3 Configuring the SOA Infrastructure
This chapter describes how to configure the properties of the SOA Infrastructure. These property settings can apply to all SOA composite applications running in the SOA Infrastructure.
This chapter includes the following topics:
For more information, see Section 1.2.1, "Understanding the SOA Infrastructure Application."
3.1 Configuring SOA Infrastructure Properties
You can configure the following properties for the SOA Infrastructure:
-
Audit level
-
Composite instance state to capture
-
Payload validation
-
Callback server and server URLs
-
Universal Description, Discovery, and Integration (UDDI) registry
-
Java Naming and Directory Interface (JNDI) data source
-
Web service binding properties
The properties set at this level impact all deployed SOA composite applications, except those composites for which you explicitly set different audit level values at the composite application or service engine levels.
Additional advanced properties for the SOA Infrastructure can be configured through the System MBean Browser. To access these properties from the SOA Infrastructure menu, select Administration > System MBean Browser.
To configure SOA Infrastructure properties:
-
Access this page through one of the following options:
From the SOA Infrastructure Menu... From the SOA Folder in the Navigator... From the SOA Composite Menu... - Select SOA Administration > Common Properties.
- Right-click soa-infra.
-
Select SOA Administration > Common Properties.
- Select SOA Infrastructure Common Properties.
The SOA Infrastructure Common Properties page displays the following properties.
Note:
Some property fields are designated with an icon showing green and red arrows. If you change these properties, you must restart the SOA Infrastructure.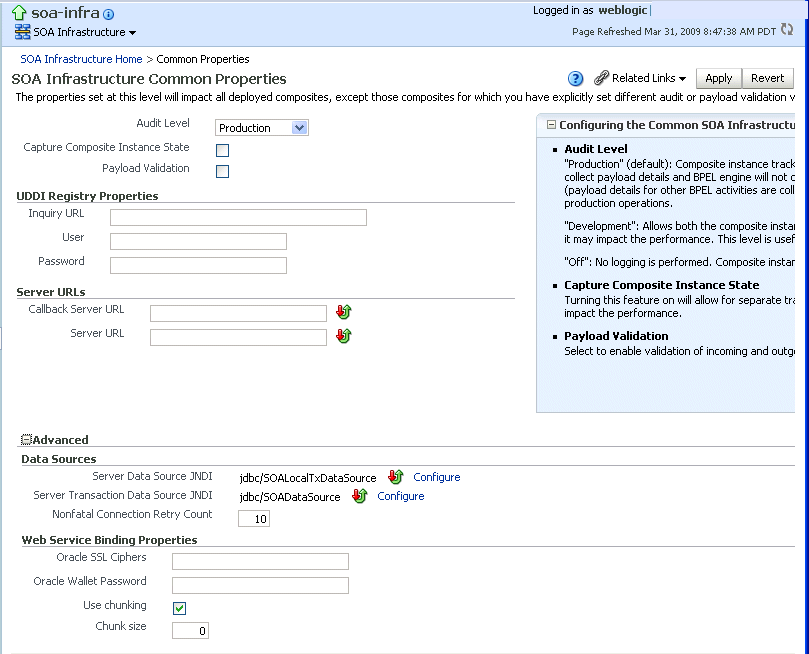
Description of the illustration soaadmin_common_props.gif
Descriptions for the properties at the top of the page are provided in the following table.
-
Make changes appropriate to your environment.
The UDDI Registry Properties section displays the following properties. You can integrate SOA composite applications running in the SOA Infrastructure with the UDDI registry. The UDDI registry provides a standards-based foundation for locating published services and managing metadata about services (security, transport, or quality of service). You can browse and select published services that meet your needs.
The User and Password properties are applicable if the UDDI registry is secured. The Inquiry URL property is public.
