This document describes the following:
Full support is offered for the following Oracle WebLogic Server versions:
Limited support is offered for the following versions:
See Supported Oracle WebLogic Server Versions for more information.
Virtual EAR technology dramatically improves iterative development performance for large applications.
Virtual EARs allow the source and generated artifacts to be kept in separate physical locations but linked together through mappings in a descriptor file. The descriptor file contains entries that map physical locations to relative locations inside the "virtual EAR".
The descriptor file is generated automatically: there is no need to manually configure the virtual EAR. Lay out the projects the way it makes sense for you and the necessary structure will be set up to minimize the time it takes to publish/deploy during iterative development.
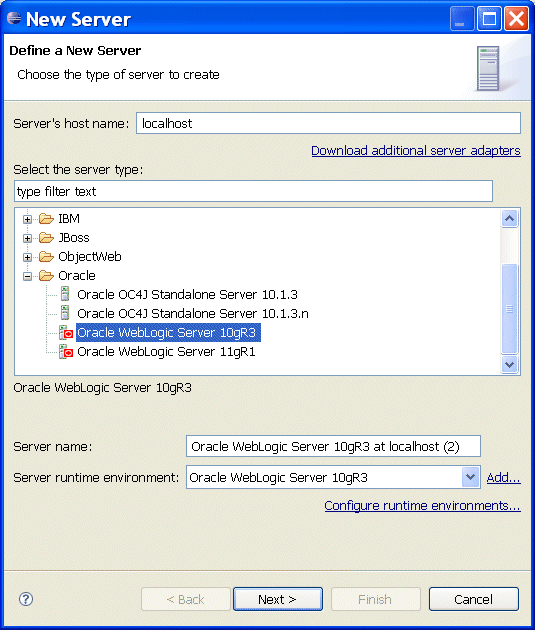
The following examples show how to define a new server instance in your workspace. To display the New Server dialog, right-click on your Servers view in Eclipse IDE, and then select New > Server from the drop-down menu.

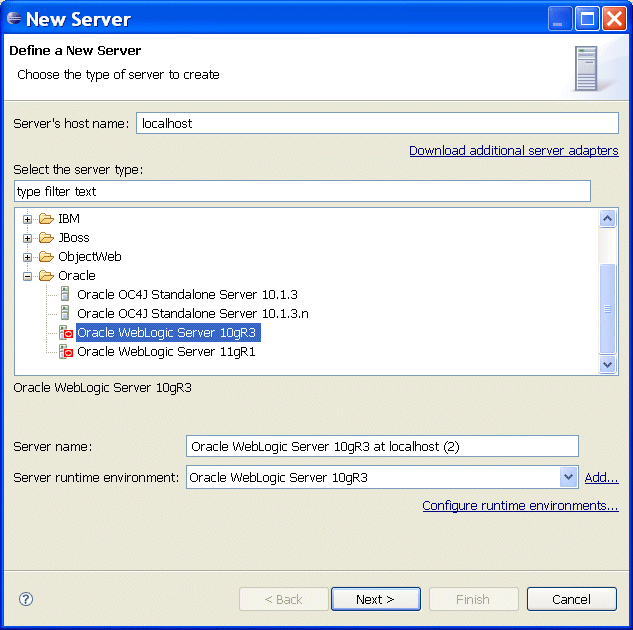
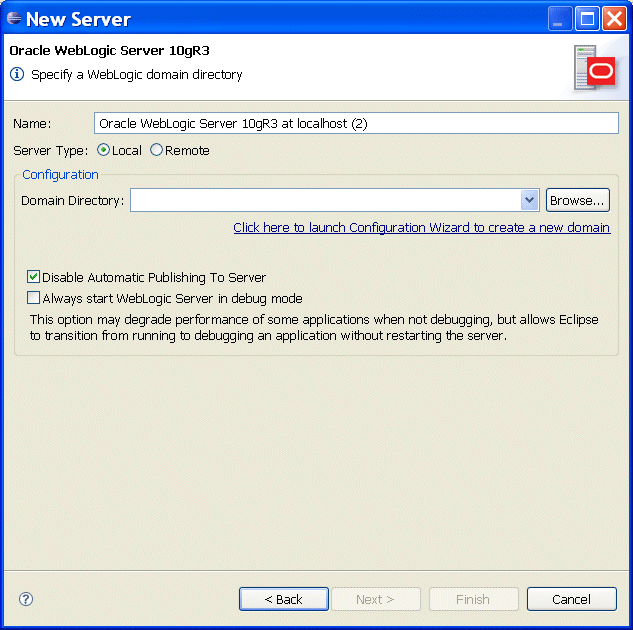
Development against remote Oracle WebLogic Servers is supported. To specify a remote server, select Remote on the New Server dialog, as the following example shows.
