 140 | 171% |
| 07-FEB | 480 | 140 | 343% |
| Table 1 - 23. Capacity Utilization for D1, R2 (Page 1 of 1) | |||
Notice that D1, R2 is overloaded for both weeks.
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index | Navigation | Glossary | Library |