Element Description Example Inquiry URL Enter the URL of the master registry you want to query. The URL must not refer to the slave registry itself. Otherwise, you can lose some data. The inquiry URL obtains full-standard UDDI version 3 structures. http://master.mycompany.com:8888/registry/uddi/inquiryUser Enter the registry inquiry user. adminPassword Enter the password for the master registry inquiry user. Enter a password that utilizes good security practices. For more information about the UDDI registry, visit the following URL:
http://www.oracle.com/technology/tech/soa/uddi/index.html
-
Make changes appropriate to your environment.
The Server URLs section displays the following properties. If not explicitly set here, these values are determined at run time by querying the Oracle WebLogic Server cluster, the Web server, or the local server properties.
Element Description Callback Server URL Enter the callback server URL. This URL is sent by the server as part of the invocation to a foreign service provider. Server URL Enter the server URL. This URL is published as part of the SOAP address of a service in the concrete WSDL file. Note: In previous releases, you manually configured SOAP optimization with the
optSoapShortcutproperty. For this release, SOAP optimization is automatically configured. Therefore, if you upgrade to 11g R1 and are using the optimized shortcut approach in existing applications, note that optimized calls are activated only when the host name value (as referred to in the WSDL URL in thecomposite.xmlfile) matches the Server URL value. Either set both values to the host name (for example, myhost) or to the full domain name (for example, myhost.domain.com). If these values do not match, a regular SOAP call is performed instead of an optimized local call. -
Make changes appropriate to your environment.
-
Expand the Advanced section.
The Data Sources section displays the following properties. A data source enables you to retrieve a connection to a database server.
Element Description Example Server Data Source JNDI Displays the JNDI location for the server data source. Click Configure to go to the data source configuration page of the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console. Global transaction support should be disabled for this data source. jdbc/SOALocalTxDataSourceServer Transaction Data Source JNDI Displays the JNDI location for the server transactional data source. Click Configure to go to the data source configuration page of the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console. You must configure the data source for global transactions. jdbc/SOADataSourceNonfatal Connection Retry Count Enter the maximum number of times a nonfatal connection error can be retried before failing. These type of errors occur for any connection error with the dehydration store (for example, Oracle Real Application Clusters failover, database shutdown, and so on). 10 -
Make changes appropriate to your environment.
The Web Service Binding Properties section displays the following options.
-
Make changes appropriate to your environment.
-
Click Apply.
-
If you make changes and want to reset these properties to their previous values, click Revert.
3.2 Stopping and Starting the SOA Infrastructure
You can stop and start the SOA Infrastructure for maintenance or for configuration restarts.
To start and stop the SOA Infrastructure:
| From the SOA Infrastructure Menu... | From the SOA Folder in the Navigator... |
|---|---|
|
|
-
To shut down the SOA Infrastructure, select Shut Down.
-
Click OK when prompted to shut down the SOA Infrastructure.
-
Wait for SOA Infrastructure shutdown to complete.
-
To start the SOA Infrastructure, select Start Up.
3.2.1 SOA Composite Application States and SOA Infrastructure Shutdown
SOA composite application states are not updated to indicate that they are down after SOA Infrastructure shutdown. If you attempt to access the composite, you receive an error message stating that composite details cannot be retrieved:
soa-infra runtime connection error An error happened while connecting to soa-infra runtime at t3://152.61.150.106:8001/soa-infra.
This message may lead you to believe that another issue exists in the system. However, this is not the case.
These composite states display as up, or in some cases pending, because this metric indicates whether the composite is enabled, and is independent of whether the SOA Infrastructure is started. In addition, the composite is still active and can receive requests on other managed servers in a cluster.
3.3 Changing the SOA Infrastructure Server URL Property Port
You can change the SOA Infrastructure ServerURL property port from Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control Console. This automatically updates the port setting in the soa-infra-config.xml file under $DOMAIN_HOME/config/Domain_Name/configuration.
When changing the port, note the following details:
-
If the SOA Infrastructure and managed Oracle WebLogic Server port numbers are different, you receive a
ConnectExceptionerror when trying to connect to the Oracle BPM Worklist. Ensure that these port numbers match. -
You cannot change the SOA Infrastructure port from the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console. Only the port for the managed Oracle WebLogic Server can be changed from the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console.