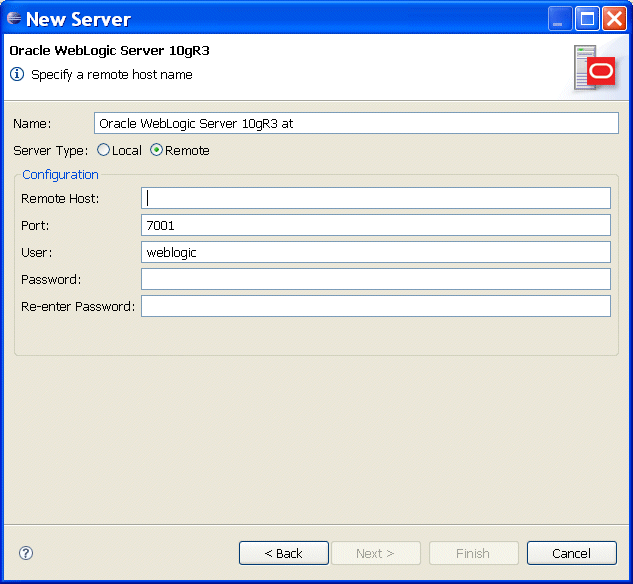
Note: Eclipse IDE includes a Web browser to let you access the Internet from within the IDE. If your machine is located inside of a network, which requires a proxy to access outside resource such as the Internet, you typically define this using the Eclispe IDE's Window > Preferences > General > Network Connections, proxy settings. These settings may impact the deployment of Java EE application from local IDE to a remote Oracle WebLogic Server located in the same network: the WebLogic deployer might not be able to upload the Java EE application to the remote instance of Oracle WebLogic Server, if the server host is not explicitly specified in the No Proxy for list of the Preferences > General > Network Connections dialog. This condition occurs with Oracle WebLogic Server versions 11g Release 1, 10g Release 3, and, possibly, some earlier versions. To eliminate this condition, add the remote Oracle WebLogic Server host name to the No Proxy for list.
Oracle WebLogic Server-specific functionality, such as shared library support, is made possible through "extensions" facets. The four project types - EAR, Web App, Utility, and EJB projects - each have one of the following associated facets:
These facets also provide support for the WebLogic-specific deployment descriptors
(weblogic.xml and weblogic-application.xml) and their graphical
editors for
EAR, Web Applications, and EJB projects. These deployment descriptors are automatically
added to these projects types when the corresponding extension facet is
added.
OEPE provides a graphical design view for editing WebLogic-specific deployment
descriptors - weblogic.xml and weblogic-application.xml.
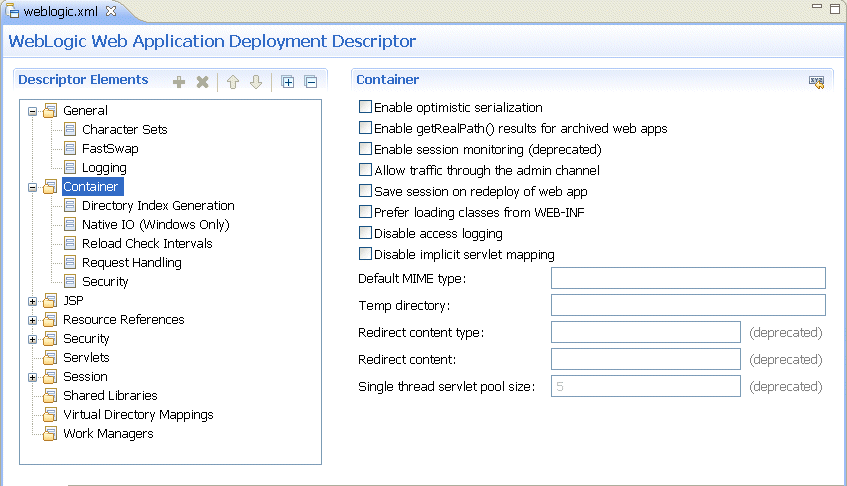
For more information, see Using a Deployment Descriptor Editor.
