Release 1 (9.0.1)
Part Number A87502-01
Home |
Book List |
Contents |
Index | Master Index | Feedback |
| Oracle9i
Replication Management API Reference Release 1 (9.0.1) Part Number A87502-01 |
|
This chapter illustrates how to create a master group at a master replication site. This chapter contains these topics:
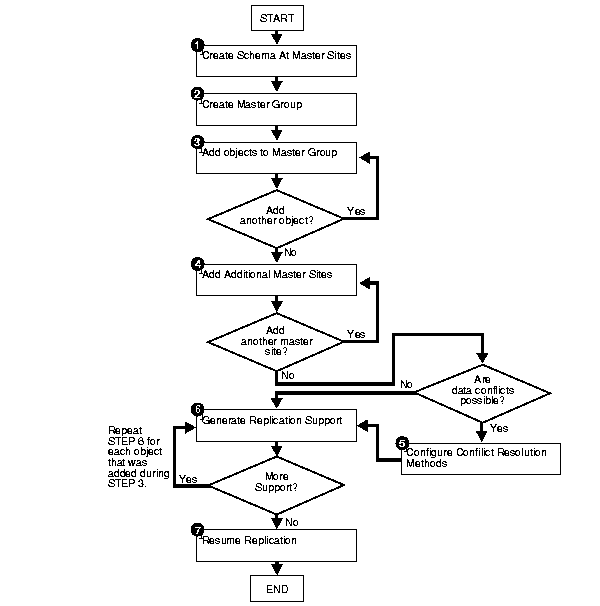
After you have set up your master sites, you are ready to build a master group. As illustrated in Figure 3-2, you need to follow a specific sequence to successfully build a replication environment.
In this chapter, you create the hr_repg master group and replicate the objects illustrated in Figure 3-1.
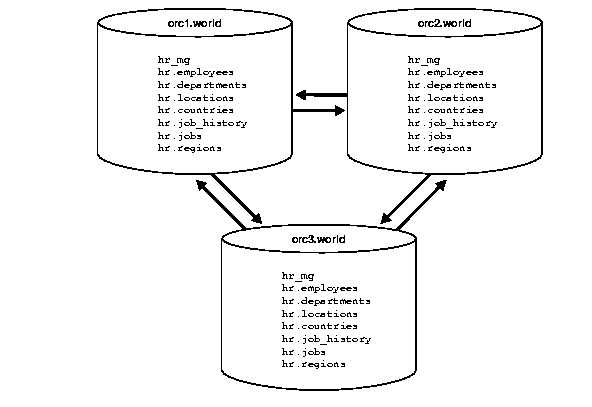
In order for the script in this chapter to work as designed, it is assumed that the hr schema exists
at orc1.world, orc2.world, and orc3.world. The hr schema
includes the following database objects:
countries table
departments table
employees table
jobs table
job_history table
locations table
regions table
dept_location_ix index
emp_department_ix index
emp_job_ix index
emp_manager_ix index
jhist_department_ix index
jhist_employee_ix index
jhist_job_ix index
loc_country_ix index
The indexes listed are the indexes based on foreign key columns in the hr schema. When replicating
tables with foreign key referential constraints, Oracle Corporation recommends that you always index foreign key
columns and replicate these indexes, unless no updates and deletes are allowed in the parent table. Indexes are
not replicated automatically.
By default, the hr schema is installed automatically when you install Oracle9i. The example script in this chapter assumes that the hr schema exists at all master sites
and that the schema contains all of these database objects at each site. The example script also assumes that the
tables contain the data that is inserted automatically during Oracle installation. If the hr schema
is not installed at your replication sites, then you can install it manually.
|
See Also:
Oracle9i Sample Schemas for information about the
|
Complete the following steps to create the hr_repg master group.
/************************* BEGINNING OF SCRIPT ******************************
If the schema does not already exist at all of the master sites participating in the master group, then create the
schema now and grant it all of the necessary privileges. This example uses the hr schema, which is
one of the sample schemas that are installed by default when you install Oracle. So, the hr schema
should exist at all master sites.