-
Oracle recommends that you change the SOA Infrastructure port from Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control Console. However, to manually change the SOA Infrastructure port in the
soa-infra-config.xmlfile, perform the following steps:-
Shut down the SOA Infrastructure. If you do not perform a shutdown before making changes, the changes are not persisted upon SOA Infrastructure restart.
-
Change the SOA Infrastructure port in the
soa-infra-config.xmlfile. -
Restart the SOA Infrastructure.
-
Change the managed Oracle WebLogic Server port in the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console to the same value.
-
To change the SOA Infrastructure port:
-
From the SOA Infrastructure menu, select Administration > System MBean Browser.
-
Under Application Defined MBeans, expand oracle.as.soainfra.config > Server: server_soa > SoaInfraConfig > soa-infra.
where server_soa is the name of the server provided during post installation configuration. By default, this name is soa_server1.
-
In the Name column, click ServerURL.
The Attribute: ServerURL page appears.
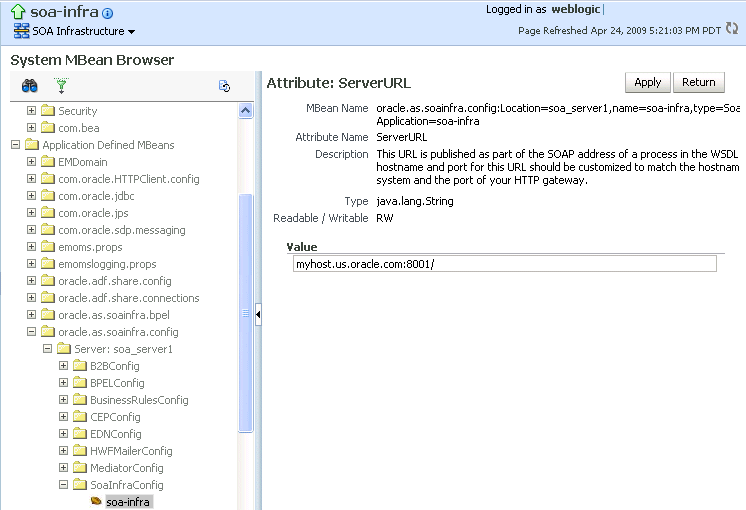
Description of the illustration hwf_wlist_port.gif
-
In the Value field, change the port.
-
Click Apply.
-
Change the managed Oracle WebLogic Server port in the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console to the same value.
In environments in which a load balancer is used in front of an Oracle WebLogic Server cluster, the ServerURL property host and port can be different from the Oracle WebLogic Server server host and port. This is typical for enterprise deployment environments in which a load balancer distributes requests across the managed servers in the Oracle WebLogic Server cluster. For more details, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Enterprise Deployment Guide for Oracle SOA Suite.
3.4 Configuring Log Files
Oracle SOA Suite components generate log files containing messages that record all types of events, including startup and shutdown information, errors, warning messages, access information on HTTP requests, and additional information.
To configure log files:
-
Access this page through one of the following options:
From the SOA Infrastructure Menu... From the SOA Folder in the Navigator... - Select Logs > Log Configuration.
- Right-click soa-infra.
-
Select Logs > Log Configuration.
The Log Configuration page displays the following details:
-
A View list for selecting the type of loggers for which to view information:
-
Persistent: Loggers that become active when a component is started. Their configuration details are saved in a file and their log levels are persisted across component restarts.
-
Active run time: Loggers that are automatically created during run time and become active when a particular feature area is exercised (for example, oracle.soa.b2b or oracle.soa.bpel). Their log levels are not persisted across component restarts.
-
-
A table that displays the logger name, Oracle Diagnostic Logging (ODL) level for setting the amount and type of information to write to a log file, the log file, and the log level state.