OEPE provides a graphical design view that you can use to edit your WebLogic deployment plan.
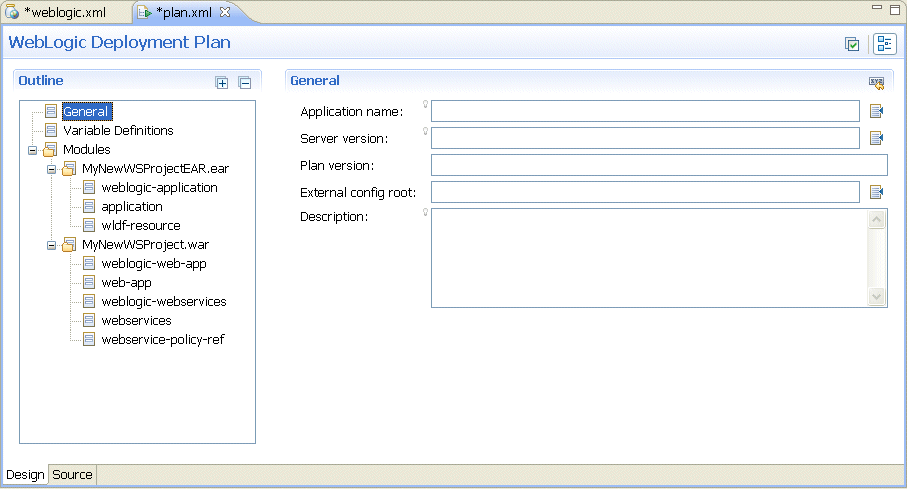
For more information, see Using a Deployment Plan Editor.
WebLogic shared libraries provide an easy way to share one or more types of Java EE modules among multiple applications.
A shared library can be one of the following:
After the library has been registered, you can deploy multiple applications that reference the library. Each referencing application can use the library as if it were packaged as part of the referencing application itself. The shared library classes are added to the classpath of the referencing application, and the referencing application's deployment descriptors are merged (in memory) with those of the library.
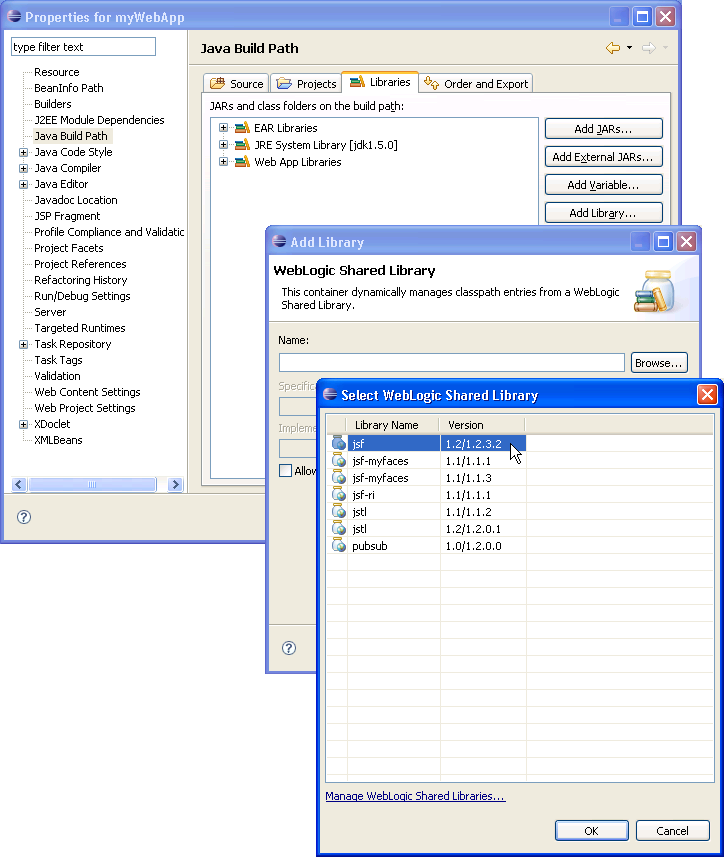
A registry of shared libraries can be viewed and edited using the workspace Preference page accessible through Window > Preferences > WebLogic > Shared Libraries. For more information, see WebLogic Shared Libraries.
