6 Administering Web Services
Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control is the primary interface that you can use to manage Oracle Fusion Middleware Web Services. You can also use WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST) commands to perform some configuration tasks for SOA, ADF, and WebCenter services. This chapter describes how to navigate to the pages in Fusion Middleware Control where you perform many of the tasks to manage your Web services, and it describes how to perform basic administration tasks. When applicable, it describes how to perform the task using WLST also. This chapter includes the following sections:
-
Navigating to the Web Services Summary Page for an Application
-
Enabling or Disabling the Display of the Web Service WSDL Document
Note:
As described in Chapter 17, "Securing and Administering WebLogic Web Services", you use Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control to test and monitor Java EE Web services. For all other configuration tasks you use the WebLogic Server Administration Console.The Web services pages described in this chapter have different content for Java EE, ADF and WebCenter Web and SOA services. The pages for ADF and WebCenter and SOA Web services are shown in the figures.
Viewing All Current Web Services for a Server
Follow the procedures below to view all of the currently-deployed Web services for a given server.
Using Fusion Middleware Control
To view all current Web services for a server:
-
In the navigator pane, expand WebLogic Domain to show the domain in which you want to see the Web services.
-
Expand the domain.
-
Select the server for which you want to view all current Web services.
-
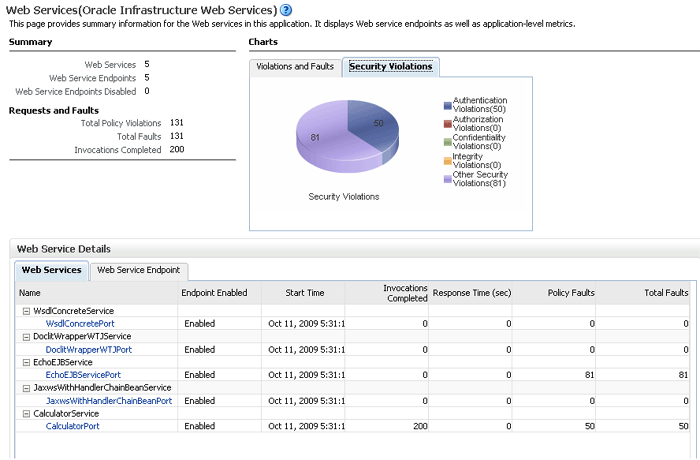
Using Fusion Middleware Control, click WebLogic Server and then Web Services. The server-specific Web Services Summary page appears, as shown in Figure 6-1.
You can view tabs for Java EE Web services, non-SOA Oracle Web services such as those for ADF and WebCenter, and SOA Web services.
The tabs that are displayed depend on the Web services deployed on that server.
For ADF and WebCenter and SOA Services, from this page you can click Attach Policies to attach one or more policies to one or more Web services.
Figure 6-1 Server-Specific Web Services Summary Page
Description of "Figure 6-1 Server-Specific Web Services Summary Page"
Using WLST
To view all the current Web services for a server:
-
Connect to the running instance of WebLogic Server for which you want to view the Web services as described in "Accessing the Web Services Custom WLST Commands".
-
Use the
listWebServices()WLST command to display a list of the Web services.listWebServices (application,composite,[detail]
For example:
wls:/wls-domain/serverConfig>listWebServices() /wls-domain/AdminServer/jaxwsejb30ws: moduleName=jaxwsejb,moduleType=web,serviceName=JaxwsWithHandlerChainBeanService moduleName=jaxwsejb, moduleType=web, serviceName=WsdlConcreteService moduleName=jaxwsejb, moduleType=web, serviceName=EchoEJBService -
Set the
detailargument of thelistWebServicescommand totrueto view port and policy information for the Web services.For example:
wls:/wls-domain/serverConfig> listWebServices(None,None,true) /wls-domain/AdminServer/jaxwsejb30ws : moduleName=jaxwsejb, moduleType=web, serviceName=JaxwsWithHandlerChainBeanService enableTestPage: true enableWSDL: true JaxwsWithHandlerChainBeanPort http://host.us.oracle.com:7001/jaxwsejb/JaxwsWithHandlerChainIntf enable: true enableREST: false maxRequestSize: -1 loggingLevel: NULL moduleName=jaxwsejb, moduleType=web, serviceName=WsdlConcreteService enableTestPage: true enableWSDL: true WsdlConcretePort http://host.us.oracle.com:7001/jaxwsejb/WsdlAbstract enable: true enableREST: false maxRequestSize: -1 loggingLevel: NULL moduleName=jaxwsejb, moduleType=web, serviceName=EchoEJBService enableTestPage: true enableWSDL: true EchoEJBServicePort http://host.us.oracle.com:7001/jaxwsejb/EchoEJBService enable: true enableREST: false maxRequestSize: -1 loggingLevel: NULL
For more information about the listWebServices command, see "Web Services Custom WLST Commands" in Oracle Fusion Middleware WebLogic Scripting Tool Command Reference.