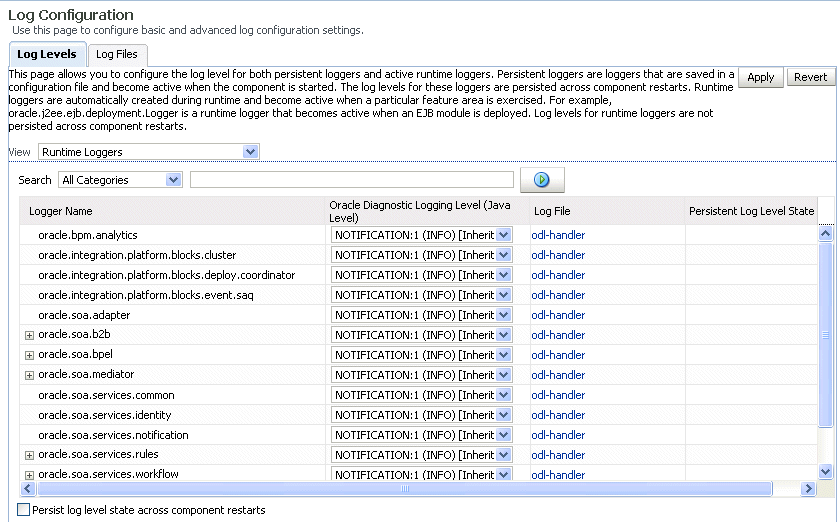
Description of the illustration sca_logconfig.gif
-
Perform the following log file tasks on this page:
-
In the Logger Name column, expand a logger name. This action enables you to specify more specific logging levels within a component.
-
In the Oracle Diagnostic Logging Level columns, select the level and type of information to write to a log file.
-
In the Log File column, click a specific log file to create and edit log file configurations.
For more information about ODL log files and the level and type of logging information to write to a log file, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide.
-
-
Click the Log Files tab.
This page enables you to create and edit log file configurations, including the log file in which the log messages are logged, the format of the log messages, the rotation policies used, and other parameters based on the log file configuration class.
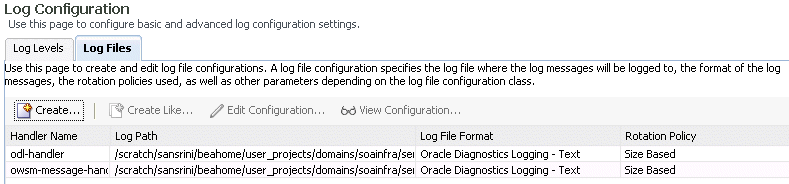
Description of the illustration sca_logfiles.gif
For more information, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide.
3.4.1 Configuring the Logging File Encoding Property
The oracle-soa-handler log handler property of the soa-diagnostic.log file has no encoding property specified in the SOA_Domain/config/fmwconfig/servers/server_soa/logging.xml file. Instead, the soa-diagnostic.log file is written in the operating system's default encoding format. This can cause the following problems:
-
Non-ASCII error messages can become unreadable because logging information is written to
soa-diagnostic.login the server's default encoding format. -
On Windows operating systems, writing in the default encoding format can lead to non-ASCII data loss.
To avoid this problem, specify a value of UTF-8 for the oracle-soa-handler log handler property in the logging.xml file.
<?xml version='1.0'?> <logging_configuration> <log_handlers> <log_handler name='wls-domain' class='oracle.core.ojdl.weblogic.DomainLogHandler' level='WARNING'/> <log_handler name='oracle-soa-handler' class='oracle.core.ojdl.logging.ODLHandlerFactory'> <property name='path' value='c:\soa1210.1411\user_ projects\domains\soa/servers/server_soa/logs/soa-diagnostic.log'/> <property name='maxFileSize' value='10485760'/> <property name='maxLogSize' value='104857600'/> <property name='supplementalAttributes' value='J2EE_APP.name,J2EE_ MODULE.name,WEBSERVICE.name,WEBSERVICE_PORT.name,composite_instance_id,component_ instance_id,composite_name,component_name'/> <property name='encoding' value='UTF-8'/> </log_handler> </log_handlers> ...
Log files are written with ODL. You can view the content of log files from Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control Console.
For more information about logging, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide.