| Previous | Next | Contents | Index | Navigation | Glossary | Library |
Initial Mass Copy copies all the assets added to your corporate book before the end of the current tax fiscal year into the open accounting period in your tax book. The following graphic illustrates the Initial Mass Copy process. In the following example, your fiscal year is from January to December. Your corporate book open accounting period is February 1994 and your tax book open period is December 1993.
When using Initial Mass Copy for the first time in your tax book, you can run it as many times as necessary for the first period to copy all existing assets. When you rerun the process, Initial Mass Copy only looks at assets which it did not copy into the tax book during previous attempts, so no data is duplicated.
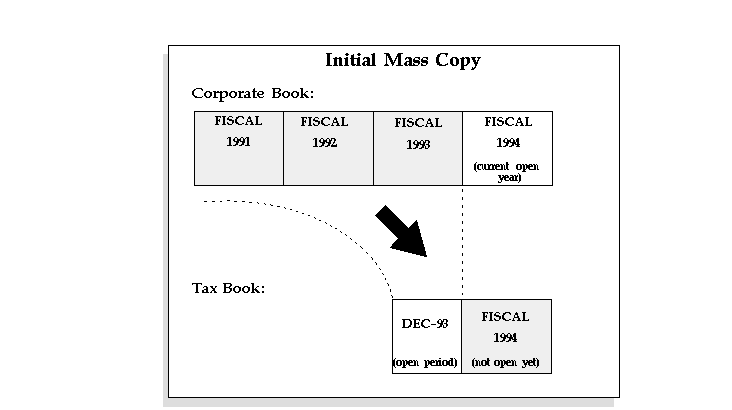
Initial Mass Copy does not copy assets retired before the end of that year or assets added after the end of that year. You do not need to copy any adjustments or partial retirements you performed before the end of the fiscal year. When you close this initial period, Oracle Assets calculates the net book value of your assets that have zero accumulated depreciation in the tax book, and opens the next period.
When the Initial Mass Copy program copies an asset into a tax book, the following basic financial information comes from the corporate book:
For subcomponent assets, copy the parent asset first. Then copy the subcomponent asset, defaulting the asset life according to the subcomponent life rule you defined for the tax category and the parent asset life. You must set up the depreciation method for the subcomponent asset life before you can use the method and life. If your subcomponent asset uses straight-line depreciation, Oracle Assets sets up the depreciation method for the calculated life for you. If the depreciation method is not straight-line, and not already set up for the subcomponent life rule default, Oracle Assets uses the asset category default life.
Updating a Tax Book with Assets and Transactions
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index | Navigation | Glossary | Library |