Navigating to the Web Services Summary Page for an Application
Follow the procedure below to navigate to the page where you can see the list of Web services for your application.
To navigate to the Web services summary page for an application:
-
From the navigator pane, click the plus sign (+) for the Application Deployments folder to expose the applications in the farm, and select the application.
The Application Deployment home page is displayed.
-
Using Fusion Middleware Control, click Application Deployment, then click Web Services.
This takes you to the Web Services summary page (Figure 6-2) for your application.
Viewing the Web Services in Your Application
Use the procedures described in the following sections to view the Web services in your application.
Using Fusion Middleware Control
Navigate to the home page for your Web service, as described in "Navigating to the Web Services Summary Page for an Application". From the Web Services Summary page, you can do the following:
-
View the Web services in the application.
-
View the Web service configuration, endpoint status, policy faults, and more.
-
View and monitor Web services faults, including Security, Reliable Messaging, MTOM, Management, and Service faults.
-
View and monitor Security violations, including authentication, authorization, message integrity, and message confidentiality violations.
-
Navigate to pages where you can configure your Web services ports, including enabling and disabling the port, and attaching policies to Web services.
Using WLST
To view the Web services in your application:
-
Connect to the running instance of WebLogic Server to which the application is deployed as described in "Accessing the Web Services Custom WLST Commands".
-
Use the
listWebServicesWLST command to display a list of the Web services in your application. You must specify the complete application path name to identify the application and the server instance to which it is deployed.listWebServices (application,composite,[detail]
For example:
wls:/wls-domain/serverConfig>listWebServices("wls-domain/AdminServer/jaxwsejb30ws") /wls-domain/AdminServer/jaxwsejb30ws: moduleName=jaxwsejb,moduleType=web,serviceName=JaxwsWithHandlerChainBeanService moduleName=jaxwsejb, moduleType=web, serviceName=WsdlConcreteService moduleName=jaxwsejb, moduleType=web, serviceName=EchoEJBService moduleName=jaxwsejb, moduleType=web, serviceName=CalculatorService moduleName=jaxwsejb, moduleType=web, serviceName=DoclitWrapperWTJService
For details about the listWebServices command, see "Web Services Custom WLST Commands" in Oracle Fusion Middleware WebLogic Scripting Tool Command Reference.
Viewing the Details for a Web Service Port
Use the procedures described in the following sections to view the details for a Web service port.
Using Fusion Middleware Control
To view the details for a Web service port:
-
Navigate to the Web Services Summary page.
-
In the Web Service Details section of the page, click on the plus (+) for the Web service to display the Web service ports if they are not already displayed.
-
Click the name of the port to navigate to the Web Service Endpoints page.
-
From the Web Service Endpoints page, you can do the following:
-
Click the Operations tab to see the list of operations for this port.
-
Click the Policies tab to see the policies attached to this port.
-
Click the Charts tab to see a graphical display of the faults for this port.
-
Click the Configuration tab to see the configuration for this port.
-
As an alternative method of viewing the details for a Web service port, you can instead navigate to the server-wide Web Services Summary page, as described in "Viewing All Current Web Services for a Server", which lists all of the Web services, and click the name of the port to navigate to the specific Web Service Endpoints page.
Using WLST
To view the details for a Web service port (endpoint):
-
Connect to the running instance of WebLogic Server to which the application is deployed as described in "Accessing the Web Services Custom WLST Commands".