*/ PAUSE Press <RETURN> to continue when the schema exists at all master sites. /*
Use the CREATE_MASTER_REPGROUP procedure to define a new master group. When you add an object to your
master group or perform other replication administrative tasks, you reference the master group name defined during
this step. This step must be completed by the replication administrator.
*/ CONNECT repadmin/repadmin@orc1.world BEGIN DBMS_REPCAT.CREATE_MASTER_REPGROUP ( gname => 'hr_repg'); END; / /*
Use the CREATE_MASTER_REPOBJECT procedure to add an object to your master group. In most cases, you
probably will be adding tables and indexes to your master group, but you can also add procedures, views, synonyms,
and so on.
*/ BEGIN DBMS_REPCAT.CREATE_MASTER_REPOBJECT ( gname => 'hr_repg', type => 'TABLE', oname => 'countries', sname => 'hr', use_existing_object => TRUE, copy_rows => FALSE); END; / BEGIN DBMS_REPCAT.CREATE_MASTER_REPOBJECT ( gname => 'hr_repg', type => 'TABLE', oname => 'departments', sname => 'hr', use_existing_object => TRUE, copy_rows => FALSE); END; / BEGIN DBMS_REPCAT.CREATE_MASTER_REPOBJECT ( gname => 'hr_repg', type => 'TABLE', oname => 'employees', sname => 'hr', use_existing_object => TRUE, copy_rows => FALSE); END; / BEGIN DBMS_REPCAT.CREATE_MASTER_REPOBJECT ( gname => 'hr_repg', type => 'TABLE', oname => 'jobs', sname => 'hr', use_existing_object => TRUE, copy_rows => FALSE); END; / BEGIN DBMS_REPCAT.CREATE_MASTER_REPOBJECT ( gname => 'hr_repg', type => 'TABLE', oname => 'job_history', sname => 'hr', use_existing_object => TRUE, copy_rows => FALSE); END; / BEGIN DBMS_REPCAT.CREATE_MASTER_REPOBJECT ( gname => 'hr_repg', type => 'TABLE', oname => 'locations', sname => 'hr', use_existing_object => TRUE, copy_rows => FALSE); END; / BEGIN DBMS_REPCAT.CREATE_MASTER_REPOBJECT ( gname => 'hr_repg', type => 'TABLE', oname => 'regions', sname => 'hr', use_existing_object => TRUE, copy_rows => FALSE); END; / BEGIN DBMS_REPCAT.CREATE_MASTER_REPOBJECT ( gname => 'hr_repg', type => 'INDEX', oname => 'dept_location_ix', sname => 'hr', use_existing_object => TRUE, copy_rows => FALSE); END; / BEGIN DBMS_REPCAT.CREATE_MASTER_REPOBJECT ( gname => 'hr_repg', type => 'INDEX', oname => 'emp_department_ix', sname => 'hr', use_existing_object => TRUE, copy_rows => FALSE); END; / BEGIN DBMS_REPCAT.CREATE_MASTER_REPOBJECT ( gname => 'hr_repg', type => 'INDEX', oname => 'emp_job_ix', sname => 'hr', use_existing_object => TRUE, copy_rows => FALSE); END; / BEGIN DBMS_REPCAT.CREATE_MASTER_REPOBJECT ( gname => 'hr_repg', type => 'INDEX', oname => 'emp_manager_ix', sname => 'hr', use_existing_object => TRUE, copy_rows => FALSE); END; / BEGIN DBMS_REPCAT.CREATE_MASTER_REPOBJECT ( gname => 'hr_repg', type => 'INDEX', oname => 'jhist_department_ix', sname => 'hr', use_existing_object => TRUE, copy_rows => FALSE); END; / BEGIN DBMS_REPCAT.CREATE_MASTER_REPOBJECT ( gname => 'hr_repg', type => 'INDEX', oname => 'jhist_employee_ix', sname => 'hr', use_existing_object => TRUE, copy_rows => FALSE); END; / BEGIN DBMS_REPCAT.CREATE_MASTER_REPOBJECT ( gname => 'hr_repg', type => 'INDEX', oname => 'jhist_job_ix', sname => 'hr', use_existing_object => TRUE, copy_rows => FALSE); END; / BEGIN DBMS_REPCAT.CREATE_MASTER_REPOBJECT ( gname => 'hr_repg', type => 'INDEX', oname => 'loc_country_ix', sname => 'hr', use_existing_object => TRUE, copy_rows => FALSE); END; / /*
After you have defined your master group at the master definition site (the site where the master group was
created becomes the master definition site by default), you can define the other sites that will participate in
the replication environment. You might have guessed that you will be adding the orc2.world and
orc3.world sites to the replication environment. This example creates the master group at all master
sites, but you have the option of creating the master group at one master site now and adding additional master
sites later without quiescing the database. In this case, you can skip this step.
