97 Configuring a Data Source Login
This chapter describes how to configure TopLink data source logins.
This chapter includes the following sections:
Table 97-1 lists the types of TopLink data source logins that you can configure and provides a cross-reference to the type-specific chapter that lists the configurable options supported by that type.
Table 97-2 lists the configurable options shared by two or more TopLink data source login types.
When using the sessions.xml file to configure login information, TopLink will override any login information in the project.xml and instead use the information from the sessions.xml configuration.
For more information, see the following:
97.1 Configuring Common Data Source Login Options
Table 97-2 lists the configurable options shared by two or more TopLink data source login types. In addition to the configurable options described here, you must also configure the options described for the specific data source login types (see Section 96.1.2, "Data Source Login Types"), as shown in Table 97-1
Table 97-2 Common Data Source Login Options
| Option to Configure | Oracle JDeveloper |
TopLink Workbench |
Java |
|---|---|---|---|
|
User name and password (see Section 97.2, "Configuring User Name and Password") |
|||
|
Password encryption (see Section 97.3, "Configuring Password Encryption") |
|||
|
External connection pooling (see Section 97.4, "Configuring External Connection Pooling") |
|||
|
Properties (see Section 97.5, "Configuring Properties") |
|||
|
Default null value (see Section 97.6, "Configuring a Default Null Value at the Login Level") |
97.2 Configuring User Name and Password
Optionally, you can specify the user name and password of a login.
Oracle recommends that you do not save the password with a deployment login.
If you specify a password, using a TopLink tool or Java, enter the plain text (not encrypted) value. TopLink will encrypt the password using JCE encryption.
By default, TopLink writes passwords to and read passwords from the sessions.xml file in encrypted form using JCE encryption.
By default, TopLink does not write passwords to and read passwords from the project.xml file unless you configure your project-level data source login accordingly. When you configure TopLink to write passwords and read passwords from the project.xml file, by default, it does so in encrypted form using JCE encryption.
For more information, see the following:
97.2.1 How to Configure User Name and Password Using TopLink Workbench
To specify a user name and password, use this procedure:
-
Select a server or database session in the Navigator. Its properties appear in the Editor.
-
Click the Login tab. The Login tab appears.
-
Click the Connection subtab. The Connection subtab appears.
Figure 97-1 Login Tab, Connection Subtab, User Name and Password Fields
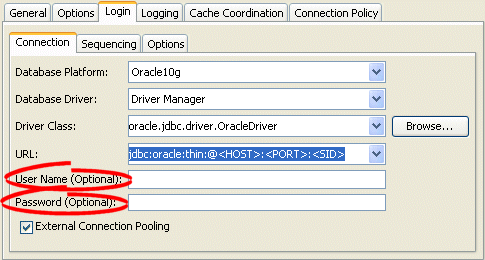
Description of "Figure 97-1 Login Tab, Connection Subtab, User Name and Password Fields"
-
Enter a user name and password in plain text (not encrypted).
Enter a user name and password in plain text (not encrypted).
97.3 Configuring Password Encryption
By default, TopLink writes passwords to and read passwords from the sessions.xml file in encrypted form using JCE encryption.
By default, TopLink does not write passwords to and read passwords from the project.xml file unless you configure your project-level data source login accordingly. When you configure TopLink to write passwords and read passwords from the project.xml file, by default, it does so in encrypted form using JCE encryption.
You can implement your own encryption class and configure your session DatasourceLogin to use it.
Currently, neither Oracle JDeveloper nor TopLink Workbench support specifying the encryption class used. To change the encryption class used, you must modify the login in Java.
For more information, see the following:
97.3.1 How to Configure Password Encryption Using Java
To configure a password encryption class, follow this procedure:
-
Create your encryption class.