-
Use the
listWebServicesWLST command to display a list of the Web services in your application as described in "Viewing the Web Services in Your Application". -
Use the
listWebServicePortscommand to display the port name and endpoint URL for a Web service.listWebServicePorts(application,moduleOrCompName,moduleType,serviceName)
For example, to display the port for the
WsdlConcreteService:wls:/wls-domain/serverConfig> listWebServicePorts("/wls-domain/AdminServer/jaxwsejb30ws","jaxwsejb", "web","WsdlConcreteService") WsdlConcretePort http://host.us.oracle.com:7001/jaxwsejb/WsdlAbstract
-
Use the
listWebServiceConfigurationcommand to view the configuration details for a Web service port.listWebServiceConfiguration(application,moduleOrCompName,moduleType,serviceName,[subjectName])
For example, to view the configuration details for the
WsdlConcretePort:wls:/wls-domain/serverConfig> listWebServiceConfiguration("/wls-domain/AdminServer/jaxwsejb30ws", "jaxwsejb","web","WsdlConcreteService","WsdlConcretePort") enable: true enableREST: false maxRequestSize: -1 loggingLevel: NULL
-
Use the
listWebServicePoliciescommand to view the policies that are attached to a Web service port.listWebServicePolicies(application,moduleOrCompName,moduleType,serviceName,subjectName)
For example, to view the policies attached to the
WsdlConcretePortport and any policy override settings:wls:/wls_domain/serverConfig> listWebServicePolicies("/wls_domain/AdminServer/jaxwsejb30ws", "jaxwsejb","web","WsdlConcreteService","WsdlConcretePort") WsdlConcretePort : addressing : oracle/wsaddr_policy , enabled=true management : oracle/log_policy , enabled=true
For more information about these WLST commands and their arguments, see "Web Services Custom WLST Commands" in Oracle Fusion Middleware WebLogic Scripting Tool Command Reference.
Viewing the Security Violations for a Web Service
Follow the procedure below to view security violations for a Web service.
To view the security violations for a Web service:
-
Navigate to the Web Services Summary page.
-
In the Charts section of the page, select the Security Violations tab.
A graphical representation of the authentication, authorization, confidentiality, and integrity faults for all Web services in the application is displayed in the pie chart.
-
In the Web Service Details section of the page, click on the plus (+) for the Web service to display the Web service ports if they are not already displayed.
-
Click the name of the port to navigate to the Web Service Endpoints page.
-
Click the Charts tab to see a graphical representation of all faults and all security faults.
-
Click the Policies tab.
A list of the policies that are attached to the port is displayed. The status of the policy (whether the policy is enabled or disabled), the number of security faults (authentication, authorization, confidentiality, and integrity), and total policy faults for each policy are displayed.
Viewing Web Service Clients
The following sections describe how to view Web service clients for your application.
Using Fusion Middleware Control
The steps you follow to view a Web service client depend on the application type (SOA reference, ADF DC, WebCenter, or asynchronous Callback client), as described in the following sections.
Viewing SOA References
Use the following procedure to view a SOA reference client:
-
From the navigator pane, click the plus sign (+) for SOA deployments, and select the target.
-
Click the Dashboard tab, if it is not already selected.
-
In the Services and References portion of the page, select the SOA reference to view.
-
In the SOA reference page, click the tabs to view the client data.
Viewing ADF DC Web Service Clients
Use the following procedure to view an ADF DC Web service client.
-
From the navigator pane, click the plus sign (+) for the Application Deployments folder to expose the applications in the farm, and select the application.
The Application Deployment home page is displayed.
-
Using Fusion Middleware Control, click Application Deployment, then click ADF.
-
Select the Administration tab.
-
Click ADF Connections.
-
In the Web Service Connections portion of the page, click Configure Web Service.
-
Select the Web service client endpoint to view.
Viewing WebCenter Portlets
Use the following procedure to view a WebCenter portlet.
-
From the navigator pane, click the plus sign (+) for the WebCenter folder and WebCenter Spaces folder to display the WebCenter spaces.
-
Click the name of the WebCenter space to view.
-
From the WebCenter menu, select Settings and Service Configuration.
The Webcenter Service Configuration page is displayed.
-
Select Portlet Producers to view the WebCenter portlets.
