| Oracle® Configuration Manager Installation and Administration Guide Release 10.3.2.1 Part Number B32294-11 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Configuration Manager Installation and Administration Guide Release 10.3.2.1 Part Number B32294-11 |
|
|
View PDF |
Oracle Configuration Manager is used to personalize the support experience by collecting configuration information and uploading it to the Oracle repository.
When customer configuration data is uploaded on a regular basis, customer support representatives can analyze this data and provide better service to the customers. For example, when a customer logs a service request, he can associate the configuration data directly with that service request. The customer support representative can then view the list of systems associated with the customer and solve problems accordingly.
Some of the benefits of using Oracle Configuration Manager are as follows:
Reduces time for resolution of support issues
Provides pro-active problem avoidance
Improves access to best practices and the Oracle knowledge base
Improves understanding of customer's business needs and provides consistent responses and services
This section lists the new features in this release.
Oracle Universal Installer now supports configuring of the Oracle Configuration Manager to use of the Oracle Support Hub
Oracle Configuration Manager uses the Oracle Support Hub to securely transmit configuration data to the Oracle repository on behalf of customers who do not have access to the Internet. For additional information regarding Oracle Support Hub, see the Oracle Enterprise Manager Companion Distribution Guide.
Verifying the contents of the response file
You can now verify the contents of the response file by using the command emocmrsp -verify.
The Oracle Configuration Manager architecture is displayed in Figure 1-1.
Figure 1-1 Oracle Configuration Manager Architecture
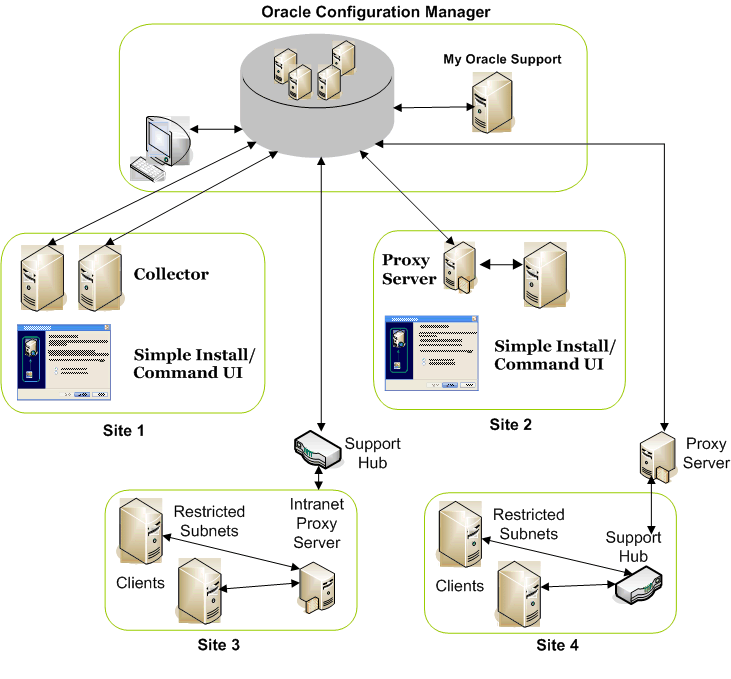
Figure 1-1 displays the following:
Oracle Configuration Manager: This is the Oracle Configuration Manager infrastructure.
Site 1: Systems that are directly connected to the Internet.
Site 2: Systems that are connected to the Internet through a proxy server.
Site 3: Systems that do not have direct access to the Internet but do have access to an Intranet proxy server which in turn has Internet connection through the Support Hub.
Site 4: Systems that do not have direct access to the Internet but do have access to the Support Hub which in turn is connected to the Internet through a proxy server.
Oracle Configuration Manager can be installed in the following modes:
Connected (Authenticated) Mode
This mode is recommended if your server has direct connection to the Internet, connection through a proxy server, or connection using Oracle Support Hub. In this mode, configuration data is automatically collected and uploaded to the Oracle server. In addition, updates to Oracle Configuration Manager occur automatically.
Connected (Unauthenticated) Mode
This mode, though not recommended, is used when only the e-mail address is specified but no password. Though this mode allows you to register and upload data, you are not able to view or use the data collected in the My Oracle Support interface.
This mode is required when your server does not have a connection to the Internet and you cannot configure an Oracle Support Hub. In this mode, you can collect configuration data manually by using the emCCR collect command. When you run this command, the collected configuration data is stored in the <OCM_CONFIG_HOME>/state/upload/ocmconfig.jar file. If problems occur, you can then upload this file to Oracle by way of a Service Request and My Oracle Support from another system that has Internet access.
Refer to Section 6.3, "emCCR collect" for details. In this mode, the only commands supported are: emCCR collect, emCCR status, emCCR enable_target, emCCR disable_target, emCCR update_components, configCCR, and emCCR help.
You can switch between Connected and Disconnected modes by using the configCCR command. Refer to Section 6.19, "configCCR" for details.
A shared home is an installation of an Oracle product that can be used and accessed by multiple hosts, or across multiple configurations on a single host. There are shared homes that require special Oracle Configuration Manager setup, and those that do not.
Examples of shared homes that do not require special Oracle Configuration Manager setup are:
When multiple database instances are created on the same host, from a single software installation.
When a single installation is shared across multiple hosts and each host has one or more database instances. In this case, though Oracle Configuration Manager requires no special setup, the collector must be setup separately on each host.
Some software products allow for the installation of the executables to be placed in a shared directory structure. Each use of the product requires a separate directory to segregate the product's runtime specific information.
An example of this is the Oracle Fusion Middleware installation with its separate directories. Typically the product-specific information collected by Oracle Configuration Manger is found in files in each of these separate directories.
To support this type of shared home, Oracle Configuration Manager treats each separate runtime state directory as an ORACLE_CONFIG_HOME.
If you have a software installation of this type, read Appendix A, "Shared Homes" before deciding whether you absolutely need shared homes.
Typically, most Oracle homes are not shared Oracle homes, therefore special Oracle Configuration Manager setup is not required.
Important:
If you are upgrading from an existing version of Oracle Configuration Manager that is prior to release 10.2.7, you cannot take advantage of the Shared Homes functionality. This functionality is only available with a new installation of Oracle Configuration Manager release 10.2.7 or later.To use this feature, you must deinstall the current installation of Oracle Configuration Manager and then reinstall Oracle Configuration Manager release 10.2.7 or later.