Release 1 (9.0.1)
Part Number A90125-01
Home |
Book List |
Contents |
Index | Master Index | Feedback |
| Oracle9i SQL Reference Release 1 (9.0.1) Part Number A90125-01 |
|
SQL Statements:
ALTER TRIGGER to constraint_clause, 5 of 12
Use the ALTER VIEW statement to explicitly recompile a view that is invalid. Explicit recompilation lets you locate recompilation errors before run time. You may want to recompile a view explicitly after altering one of its base tables to ensure that the alteration does not affect the view or other objects that depend on it.
You can also use ALTER VIEW to define, modify, or drop view constraints.
When you issue an ALTER VIEW statement, Oracle recompiles the view regardless of whether it is valid or invalid. Oracle also invalidates any local objects that depend on the view.
|
See Also:
|
The view must be in your own schema or you must have ALTER ANY TABLE system privilege.
alter_view::=
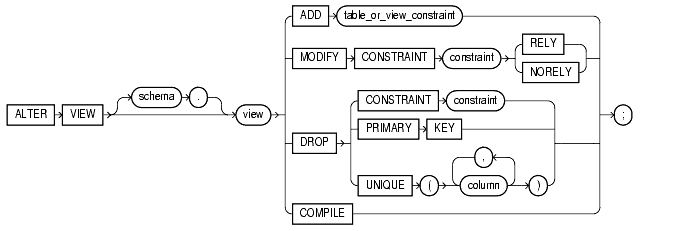
alter_view
table_or_view_constraint: See constraint_clause.
Specify the schema containing the view. If you omit schema, Oracle assumes the view is in your own schema.
Specify the name of the view to be recompiled.
Use the ADD clause to add a constraint to view.
Use the MODIFY CONSTRAINT clause to change the RELY or NORELY setting of an existing view constraint.
Restriction: You cannot change the setting of a unique or primary key constraint if it is part of a referential integrity constraint without dropping the foreign key or changing its setting to match that of view.
Use the DROP clause to drop an existing view constraint.
Restriction: You cannot drop a unique or primary key constraint if it is part of a referential integrity constraint on a view.
The COMPILE keyword is required. It directs Oracle to recompile the view.
To recompile the view customer_view, issue the following statement:
ALTER VIEW bombay_inventory COMPILE;
If Oracle encounters no compilation errors while recompiling customer_view, customer_view becomes valid. If recompiling results in compilation errors, Oracle returns an error and customer_view remains invalid.
Oracle also invalidates all dependent objects. These objects include any procedures, functions, package bodies, and views that reference customer_view. If you subsequently reference one of these objects without first explicitly recompiling it, Oracle recompiles it implicitly at run time.
|
|
 Copyright © 1996-2001, Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|