Your encryption class must implement the
oracle.toplink.internal.security.Securableinterface, as Example 97-1 shows. -
Create a session event listener class for the
preLoginevent that callsDatasourceLoginmethodsetEncryptionClassNameto configure your session with your encryption class.Use the
SessionEventAdapterto simplify your session event listener, as Example 97-2 shows.Example 97-2 Specifying a Custom Encryption Class in a Session Event Listener
import oracle.toplink.tools.sessionconfiguration.SessionEventAdapter; import oracle.toplink.sessions.SessionEvent; import oracle.toplink.sessions.Session; import oracle.toplink.sessions.DatasourceLogin; public class MySessionEventListener extends SessionEventAdapter { public void preLogin(SessionEvent event) { Session session = event.getSession(); DatasourceLogin login = session.getDatasourceLogin(); login.setEncryptionClassName(MyEncryptor.class.getName()); } } -
Associate your session event listener class with your session.
For more information, see Section 89.10, "Configuring Session Event Listeners".
97.4 Configuring External Connection Pooling
For non-Java EE applications, you typically use internal connection pools provided by TopLink (see Section 96.1.6.1, "Internal Connection Pools"). In this case, you can use Oracle JDeveloper or TopLink Workbench to configure connection pool options and to create a sequence connection pool and application-specific (named) connection pools.
For Java EE applications, you typically use external connection pools provided by a JDBC driver or Java EE container (see Section 96.1.6.2, "External Connection Pools"). Optionally, you can configure a read connection pool to use a nontransactional login, and you can configure a sequence connection pool to use a separate (preferably nontransactional) login of its own.
Because JTA external transaction controllers are dependent upon the external transaction service that the application server provides, you must configure TopLink to use external connection pools if you are using an external transaction controller (see Section 115.13, "Integrating the Unit of Work with an External Transaction Service").
External connection pools enable your TopLink application to do the following:
-
Integrate into a Java EE-enabled system.
-
Integrate with JTA transactions (JTA transactions require a JTA-enabled data source).
-
Leverage a shared connection pool in which multiple applications use the same data source.
-
Use a data source configured and managed directly on the server.
For more information about connection pools, see Section 96.1.6, "Connection Pools".
97.4.1 How to Configure External Connection Pooling Using TopLink Workbench
To specify if the session login uses external connection pooling, use this procedure:
-
Configure a data source on the application server.
If you are using the external connection pool with an external transaction controller (see Section 89.9, "Configuring the Server Platform"), be sure to configure a JTA-enabled data source.
For more information, see your Java EE container documentation.
-
Select a server or database session in the Navigator. Its properties appear in the Editor.
-
Click the Login tab. The Login tab appears.
-
Click the Connection subtab. The Connection subtab appears.
Figure 97-2 Login Tab, Connection Subtab, External Connection Pooling Field, Database Driver
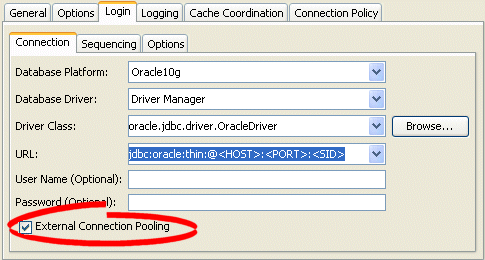
Description of "Figure 97-2 Login Tab, Connection Subtab, External Connection Pooling Field, Database Driver"
Figure 97-3 Connection Tab, External Connection Pooling Field, Java EE Data Source
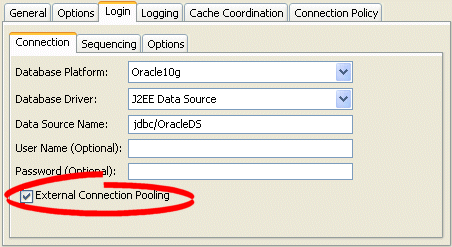
Description of "Figure 97-3 Connection Tab, External Connection Pooling Field, Java EE Data Source"
Specify if this login uses External Connection Pooling. For a database driver, external connection pooling is optional. For a Java EE data source, external connection pooling is mandatory.