In this example, the use_existing_objects parameter in the ADD_MASTER_DATABASE procedure
is set to TRUE because it is assumed that the hr schema already exists at all master sites. In other
words, it is assumed that the objects in the hr schema are precreated at all master sites. Also, the
copy_rows parameter is set to FALSE because it is assumed that the identical data is
stored in the tables at each master site.
*/ BEGIN DBMS_REPCAT.ADD_MASTER_DATABASE ( gname => 'hr_repg', master => 'orc2.world', use_existing_objects => TRUE, copy_rows => FALSE, propagation_mode => 'ASYNCHRONOUS'); END; / /*
*/ PAUSE Press <RETURN> to continue. BEGIN DBMS_REPCAT.ADD_MASTER_DATABASE ( gname => 'hr_repg', master => 'orc3.world', use_existing_objects => TRUE, copy_rows => FALSE, propagation_mode => 'ASYNCHRONOUS'); END; / /*
*/ PAUSE Press <RETURN> to continue. /*
Chapter 6, "Configure Conflict Resolution" for information about configuring
conflict resolution methods
See Also:
*/ PAUSE Press <RETURN> to continue after configuring conflict resolution methods or if no conflict resolution methods are required. /*
*/ BEGIN DBMS_REPCAT.GENERATE_REPLICATION_SUPPORT ( sname => 'hr', oname => 'countries', type => 'TABLE', min_communication => TRUE); END; / BEGIN DBMS_REPCAT.GENERATE_REPLICATION_SUPPORT ( sname => 'hr', oname => 'departments', type => 'TABLE', min_communication => TRUE); END; / BEGIN DBMS_REPCAT.GENERATE_REPLICATION_SUPPORT ( sname => 'hr', oname => 'employees', type => 'TABLE', min_communication => TRUE); END; / BEGIN DBMS_REPCAT.GENERATE_REPLICATION_SUPPORT ( sname => 'hr', oname => 'jobs', type => 'TABLE', min_communication => TRUE); END; / BEGIN DBMS_REPCAT.GENERATE_REPLICATION_SUPPORT ( sname => 'hr', oname => 'job_history', type => 'TABLE', min_communication => TRUE); END; / BEGIN DBMS_REPCAT.GENERATE_REPLICATION_SUPPORT ( sname => 'hr', oname => 'locations', type => 'TABLE', min_communication => TRUE); END; / BEGIN DBMS_REPCAT.GENERATE_REPLICATION_SUPPORT ( sname => 'hr', oname => 'regions', type => 'TABLE', min_communication => TRUE); END; / /*
*/ PAUSE Press <RETURN> to continue. /*
After creating your master group, adding replication objects, generating replication support, and adding
additional master databases, you need to resume replication activity. The RESUME_MASTER_ACTIVITY
procedure procedure "turns on" replication for the specified master group.
*/ BEGIN DBMS_REPCAT.RESUME_MASTER_ACTIVITY ( gname => 'hr_repg'); END; /
/************************* END OF SCRIPT **********************************/
|
|
 Copyright © 1996-2001, Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|