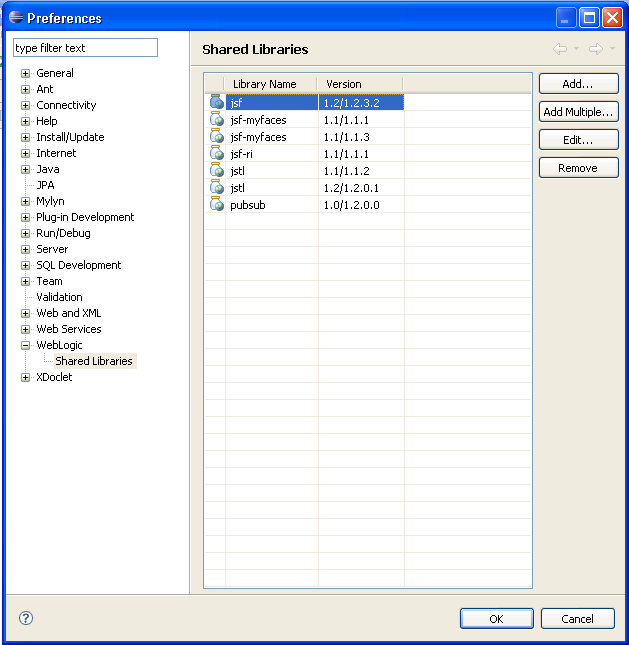
To add a shared library to your project, select Project > Properties > Java Build Path > Libraries tab > Add Library button > WebLogic Shared Libraries > Next. Then browse to a registered shared library.
OEPE provides support for WebLogic SCA container, which is used to populate the Spring context file and bundle as part of any regular Java EE deployment bundles, such as EAR or WAR.

For more information, see Configuring a Project to Use WebLogic SCA.
OEPE provides support for WebLogic Scripting Tool, which is used for for monitoring, managing and configuring Oracle WebLogic Server from the command line.
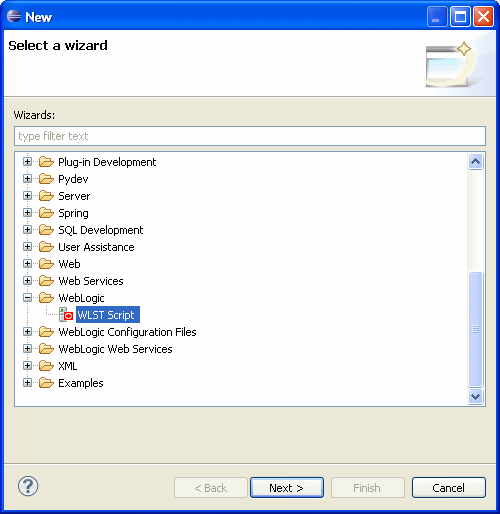
For more information, see Using WebLogic Scripting Tool.
Apache XMLBeans is a XML/Java binding technology that provides an intuitive
way to access and manipulate XML data using Java. For example, you can generate
Java types from a given XML schema, and then access XML document instances
of that schema using JavaBean accessors (get and set methods). This
way of accessing XML is much easier and more predictable than traditional
cursor-style access.
