Release 2 (9.2)
Part Number A96612-01
Home |
Book List |
Contents |
Index |
 Master Index |
 Feedback |
| Oracle9i Supplied PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference Release 2 (9.2) Part Number A96612-01 |
|
DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER, 2 of 2
This procedure creates entries which define resource plans. For release 8.2, max_active_sess_target_mth was renamed active_sess_pool_mth and new_queueing_mth was added.
DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.CREATE_PLAN ( plan IN VARCHAR2, comment IN VARCHAR2, cpu_mth IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT 'EMPHASIS', active_sess_pool_mth IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT 'ACTIVE_SESS_POOL_ABSOLUTE', parallel_degree_limit_mth IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT 'PARALLEL_DEGREE_LIMIT_ABSOLUTE', queueing_mth IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT 'FIFO_TIMEOUT',);
This procedure creates a single-level resource plan containing up to eight consumer groups in one step. You do not need to create a pending area manually before creating a resource plan, or use the CREATE_CONSUMER_GROUP and CREATE_RESOURCE_PLAN_DIRECTIVES procedures separately.
DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.CREATE_SIMPLE_PLAN ( SIMPLE_PLAN IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT, CONSUMER_GROUP1 IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT, GROUP1_CPU IN NUMBER DEFAULT, CONSUMER_GROUP2 IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT, GROUP2_CPU IN NUMBER DEFAULT, CONSUMER_GROUP3 IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT, GROUP3_CPU IN NUMBER DEFAULT, CONSUMER_GROUP4 IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT, GROUP4_CPU IN NUMBER DEFAULT, CONSUMER_GROUP5 IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT, GROUP5_CPU IN NUMBER DEFAULT, CONSUMER_GROUP6 IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT, GROUP6_CPU IN NUMBER DEFAULT, CONSUMER_GROUP7 IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT, GROUP7_CPU IN NUMBER DEFAULT, CONSUMER_GROUP8 IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT, GROUP8_CPU IN NUMBER DEFAULT);
This procedure updates entries which define resource plans.For release 8.2 new_max_active_sess_target_mth was renamed new_active_sess_pool_mth and new_queueing_mth was added.
DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.UPDATE_PLAN ( plan IN VARCHAR2, new_comment IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL, new_cpu_mth IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL, new_active_sess_pool_mth IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL, new_parallel_degree_limit_mth IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL, new_queueing_mth IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL, new_group_switch_mth IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL);
If the parameters to UPDATE_PLAN are not specified, then they remain unchanged in the data dictionary.
This procedure deletes the specified plan as well as all the plan directives to which it refers.
DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.DELETE_PLAN ( plan IN VARCHAR2);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
plan |
Name of resource plan to delete. |
This procedure deletes the specified plan and all of its descendants (plan directives, subplans, consumer groups). Mandatory objects and directives are not deleted.
DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.DELETE_PLAN_CASCADE ( plan IN VARCHAR2);
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
|
plan |
Name of plan. |
If DELETE_PLAN_CASCADE encounters any error, then it rolls back, and nothing is deleted.
|
Note: If you want to use any default resource allocation method, then you do not need not specify it when creating or updating a plan. |
Defaults are:
cpu_method = EMPHASISparallel_degree_limit_mth = PARALLEL_DEGREE_LIMIT_ABSOLUTEMAX_ACTIVE_SESS_ABSOLUTE
This procedure lets you create entries which define resource consumer groups.
DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.CREATE_CONSUMER_GROUP ( consumer_group IN VARCHAR2, comment IN VARCHAR2, cpu_mth IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT 'ROUND-ROBIN');
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
consumer_group |
Name of consumer group. |
|
comment |
User's comment. |
|
cpu_mth |
Name of CPU resource allocation method. |
This procedure lets you update entries which define resource consumer groups.
DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.UPDATE_CONSUMER_GROUP ( consumer_group IN VARCHAR2, new_comment IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL, new_cpu_mth IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
consumer_group |
Name of consumer group. |
|
new_comment |
New user's comment. |
|
new_cpu_mth |
Name of new method for CPU resource allocation. |
If the parameters to the UPDATE_CONSUMER_GROUP procedure are not specified, then they remain unchanged in the data dictionary.
This procedure lets you delete entries which define resource consumer groups.
DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.DELETE_CONSUMER_GROUP ( consumer_group IN VARCHAR2);
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
|
consumer_group |
Name of consumer group to be deleted. |
This procedure lets you create resource plan directives.For release 8.2 new_max_active_sess_target_mth was renamed new_active_sess_pool_mth and several new parameters added.
DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.CREATE_PLAN_DIRECTIVE ( plan IN VARCHAR2, group_or_subplan IN VARCHAR2, comment IN VARCHAR2, cpu_p1 IN NUMBER DEFAULT NULL, cpu_p2 IN NUMBER DEFAULT NULL, cpu_p3 IN NUMBER DEFAULT NULL, cpu_p4 IN NUMBER DEFAULT NULL, cpu_p5 IN NUMBER DEFAULT NULL, cpu_p6 IN NUMBER DEFAULT NULL, cpu_p7 IN NUMBER DEFAULT NULL, cpu_p8 IN NUMBER DEFAULT NULL, active_sess_pool_p1 IN NUMBER DEFAULT UNLIMITED, queueing_p1 IN NUMBER DEFAULT UNLIMITED, switch_group IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL, switch_time IN NUMBER DEFAULT UNLIMITED, switch_estimate IN BOOLEAN DEFAULT FALSE, max_est_exec_time IN NUMBER DEFAULT UNLIMITED, undo_pool IN NUMBER DEFAULT UNLIMITED, parallel_degree_limit_p1 IN NUMBER DEFAULT UNLIMITED);
All parameters default to NULL. However, for the EMPHASIS CPU resource allocation method, this case would starve all the users.
This procedure lets you update resource plan directives. For release 8.2 new_max_active_sess_target_mth was renamed new_active_sess_pool_mth and several new parameters added
DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.UPDATE_PLAN_DIRECTIVE ( plan IN VARCHAR2, group_or_subplan IN VARCHAR2, new_comment IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL, new_cpu_p1 IN NUMBER DEFAULT NULL, new_cpu_p2 IN NUMBER DEFAULT NULL, new_cpu_p3 IN NUMBER DEFAULT NULL, new_cpu_p4 IN NUMBER DEFAULT NULL, new_cpu_p5 IN NUMBER DEFAULT NULL, new_cpu_p6 IN NUMBER DEFAULT NULL, new_cpu_p7 IN NUMBER DEFAULT NULL, new_cpu_p8 IN NUMBER DEFAULT NULL, new_active_sess_pool_p1 IN NUMBER DEFAULT NULL, new_queueing_p1 IN NUMBER DEFAULT NULL, new_parallel_degree_limit_p1 IN NUMBER DEFAULT NULL new_switch_group IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL, new_switch_time IN NUMBER DEFAULT NULL, new_switch_estimate IN BOOLEAN DEFAULT FALSE, new_max_est_exec_time IN NUMBER DEFAULT NULL, new_undo_pool IN NUMBER DEFAULT UNLIMITED);
If the parameters for UPDATE_PLAN_DIRECTIVE are left unspecified, then they remain unchanged in the data dictionary.
This procedure lets you delete resource plan directives.
DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.DELETE_PLAN_DIRECTIVE ( plan IN VARCHAR2, group_or_subplan IN VARCHAR2);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
plan |
Name of resource plan. |
|
group_or_subplan |
Name of group or subplan. |
This procedure lets you make changes to resource manager objects.
All changes to the plan schema must be done within a pending area. The pending area can be thought of as a "scratch" area for plan schema changes. The administrator creates this pending area, makes changes as necessary, possibly validates these changes, and only when the submit is completed do these changes become active.
You may, at any time while the pending area is active, view the current plan schema with your changes by selecting from the appropriate user views.
At any time, you may clear the pending area if you want to stop the current changes. You may also call the VALIDATE procedure to confirm whether the changes you has made are valid. You do not have to do your changes in a given order to maintain a consistent group of entries. These checks are also implicitly done when the pending area is submitted.
DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.CREATE_PENDING_AREA;
The following rules must be adhered to, and they are checked whenever the validate or submit procedures are executed:
parallel_degree_limit_p1, may only appear in plan directives that refer to consumer groups (that is, not at subplans).OTHER_GROUPS somewhere in any active plan schema.This ensures that a session not covered by the currently active plan is allocated resources as specified by the OTHER_GROUPS directive.If any of the preceding rules are broken when checked by the VALIDATE or SUBMIT procedures, then an informative error message is returned. You may then make changes to fix the problem(s) and reissue the validate or submit procedures.
This procedure lets you validate pending changes for the resource manager.
DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.VALIDATE_PENDING_AREA;
This procedure lets you clear pending changes for the resource manager.
DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.CLEAR_PENDING_AREA;
This procedure lets you submit pending changes for the resource manager: It clears the pending area after validating and committing the changes (if valid).
DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.SUBMIT_PENDING_AREA;
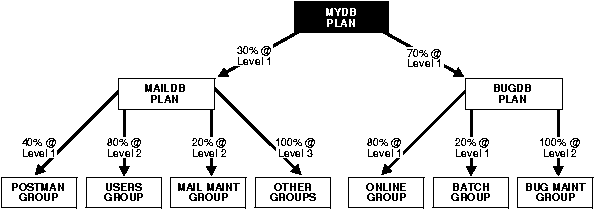
One of the advantages of plans is that they can refer to each other. The entries in a plan can either be consumer groups or subplans. For example, the following is also a set of valid CPU plan directives:
| Subplan/Group | CPU_Level 1 |
|---|---|
|
MAILDB Plan |
30% |
|
BUGDB Plan |
70% |
If these plan directives were in effect and there were an infinite number of runnable sessions in all consumer groups, then the MAILDB plan would be assigned 30% of the available CPU resources, while the BUGDB plan would be assigned 70% of the available CPU resources. Breaking this further down, sessions in the "Postman" consumer group would be run 12% (40% of 30%) of the time, while sessions in the "Online" consumer group would be run 56% (80% of 70%) of the time. Figure 58-1 diagram depicts this scenario:
Conceptually below the consumer groups are the active sessions. In other words, a session belongs to a resource consumer group, and this consumer group is used by a plan to determine allocation of processing resources.
A multiplan (plan with one or more subplans) definition of CPU plan directives cannot be collapsed into a single plan with one set of plan directives, because each plan is its own entity. The CPU quanta that is allotted to a plan or subplan gets used only within that plan, unless that plan contains no consumer groups with active sessions. Therefore, in this example, if the Bug Maintenance Group did not use any of its quanta, then it would get recycled within that plan, thus going back to level 1 within the BUGDB PLAN. If the multiplan definition in the preceding example got collapsed into a single plan with multiple consumer groups, then there would be no way to explicitly recycle the Bug Maintenance Group's unused quanta. It would have to be recycled globally, thus giving the mail sessions an opportunity to use it.
The resources for a database can be partitioned at a high level among multiple applications and then repartitioned within an application. If a given group within an application does not need all the resources it is assigned, then the resource is only repartitioned within the same application.
The following example uses the default plan and consumer group allocation methods:
BEGIN DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.CREATE_PENDING_AREA(); DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.CREATE_PLAN(PLAN => 'bugdb_plan', COMMENT => 'Resource plan/method for bug users sessions'); DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.CREATE_PLAN(PLAN => 'maildb_plan', COMMENT => 'Resource plan/method for mail users sessions'); DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.CREATE_PLAN(PLAN => 'mydb_plan', COMMENT => 'Resource plan/method for bug and mail users sessions'); DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.CREATE_CONSUMER_GROUP(CONSUMER_GROUP => 'Bug_Online_group', COMMENT => 'Resource consumer group/method for online bug users sessions'); DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.CREATE_CONSUMER_GROUP(CONSUMER_GROUP => 'Bug_Batch_group', COMMENT => 'Resource consumer group/method for bug users sessions who run batch jobs'); DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.CREATE_CONSUMER_GROUP(CONSUMER_GROUP => 'Bug_Maintenance_group', COMMENT => 'Resource consumer group/method for users sessions who maintain the bug db'); DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.CREATE_CONSUMER_GROUP(CONSUMER_GROUP => 'Mail_users_group', COMMENT => 'Resource consumer group/method for mail users sessions'); DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.CREATE_CONSUMER_GROUP(CONSUMER_GROUP => 'Mail_Postman_group', COMMENT => 'Resource consumer group/method for mail postman'); DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.CREATE_CONSUMER_GROUP(CONSUMER_GROUP => 'Mail_Maintenance_group', COMMENT => 'Resource consumer group/method for users sessions who maintain the mail db'); DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.CREATE_PLAN_DIRECTIVE(PLAN => 'bugdb_plan', GROUP_OR_SUBPLAN => 'Bug_Online_group', COMMENT => 'online bug users sessions at level 1', CPU_P1 => 80, CPU_P2=> 0, PARALLEL_DEGREE_LIMIT_P1 => 8); DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.CREATE_PLAN_DIRECTIVE(PLAN => 'bugdb_plan', GROUP_OR_SUBPLAN => 'Bug_Batch_group', COMMENT => 'batch bug users sessions at level 1', CPU_P1 => 20, CPU_P2 => 0, PARALLEL_DEGREE_LIMIT_P1 => 2); DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.CREATE_PLAN_DIRECTIVE(PLAN => 'bugdb_plan', GROUP_OR_SUBPLAN => 'Bug_Maintenance_group', COMMENT => 'bug maintenance users sessions at level 2', CPU_P1 => 0, CPU_P2 => 100, PARALLEL_DEGREE_LIMIT_P1 => 3); DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.CREATE_PLAN_DIRECTIVE(PLAN => 'bugdb_plan', GROUP_OR_SUBPLAN => 'OTHER_GROUPS', COMMENT => 'all other users sessions at level 3', CPU_P1 => 0, CPU_P2 => 0, CPU_P3 => 100); DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.CREATE_PLAN_DIRECTIVE(PLAN => 'maildb_plan', GROUP_OR_SUBPLAN => 'Mail_Postman_group', COMMENT => 'mail postman at level 1', CPU_P1 => 40, CPU_P2 => 0, PARALLEL_DEGREE_LIMIT_P1 => 4); DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.CREATE_PLAN_DIRECTIVE(PLAN => 'maildb_plan', GROUP_OR_SUBPLAN => 'Mail_users_group', COMMENT => 'mail users sessions at level 2', CPU_P1 => 0, CPU_P2 => 80, PARALLEL_DEGREE_LIMIT_P1 => 4); DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.CREATE_PLAN_DIRECTIVE(PLAN => 'maildb_plan', GROUP_OR_SUBPLAN => 'Mail_Maintenance_group', COMMENT => 'mail maintenance users sessions at level 2', CPU_P1 => 0, CPU_P2 => 20, PARALLEL_DEGREE_LIMIT_P1 => 2); DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.CREATE_PLAN_DIRECTIVE(PLAN => 'maildb_plan', GROUP_OR_SUBPLAN => 'OTHER_GROUPS', COMMENT => 'all other users sessions at level 3', CPU_P1 => 0, CPU_P2 => 0, CPU_P3 => 100); DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.CREATE_PLAN_DIRECTIVE(PLAN => 'mydb_plan', GROUP_OR_SUBPLAN => 'maildb_plan', COMMENT=> 'all mail users sessions at level 1', CPU_P1 => 30); DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.CREATE_PLAN_DIRECTIVE(PLAN => 'mydb_plan', GROUP_OR_SUBPLAN => 'bugdb_plan', COMMENT => 'all bug users sessions at level 1', CPU_P1 => 70); DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.VALIDATE_PENDING_AREA(); DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.SUBMIT_PENDING_AREA(); end;
The preceding call to VALIDATE_PENDING_AREA is optional, because the validation is implicitly done in SUBMIT_PENDING_AREA.
The initial consumer group of a user is the consumer group to which any session created by that user initially belongs. This procedure sets the initial resource consumer group for a user.
DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.SET_INITIAL_CONSUMER_GROUP ( user IN VARCHAR2, consumer_group IN VARCHAR2);
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
|
user |
Name of the user. |
|
consumer_group |
The user's initial consumer group. |
The ADMINISTER_RESOURCE_MANAGER or the ALTER USER system privilege are required to be able to execute this procedure. The user, or PUBLIC, must be directly granted switch privilege to a consumer group before it can be set to be the user's initial consumer group. Switch privilege for the initial consumer group cannot come from a role granted to that user.
If the initial consumer group for a user has never been set, then the user's initial consumer group is automatically the consumer group: DEFAULT_CONSUMER_GROUP.
DEFAULT_CONSUMER_GROUP has switch privileges granted to PUBLIC; therefore, all users are automatically granted switch privilege for this consumer group. Upon deletion of a consumer group, all users having the deleted group as their initial consumer group now have DEFAULT_CONSUMER_GROUP as their initial consumer group. All currently active sessions belonging to a deleted consumer group are switched to DEFAULT_CONSUMER_GROUP.
This procedure lets you change the resource consumer group of a specific session. It also changes the consumer group of any (PQ) slave sessions that are related to the top user session.
DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.SWITCH_CONSUMER_GROUP_FOR_SESS ( session_id IN NUMBER, session_serial IN NUMBER, consumer_group IN VARCHAR2);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
session_id |
SID column from the view |
|
session_serial |
|
|
consumer_group |
Name of the consumer group to switch to. |
This procedure lets you change the resource consumer group for all sessions with a given user ID. It also change the consumer group of any (PQ) slave sessions that are related to the top user session.
DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER.SWITCH_CONSUMER_GROUP_FOR_USER ( user IN VARCHAR2, consumer_group IN VARCHAR2);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
user |
Name of the user. |
|
consumer_group |
Name of the consumer group to switch to. |
The SWITCH_CONSUMER_GROUP_FOR_SESS and SWITCH_CONSUMER_GROUP_FOR_USER procedures let you to raise or lower the allocation of CPU resources of certain sessions or users. This provides a functionality similar to the nice command on UNIX.
These procedures cause the session to be moved into the newly specified consumer group immediately.
|
 Copyright © 2000, 2002 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|