| Oracle® Enterprise Manager Grid Control Quick Start Guide 10g Release 2 (10.2) Part Number B28678-03 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Enterprise Manager Grid Control Quick Start Guide 10g Release 2 (10.2) Part Number B28678-03 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
With today's complex IT infrastructures, most of an administrator's time may be spent trying to keep the underlying software up to date. Operating systems, applications, and other software must be installed, propagated, patched to the latest level, and duplicated. Without automation and central management, deployment management could present a huge obstacle to the growth and maintenance of your enterprise.With Enterprise Manager Grid Control, monitoring, managing, and maintaining your IT infrastructure is simplified through its powerful tools for configuration management and policy management.
This chapter covers configuration management in the following sections:
The Oracle Management Repository stores host configurations, client configurations and database configurations that are collected by the Oracle Management Agent. The set of all of the host configurations, database configurations, and client configurations stored in a Management Repository is referred to as the enterprise configuration.Host configuration consists of the configuration information that Enterprise Manager collects for a host that is a managed target, including the hardware, the operating system information, installed Oracle software and patches, and operating system-registered software. Client configuration information includes these as well as network data and browser-specific information. Database configuration information for an Oracle database includes information pertaining to the database, instances, high availability and licensing information as well as parameters and other values pertaining to initialization, system global area, tablespaces, datafiles, control files, redo logs and rollback segments.
Grid Control offers several summary views of your enterprise that you can use to monitor the state of your host and target configurations. Sometimes, you may want to search your enterprise configuration to identify hosts that have not had operating system patch 105181-05 installed, hosts that have an Oracle version 9.0.1.0.0 database installed, Oracle home directories where specific databases are installed, and so on. Enterprise Manager lets you perform such user-defined searches and also lets you use or customize predefined searches.
Linda would like to examine configuration data while creating a complete inventory of hardware and software in her managed environment. She needs to adhere to standards like ITIL or CoBiT. She wants to update all OSs and Oracle homes to her company's standards, but every machine seems to be at different level of configuration. Once all of her systems meet the company standards, she must maintain a 90% level of compliance.
The Configuration page of a host shows summaries of various hardware, operating systems, database installations and application server installations in the enterprise. You can perform various configuration operations from this page and also can drill down to host pages.
To work with host configuration information:
Click Targets in the Grid Control console.
Select a host to go to its home page.
Click the Configuration subtab to see the configuration details of the host.
On this page, you can see hardware, operating systems, Oracle software, OS-Registered software on the system.
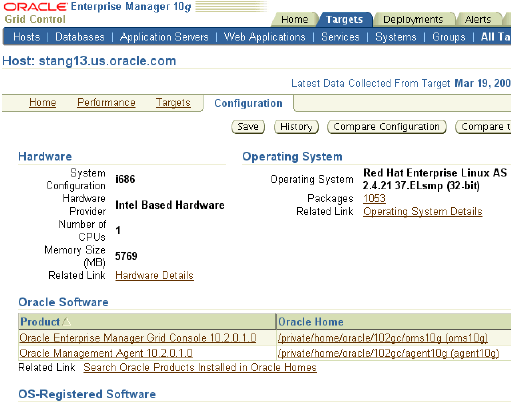
Click various links for more details.
Click Save to save the configuration.
A saved configuration serves as a record of what the configuration was like at a certain point in time or it can be used as a benchmark to evaluate other hosts in the enterprise.
Opt to save it to the Enterprise Manager Repository or to a file that can later be shared with a wider group, and click OK.
Linda can use this configuration to evaluate and update other hosts in her environment so that they are all similarly configured.
Enterprise Manager lets you compare these configurations and determine differences between two or more hosts or databases. The Generic Compare wizard enables you to compare various types of configurations with one or more other configurations.
Linda is having a problem with a production box that was functioning properly when it was tested in QA. She had configured it to work just like the QA box but some changes have crept in. She wants to compare the QA computer and her production computer to be able to determine the cause for the difference in performance.
This topic describes the procedure that Linda can follow to compare two hosts.
To compare configurations of two hosts:
Click Compare Configuration under Configuration in the Deployments page.
The Compare Configurations: First Configuration page appears.
Select a configuration and click Continue.
The Compare Configurations: Second Configuration page appears. This page appears also when you click the Compare Configuration button in the Configuration page of a host.
Select another configuration and click Compare.
The Comparison Results Summary page appears providing a comparison of various configurations details for the selected hosts.
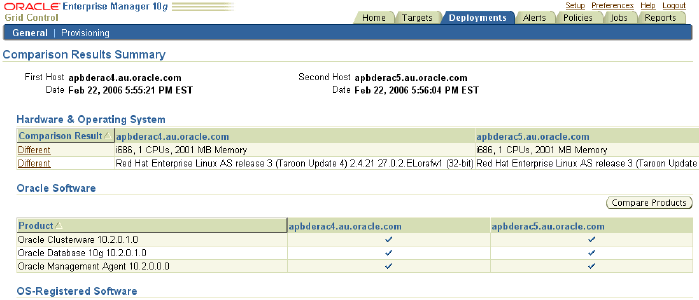
Click the Different link in the Hardware and Operating Systems table to see what is different between the selected hosts.