Viewing Asynchronous Web Service Callback Clients
Use the following procedure to view an asynchronous Web service Callback client. Callback clients are used only by asynchronous Web services to return the response to the caller. For more information, see "Developing Asynchronous Web Services" in Concepts Guide for Oracle Infrastructure Web Services.
-
Navigate to the endpoint for the asynchronous Web service, as described in "Viewing the Details for a Web Service Port".
-
Click Callback Client in the upper right portion of the endpoint page.
Using WLST
Use the following procedure to view the Web service clients using WLST commands:
-
Connect to the running instance of WebLogic Server to which the application is deployed as described in "Accessing the Web Services Custom WLST Commands".
-
Use the
listWebServiceClientsWLST command to display a list of the Web service clients.listWebServiceClients(application,composite,[detail ]
This command enables you to list the clients for an application, a SOA composite, or a domain. To list the client information for an application or SOA composite, specify the appropriate argument. If you do not specify an application or SOA composite, the command outputs information, including the module name, module type, and SOA reference name for all the Web service clients in all applications and composites in every server instance in the domain. To view details about each client, including the port and policies, set the
detailargument totrue.For example:
wls:/base_domain/serverConfig> listWebServiceClients(None,None,true) /base_domain/soa_server1/soa-infra : compositeName=sdo-ejb-cust-nobpel[1.0], moduleType=soa, serviceRefName=EJBReference compositeName=EventMediatorDemo[1.0], moduleType=soa, serviceRefName=OrderLogger /base_domain/AdminServer/application1#V2.0 : moduleName=test1, moduleType=wsconn, serviceRefName=client HelloWorld_pt keystore.recipient.alias=A1 saml.issuer.name=B1 user.roles.include=C1 management : oracle/log_policy , enabled=true addressing : oracle/wsaddr_policy , enabled=true /base_domain/soa_server1/ServiceClient : moduleName=test1, moduleType=wsconn, serviceRefName=AppModuleService AppModuleServiceSoapHttpPort security : oracle/wss10_saml_token_client_policy , enabled=true management : oracle/log_policy , enabled=true addressing : oracle/wsaddr_policy , enabled=trueNote that the output displays SOA references (using the
serviceRefNameargument) for the SOA compositessdo-ejb-cust-nobpel[1.0]andEventMediatorDemo[1.0]. To list the SOA references for a SOA composite, specify the composite name in the command, for examplelistWebServiceClients(None,'EventMediatorDemo[1.0]').ADF and WebCenter clients are specified by the
moduleType=wsconnargument in the output.For more information about the WLST commands and their arguments, see "Web Services Custom WLST Commands" in Oracle Fusion Middleware WebLogic Scripting Tool Command Reference.
Displaying the Web Service WSDL Document
Follow the procedure below to display the WSDL document for a Web service.
To display the WSDL document for a Web service:
-
Navigate to the Web Services Summary page.
-
In the Web Service Details section of the page, click on the plus (+) for the Web service to display the Web service ports if they are not already displayed.
-
Click the name of the port to navigate to the Web Service Endpoints page.
-
In the WSDL Document field, click the port name to display the WSDL for the Web service (Figure 6-3).
Figure 6-3 Web Service Endpoints Page with Web Service WSDL
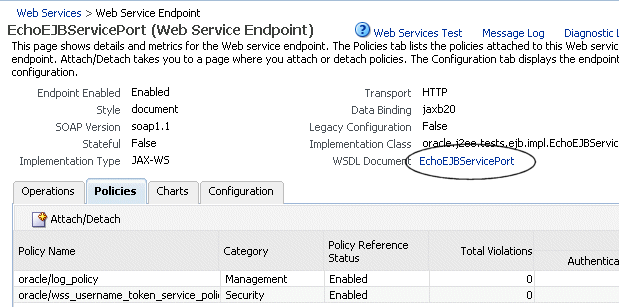
Description of "Figure 6-3 Web Service Endpoints Page with Web Service WSDL"
Configuring the Web Service Port
Follow the procedures below to configure the Web service endpoint (or port).
Using Fusion Middleware Control
Use the following procedure to configure the Web service port using Fusion Middleware Control:
-
Navigate to the application's Web Services Summary page, as described in "Navigating to the Web Services Summary Page for an Application".
-
In the Web Service Details section of the page, click on the plus (+) for the Web service to display the Web service ports if they are not already displayed.
