37 Configuring a Relational Aggregate Object Mapping
This chapter describes the various components that you must configure in order to use a relational aggregate object mapping.
Note:
You configure the relational aggregate object mapping in the source object's descriptor. However, before doing so, you must designate the target object's descriptor as an aggregate (see Section 23.6, "Configuring a Relational Descriptor as a Class or Aggregate Type").This chapter includes the following sections:
For information on how to configure TopLink mappings options common to two or more mapping types, see Chapter 121, "Configuring a Mapping".
For information on how to create TopLink mappings, see Chapter 120, "Creating a Mapping".
Table 37-1 lists the configurable options for a relational aggregate object mapping.
37.1 Introduction to Relational Aggregate Object Mapping Configuration
Table 37-1 lists the configurable options for a relational aggregate object mapping.
Table 37-1 Configurable Options for Relational Aggregate Object Mapping
| Option | Oracle JDeveloper |
TopLink Workbench |
Java |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Reference descriptor (see Section 28.4, "Configuring Reference Descriptor") |
|||
|
Method or direct field access (see Section 121.6, "Configuring Method or Direct Field Accessing at the Mapping Level") |
|||
|
Read-only mapping (see Section 121.2, "Configuring Read-Only Mappings") |
|||
|
Allowing null values (see Section 37.3, "Configuring Allowing Null Values") |
|||
|
Mapping comments (see Section 121.8, "Configuring Mapping Comments") |
|||
|
Aggregate fields (see Section 37.2, "Configuring Aggregate Fields") |
Example 37-1 shows how to create an aggregate object mapping and add it to a descriptor using Java code.
Example 37-1 Aggregate Object Mapping
public void customize(ClassDescriptor descriptor) {
AggregateObjectMapping mapping = new AggregateObjectMapping();
// configure mapping
...
// add mapping to descriptor
descriptor.addMapping(mapping);
}
For more information, see the following:
37.2 Configuring Aggregate Fields
When you designate a descriptor as an aggregate, TopLink allows you to specify a mapping type for each field in the target class, but defers associating the field with a database table until you configure the aggregate object mapping in the source class descriptor. In other words, the target class descriptor defines how each target class field is mapped but the source class descriptor defines where each target class field is mapped.
This section explains how to configure the source class descriptor to define where each target class field is mapped.
For more information on how to configure the target class descriptor to define how each target class field is mapped, see Section 23.6, "Configuring a Relational Descriptor as a Class or Aggregate Type".
37.2.1 How to Configure Aggregate Fields Using TopLink Workbench
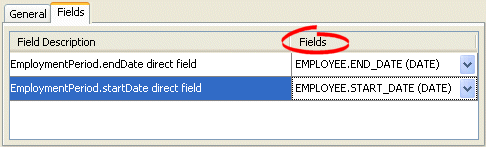
To specify the mapped fields of an aggregate mapping, use this procedure.
-
Select the mapped attribute in the Navigator. Its properties appear in the Editor.
Use the following information to complete each field on the tab:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Field Description | This column shows the name of the fields from the target object, whose descriptor is designated as an aggregate (see Section 23.6, "Configuring a Relational Descriptor as a Class or Aggregate Type"). These are for display only and cannot be changed. |
| Fields | Use this column to select the source object database table field that TopLink will map to the corresponding target object field. |
37.2.2 How to Configure Aggregate Fields Using Java
Using the AggregateObjectMapping method addFieldNameTranslation you can set a field name translation that maps from a field name in the source table to a field name in the aggregate descriptor
For more information about the available methods for AggregateObjectMapping, see the Oracle Fusion Middleware Java API Reference for Oracle TopLink.
37.3 Configuring Allowing Null Values
If all the fields in the database row for the aggregate object are null, then, by default, TopLink places null in the appropriate source object, as opposed to filling an aggregate object with null values.
37.3.1 How to Configure Allowing Null Values Using TopLink Workbench
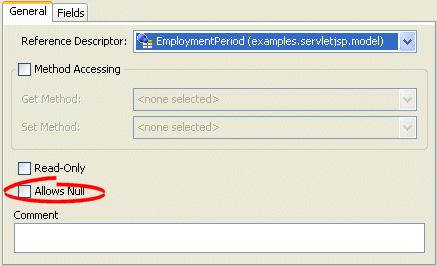
To allow a mapping to contain a null value, use this procedure.
-
Select the mapped attribute in the Navigator. Its properties appear in the Editor.
-
Click the General tab. The General tab appears.
Figure 37-2 General Tab, Allow Null Option
Description of "Figure 37-2 General Tab, Allow Null Option"
Select the Allows Null option to allow this mapping to contain a null value.
37.3.2 How to Configure Allowing Null Values Using Java
You can configure whether or not to allow null values using the AggregateObjectMapping methods allowNull and dontAllowNull.
For more information about the available methods for AggregateObjectMapping, see the Oracle Fusion Middleware Java API Reference for Oracle TopLink.