| Oracle® Identity Manager Audit Report Developer's Guide Release 9.1.0.1 Part Number E14045-03 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Identity Manager Audit Report Developer's Guide Release 9.1.0.1 Part Number E14045-03 |
|
|
View PDF |
Oracle Identity Manager provides a powerful audit engine to collect extensive data for audit and compliance purposes. It also provides a flexible reporting engine to run reports on that data. The customer can use the Audit and Report functionality together to capture, archive, and view entity and transactional data for compliance monitoring and IT-centric processes and forensic auditing. Therefore, with the audit and compliance modules, Oracle Identity Manager provides profile auditing, reporting, and attestation features. You can capture, transport, store, retrieve, and remove historical data over its life cycle. Security is maintained at every stage of the data life cycle.
This guide discusses the profile auditing and reporting features of Oracle Identity Manager. See Oracle Identity Manager Administrative and User Console Guide for attestation details.
This chapter discusses the following topics:
Figure 1-1 shows the design components of the Oracle Identity Manager auditing process.
Figure 1-1 Design Components of the Auditing Process
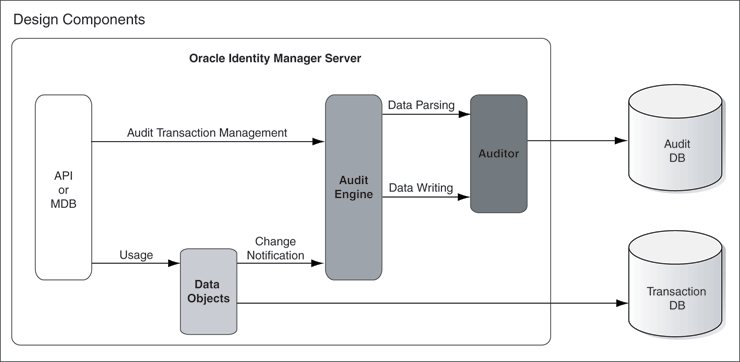
Any action that a user performs in Oracle Identity Manager translates into an Application Programming Interface (API) call or into a Message Driven Bean (MDB) picking up a message to process an action.
One action can cause multiple changes. All changes are combined into an audit transaction. Each API method that can modify data objects calls the startTransaction method in the audit engine at the beginning of the API call and the endTransaction method at the end of the API call. This defines boundaries for the audit transaction. The audit engine generates a transaction ID to identify the changes made in the transaction.
Oracle Identity Manager provides auditing and historical archiving of profile information. It takes a snapshot of a profile, stores the snapshot in an audit table in the database, and updates the snapshot each time the profile data changes.
Note:
In the context of profile auditing, the term snapshot means a copy taken of the entire profile data at any instant when the data is modified.Oracle Identity Manager provides standard reports for viewing archived data. You can also create customized reports.
When you first install Oracle Identity Manager, it uses a primary data source for creating reports. To reduce the load on the primary data source, you can configure a secondary data source for reporting. To use a secondary database, you must configure the replication of data between transactional data and the reporting database.