97.4.2 How to Configure External Connection Pooling Using Java
To configure the use of an external connection pool in Java, do the following:
-
Configure the data source on the application server.
If you are using the external connection pool with an external transaction controller (see Section 89.9, "Configuring the Server Platform"), be sure to configure a JTA-enabled data source.
For more information, see your Java EE container documentation.
-
Configure the
DatasourceLoginto specify the data source and to use an external connection pool by using theuseExternalConnectionPoolingmethod.
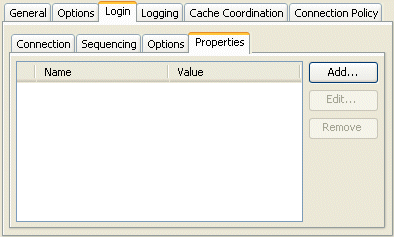
97.5 Configuring Properties
For all DatasourceLogin types, you can specify custom named values, called properties. Some data sources require additional, driver-specific properties not supported in the DatasourceLogin API (for example, see Section 12.11.1, "How to Optimize JDBC Driver Properties"). Add these properties to the DatasourceLogin so that TopLink can pass them to the driver.
For relational sessions, you must first enable advanced option Use Properties (see Section 98.7, "Configuring Advanced Options").
For EIS sessions, properties are always enabled.
Note:
Do not set a password as a property. Always use Oracle JDeveloper, TopLink Workbench, orDatabaseLogin method setPassword. For more information on configuring a password, see Section 97.2, "Configuring User Name and Password".When using TopLink Workbench, you can only set character values, which TopLink returns as String objects (see Section 97.5.1, "How to Configure Properties Using TopLink Workbench").
When using Java, you can set any Object value (see Section 97.5.2, "How to Configure Properties Using Java").
97.5.1 How to Configure Properties Using TopLink Workbench
To specify arbitrary named value pairs that TopLink associates with a DatasourceLogin, use this procedure:
-
Select a server or database session in the Navigator. Its properties appear in the Editor.
-
Click the Login tab. The Login tab appears.
-
If necessary, enable support for properties:
-
for relational sessions, you must first enable advanced option Use Properties (see Section 98.7, "Configuring Advanced Options");
-
for EIS sessions, properties are always enabled.
-
-
Click the Properties subtab. The Properties subtab appears.
To add (or change) a new Name/Value property, click Add (or Edit). Add Property dialog box appears.
Use the following information to add or edit a login property on the Add Property dialog box:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name by which TopLink retrieves the property value using the DatasourceLogin method getProperty. |
| Value | The value TopLink retrieves using the DatasourceLogin method getProperty passing in the corresponding property name.
Using TopLink Workbench, you can set only character values that TopLink returns as |
To delete an existing property, select the Name/Value row and click Remove.
97.5.2 How to Configure Properties Using Java
Using Java, you can set any Object value using DatasourceLogin method setProperty. To remove a property, use DatasourceLogin method removeProperty.
97.6 Configuring a Default Null Value at the Login Level
A default null value is the Java Object type and value that TopLink uses instead of null when TopLink reads a null value from a data source.
When you configure a default null value at the login level, it applies to all mappings used in a session. In this case, TopLink uses it to translate in one direction only: when TopLink reads null from the data source, it converts this null to the specified type and value.
You can also use TopLink to set a default null value on a per-mapping basis (see Section 121.5, "Configuring a Default Null Value at the Mapping Level").
Note:
A default null value must be anObject. To specify a primitive value (such as int), you must use the corresponding Object wrapper (such as Integer).97.6.1 How to Configure a Default Null Value at the Login Level Using Java
Using Java API, you can configure a default null value for all mappings used in a session with the DatabaseLogin method setDefaultNullValue(Class,Object).
For example:
// Defaults all null String values read from the database to empty String
session.getLogin().setDefaultNullValue(String.class, "");