This might help you isolate the reason for differences in the performance of the two hosts.
Linda can compare the QA box with the production box to identify in what ways they are different and then explore if those differences are responsible for a difference in the performance of the two machines.
Policies define the optimal configurations of systems. Whether you use the policies defined by Oracle or configure policies to meet your particular system requirements, any deviations to your systems or applications are reported. Examples of deviations include inappropriate settings and incorrect system configurations.
You can configure the existing policy rule settings. You can enable or disable a policy evaluation, change the importance for the compliance score calculation, assign a corrective action, prevent template override, override default parameter values (when possible), and exclude objects from the evaluation of a policy.
You can investigate policy violations by studying the statistics in the All Targets Policy Violations section on the Enterprise Manager Grid Control home page. The policy violations with Critical severity or those that have the biggest impact on your enterprise should be dealt with first. You can also check security-related violations reported in the Security Policy Violations section. Noncompliance with these policy rules can greatly impact the security of your enterprise. Ideally, you should address targets that have the lowest compliance scores. You can also investigate the policy violations of a particular target by examining the Policy Violations section in the home page for that target.
Linda would like to have consistent configuration on all her machines. She has a standard for everything from host hardware up to the software patch level that she needs to enforce, and wants to be alerted when something breaks the standard.
To apply a policy for a target, you can select the policy and associate it with a target. You can easily apply a policy consistently across several targets by setting up a monitoring template for it and applying the template to multiple targets.
To apply a policy consistently for multiple targets:
Click Setup and then Monitoring Templates in the Enterprise Manager Grid Control console.
The Monitoring Templates summary page appears.
Click Create.
Select a target that is representative of the targets on which you want to enable specific policies.
In the Policies page, select and enable the policies that you want to associate with the target. You can enable a policy by clicking the pencil icon to access the Edit Policy Rule Settings page, and then setting Policy Evaluation to Enabled.
Select the policies that you do not want to include in the template and click Remove from Template.
Click Add Policies to Template to add policies from the policy library or from another target.
From the Monitoring Templates home page, select the monitoring template you just created and click Apply.
The Apply Monitoring Template page appears.
Select all targets for which you want to enable the selected policies and click OK.
Select the Policies tab from the Grid Control console.
The Policy Violations page appears listing all the policies, violations, and compliance scores.

Linda can watch for policy violations in this manner.
The Compliance Score indicates the percentage to which a target has been compliant with the goals defined by management policies. A compliance score summarizes all existing management policies into a useful metric that can be monitored showing the level of compliance of a target.
The compliance score is a combination of severity, importance, and the percentage of objects found to be non-compliant. The severity level refers to the seriousness of the violation. A Critical severity denotes a violation that needs immediate attention. A Warning warns of serious consequences if the violation is not dealt with in a timely manner. An Informational severity imparts knowledge about an object that is violating best practices. The importance level denotes the impact of the policy violation against this target. A High importance level indicates that the system could be compromised if a security policy rule violation is ignored.
You can influence how a compliance score is calculated by configuring a policy to have an importance level of high, normal, or low so the policy best meets the needs of your environment.
To ensure that the compliance score correctly reflects the environment:
From the policy violations page, click a violation count link that you think might not contribute meaningfully to the compliance score.
The Policy Violation Details page appears. It shows the violations against the policy. You can temporarily suppress a violation so that it does not have any impact on the compliance score.
To edit the policy, click Edit Policy Rule Settings in the Related Links section.
The Edit Policy Settings page appears.
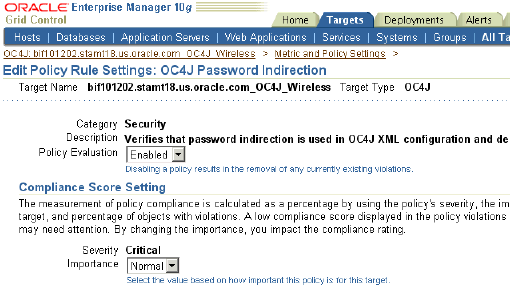
Set Policy Evaluation to Disabled.
Enterprise Manager will not evaluate the disabled policy for the target although the underlying metric collection continues.
For another policy, you can change the Compliance Score Setting to Low if you want its influence on the score to be minimal.
When the policy violations page is refreshed, it may show a better compliance score. Linda can similarly configure policies to achieve a compliance score to meet the needs of her environment.
Oracle By Example (OBE) has a series on the Oracle Enterprise Manager Grid Control Quick Start Guide.
The Configuration Management OBE covers the tasks in this chapter with annotated screen shots. It is located at
http://www.oracle.com/technology/obe/obe10gEMR2/Quick_Start/enterprise_manager_configuration/enterprise_configuration_and_policies.htm