-
Click the name of the port to navigate to the Web Service Endpoints page.
-
Click the Configuration tab.
-
Set the configuration attributes and click Apply.
For more information about setting the configuration attributes, see:
-
Restart the application that uses the Web service.
Using WLST
Use the following procedure to configure the Web service port using WLST:
-
Connect to the running instance of WebLogic Server to which the application is deployed as described in "Accessing the Web Services Custom WLST Commands".
-
Use the
listWebServicesWLST command to display a list of the Web services in your application as described in "Viewing the Web Services in Your Application". -
Use the
listWebServicePortscommand to display the port name and endpoint URL for a Web service.listWebServicePorts(application,moduleOrCompName,moduleType,serviceName)
For example, to display the port for the
WsdlConcreteService:wls:/wls-domain/serverConfig> listWebServicePorts("/wls-domain/AdminServer/jaxwsejb30ws",None,"web", "WsdlConcreteService") WsdlConcretePort http://host.us.oracle.com:7001/jaxwsejb/WsdlAbstract
-
Use the
listWebServiceConfigurationcommand to view the configuration details for a Web service port.listWebServiceConfiguration(application,moduleOrCompName,moduleType,serviceName,[subjectName])
For example, to view the configuration details for the
WsdlConcretePort:wls:/wls-domain/serverConfig> listWebServiceConfiguration("/wls-domain/AdminServer/jaxwsejb30ws","jaxwsejb", "web","WsdlConcreteService","WsdlConcretePort") enable: true enableREST: false maxRequestSize: -1 loggingLevel: NULL
Alternatively, you can set the
detailargument totruein thelistWebServicescommand to view the configuration details for the port as shown in "Using WLST" in "Viewing All Current Web Services for a Server". -
Use the
setWebServiceConfigurationcommand to set or change the port configuration. Specify the properties to be set or changed using theitemPropertiesargument.setWebServiceConfiguration(application,moduleOrCompName,moduleType, serviceName,subjectName,itemProperties)
For example, to change the logging level to SEVERE for the
WsdlConcretePort, use the following command:wls:/wls-domain/serverConfig> setWebServiceConfiguration("/wls-domain/AdminServer/jaxwsejb30ws", "jaxwsejb","web","WsdlConcreteService","WsdlConcretePort", [("loggingLevel","SEVERE")]) Please restart application to uptake the policy changes.
For more information about the configurable properties, see:
Note:
If any configuration item contains an unrecognized property name or an invalid value, this set command is rejected and an error message is displayed. -
For ADF and WebCenter applications, restart the Web service application. You do not need to restart a SOA composite.
For more information about these WLST commands and their arguments, see "Web Services Custom WLST Commands" in Oracle Fusion Middleware WebLogic Scripting Tool Command Reference.
Configuring Asynchronous Web Services
When you invoke a Web service synchronously, the invoking client application waits for the response to return before it can continue with its work. In cases where the response returns immediately, this method of invoking the Web service might be adequate. However, because request processing can be delayed, it is often useful for the client application to continue its work and handle the response later on. By calling a Web service asynchronously, the client can continue its processing, without interrupt, and will be notified when the asynchronous response is returned.
For information about developing asynchronous Web services, see "Developing Asynchronous Web Services" in Concepts Guide for Oracle Infrastructure Web Services.
The following procedure describes how to configure your deployed asynchronous Web services. You can also configure asynchronous Callback client, as described in "Configuring Asynchronous Web Service Callback Clients".
To configure asynchronous Web services:
-
Navigate to the Web Services Summary page.
-
In the Web Service Details section of the page, click on the plus (+) for the Web service to display the Web service ports if they are not already displayed.
-
Click the name of the port of the asynchronous Web service to navigate to the Web Service Endpoints page.
For an asynchronous Web service, the Asynchronous flag at the top of the page is set to true. Review the following flags, which provide more information about the asynchronous Web service:
-
Transaction Enabled for Request Queue—Flag that specifies whether transactions are enabled on the request queue.
-
Using Response Queue—Flag that specifies whether a response queue is being used. If set to false, then the response is sent directly to the Web service client, without being stored.
-
Transaction Enabled for Response Queue—Flag that specifies whether transactions are enabled on the response queue.