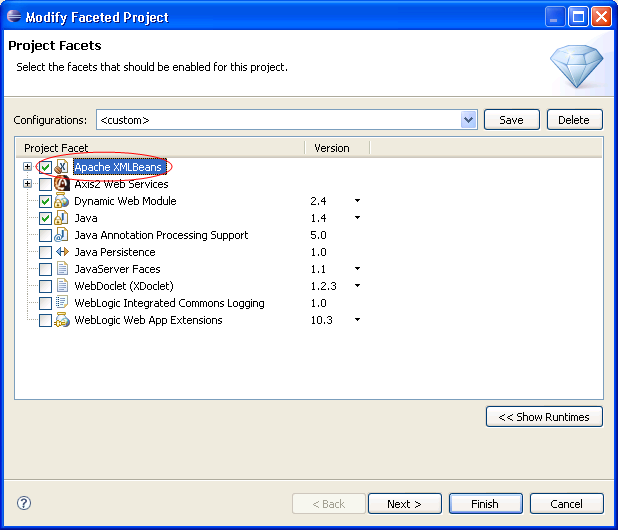
Apache XMLBeans versions 2.1, 2.2, and 2.3 are supported.
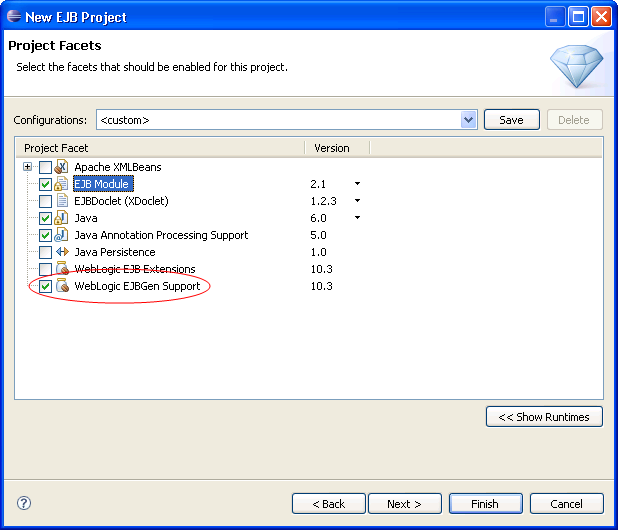
To add Apache XMLBeans support to your application, select the Apache XMLBean facet during project creation or through the project Properties dialog (Project > Properties > Project Facets > Modify Project).
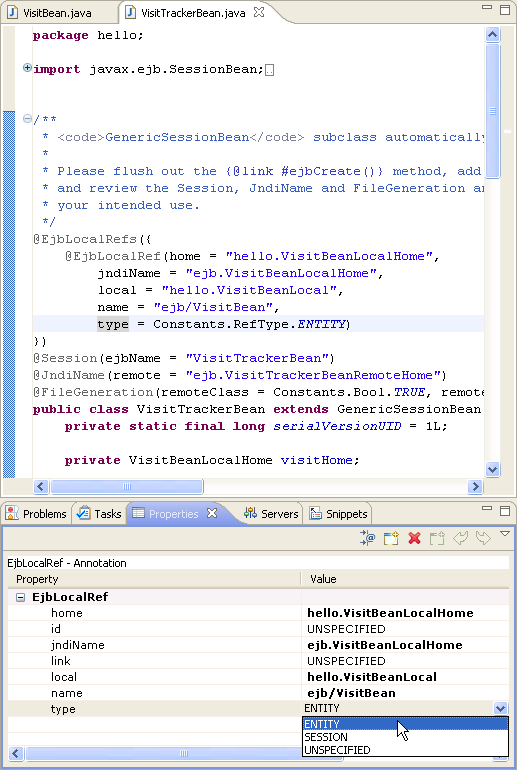
Instead of editing and maintaining all of the multiple component files of an EJB, EJBGen lets you work with only one specially annotated bean class. From this one class, EJBGen parses the annotations and generates the remote and home interfaces and deployment descriptor. This is accomplished by using EJBGen annotations. These annotations are used to mark which methods are to be exposed when generating remote and home interfaces and to specify the deployment descriptor settings.
You can edit these annotations directly, or use the Properties view, which is especially useful because it already knows the constant values that many annotation attributes require.
You can add EJBGen annotations support by adding facets during project creation or through the project Properties dialog (Project > Properties > Project Facets > Modify Project).