These flags are configured at design time. For more information, see "Developing Asynchronous Web Services" in Concepts Guide for Oracle Infrastructure Web Services.
-
-
From the Web Service Endpoints page, click the Configuration tab.
-
Under the Asynchronous Web Service section of the page, you can set the configuration properties defined in Table 6-1.
Note:
The configuration properties defined in Table 6-1 appear and are valid only for asynchronous Web services.Table 6-1 Configuration Properties for Asynchronous Web Services
Configuration Property Description JMS Request Queue Connection Factory Name
Name of the connection factory for the JMS request queue. The default JMS connection factory, weblogic.jms.XAConnectionFactory, provided with the base domain is used by default.
JMS Request Queue Name
Name of the request queue. The following queue is used by default: oracle.j2ee.ws.server.async.DefaultRequestQueue.
JMS Response Queue Connection Factory Name
Name of the connection factory for the JMS response queue. The default JMS connection factory, weblogic.jms.XAConnectionFactory, provided with the base domain is used by default.
JMS Response Queue Name
Name of the request queue. The following queue is used by default: oracle.j2ee.ws.server.async.DefaultResponseQueue.
-
Click Apply.
-
Restart the application that uses the Web service.
Enabling or Disabling a Web Service
When a Web service application is deployed, the Web service endpoint is enabled by default if no errors are encountered. If there are errors, the Web service application is deployed, but the Web service endpoint is not enabled.
You may need to temporarily make a Web service unavailable by disabling the Web service. For example, you may need to correct an invalid policy reference. When you disable a Web service, requests to the Web service will fail. To disable a Web service, you must make the port on which the Web service receives requests unavailable.
Using Fusion Middleware Control
To disable a Web service port:
-
Navigate to the Web Services Summary page.
-
In the Web Service Details section of the page, click on the plus (+) for the Web service to display the Web service ports if they are not already displayed.
-
Click the name of the port to navigate to the Web Service Endpoints page.
-
From the Web Service Endpoints page, click the Configuration tab.
-
Select Disabled from the Endpoint Enabled control, and click Apply.
-
Restart the application that uses the Web service.
Using WLST
To disable a Web service port using WLST, use the setWebServiceConfiguration command. Set the enable property of the itemProperties argument to false to disable the port and to true to enable it.
The procedure for using this command is described in "Using WLST" in "Configuring the Web Service Port".
For example, to disable the port WsdlConcretePort, use the following command:
wls:/wls-domain/serverConfig> setWebServiceConfiguration ("/wls-domain/AdminServer/jaxwsejb30ws","jaxwsejb","web","WsdlConcreteService", "WsdlConcretePort",[("enable","false")]) Please restart application to uptake the policy changes.
For more information about this WLST command, see "Web Services Custom WLST Commands" in Oracle Fusion Middleware WebLogic Scripting Tool Command Reference.
Enabling or Disabling RESTful Web Services
You can enable or disable a Web services port to accept messages in Representational State Transfer (REST) format.
Using Fusion Middleware Control
To enable or disable Web service styles:
-
From the Web Services Summary page, scroll down to the Web Services Details section of the page.
-
Click the plus sign (+) of the Web service to display the ports if they are not already displayed.
-
Click the port to display the Web Service Endpoint page.
-
Click the Configuration tab.
-
Select True from the REST Enabled list to enable REST, or select False to disable REST.
Figure 6-4 Enabling and Disabling RESTful Web Services
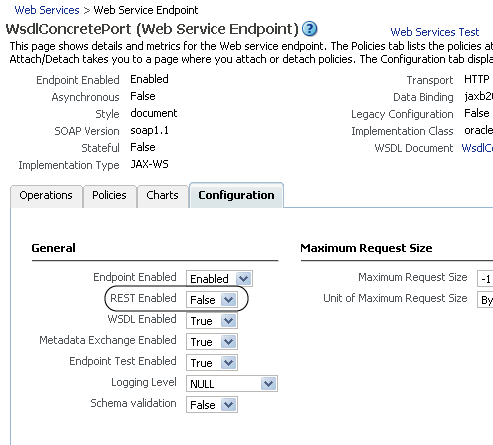
Description of "Figure 6-4 Enabling and Disabling RESTful Web Services"
-
Restart the application that uses the Web service.
Using WLST
To enable or disable a Web services port to accept messages in REST format using WLST, use the setWebServiceConfiguration command. Set the enableREST property of the itemProperties argument to true to enable REST and to false to disable it.
The procedure for using this command is described in "Using WLST" in "Configuring the Web Service Port".
For example, to enable the REST format for the WsdlConcretePort, use the following command:
wls:/wls-domain/serverConfig> setWebServiceConfiguration ("/wls-domain/AdminServer/jaxwsejb30ws","jaxwsejb","web","WsdlConcreteService", "WsdlConcretePort",[("enableREST","true")]) Please restart application to uptake the policy changes.
For more information about this WLST command, see "Web Services Custom WLST Commands" in Oracle Fusion Middleware WebLogic Scripting Tool Command Reference.
Enabling or Disabling the Display of the Web Service WSDL Document
The following procedures describe how to enable or disable the display of the Web service WSDL document.
Using Fusion Middleware Control
To enable or disable the display of the Web service WSDL document:
-
Navigate to the Web Services Summary page.
-
In the Web Service Details section of the page, click on the plus (+) for the Web service to display the Web service ports if they are not already displayed.
-
Click the name of the port to navigate to the Web Service Endpoints page.
-
From the Web Service Endpoints page, click the Configuration tab.
-
Select Enabled or Disabled from the WSDL Enabled control, and click Apply.
-
Restart the application that uses the Web service.
Using WLST
To enable or disable the display of a WSDL document for a Web service port, use the setWebServiceConfiguration command. Set the enableWSDL property of the itemProperties argument to true to enable display the WSDL and to false to disable it.
The procedure for using this command is described in "Using WLST" in "Configuring the Web Service Port".
For example, to enable the WSDL display for the WsdlConcretePort, use the following command:
wls:/wls-domain/serverConfig> setWebServiceConfiguration ("/wls-domain/AdminServer/jaxwsejb30ws","jaxwsejb","web", "WsdlConcreteService","WsdlConcretePort",[("enableWSDL","true")]) Please restart application to uptake the policy changes.
For more information about this WLST command, see "Web Services Custom WLST Commands" in Oracle Fusion Middleware WebLogic Scripting Tool Command Reference.
Enabling or Disabling the Exchange of Metadata
The following procedure describes how to enable or disable the exchange of Web service metadata.
To enable or disable the exchange of metadata:
-
Navigate to the Web Services Summary page.
-
In the Web Service Details section of the page, click on the plus (+) for the Web service to display the Web service ports if they are not already displayed.
-
Click the name of the port to navigate to the Web Service Endpoints page.
-
From the Web Service Endpoints page, click the Configuration tab.
-
Select Enabled or Disabled from the Metadata Exchange control, and click Apply.
-
Restart the application that uses the Web service.
Enabling or Disabling the Web Service Test Endpoint
The following procedure describes how to enable or disable the Web service test endpoint.
Using Fusion Middleware Control
To enable or disable the Web service test endpoint:
Note:
This flag does not control the availability of the Web Services Test link.-
Navigate to the Web Services Summary page.
-
In the Web Service Details section of the page, click on the plus (+) for the Web service to display the Web service ports if they are not already displayed.
-
Click the name of the port to navigate to the Web Service Endpoints page.
-
From the Web Service Endpoints page, click the Configuration tab.
-
Select Enabled or Disabled from the Endpoint Test Enabled control, and click Apply.
-
Restart the application that uses the Web service.
Using WLST
To enable or disable the Web service test endpoint, use the setWebServiceConfiguration command. Set the enableTestPage property of the itemProperties argument to true to enable the test endpoint and to false to disable it.
The procedure for using this command is described in "Using WLST" in "Configuring the Web Service Port".
For example, to enable the test endpoint for the WsdlConcretePort, use the following command:
wls:/wls-domain/serverConfig> setWebServiceConfiguration ("/wls-domain/AdminServer/jaxwsejb30ws","jaxwsejb","web","WsdlConcreteService", "WsdlConcretePort",[("enableTestPage","true")]) Please restart application to uptake the policy changes.
For more information about this WLST command, see "Web Services Custom WLST Commands" in Oracle Fusion Middleware WebLogic Scripting Tool Command Reference.
Validating the Request Message
The following procedure describes how to enable or disable the validation of the request message against the schema.
To enable or disable schema validation:
-
Navigate to the Web Services Summary page.
-
In the Web Service Details section of the page, click on the plus (+) for the Web service to display the Web service ports if they are not already displayed.
-
Click the name of the port to navigate to the Web Service Endpoints page.
-
From the Web Service Endpoints page, click the Configuration tab.
-
Select Enabled or Disabled from the Schema validation control, and click Apply.
-
Restart the application that uses the Web service.
Setting the Size of the Request Message
The maximum size of the request message to the Web service can be configured using the procedures provided in the following sections.
Using Fusion Middleware Control
To set the size of the request message:
-
Navigate to the Web Services Summary page.
-
In the Web Service Details section of the page, click on the plus (+) for the Web service to display the Web service ports if they are not already displayed.
-
Click the name of the port to navigate to the Web Service Endpoints page.
-
Click the Configuration tab.
-
Set the Maximum Request Size and the Unit of Maximum Request Size and click Apply.
Note:
If you set the Maximum Request Size to -1, indicating that there is no maximum request size, then the Unit of Maximum Request Size setting is irrelevant and defaults to bytes.Figure 6-5 Setting Size of Request Message
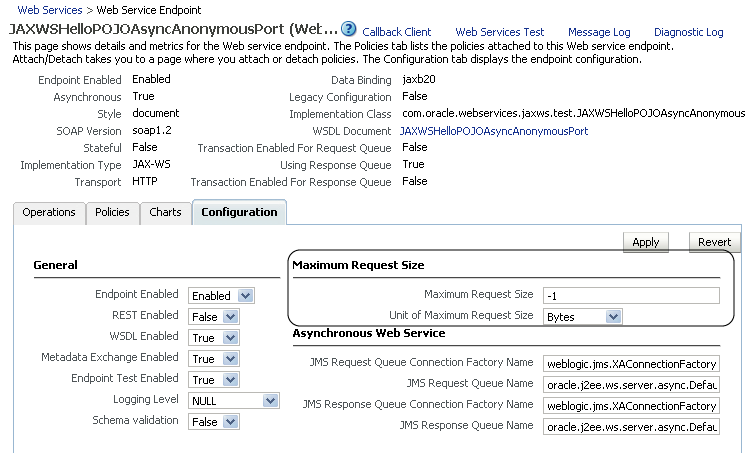
Description of "Figure 6-5 Setting Size of Request Message"
-1 sets no limit to the size of the message. Or, you can set a maximum limit to the message by entering a number in the text box and selecting the unit of measurement.
-
Restart the application that uses the Web service.
Using WLST
To set the size of a request message for a Web service port, use the setWebServiceConfiguration command. Set the maxRequestSize property of the itemProperties argument to the desired value. Enter a long integer to set the maximum value, or -1 to set no limit to the size of the message. The default is -1.
The procedure for using this command is described in "Using WLST" in "Configuring the Web Service Port".
For example, to specify that there is no message limit size for the WsdlConcretePort, use the following command:
wls:/wls-domain/serverConfig> setWebServiceConfiguration ("/wls-domain/AdminServer/jaxwsejb30ws","jaxwsejb","web","WsdlConcreteService", "WsdlConcretePort",[("maxRequestSize","-1")])
For more information about this WLST command, see "Web Services Custom WLST Commands" in Oracle Fusion Middleware WebLogic Scripting Tool Command Reference.
Enabling and Disabling MTOM
Support for MTOM is provided by attaching the oracle/wsmtom_policy policy to a Web service. You can enable or disable MTOM for a Web service by enabling or disabling this policy. See "Disabling a Policy for a Single Policy Subject" for more information.
You must restart the application after enabling or disabling MTOM.
Configuring the Web Service Client
For the Web service clients in your application, including SOA references, ADF data control, and asynchronous Web service Callback clients, you can set the configuration properties defined in Table 6-2.
Table 6-2 Configuration Properties for Web Service Clients
| Configuration Property | Property Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Endpoint Address |
javax.xml.ws.service.endpoint.address |
Port URL to which the client will send the request. Note: This property is not available for asynchronous Web service Callback clients. |
|
Maintain Session |
javax.xml.ws.session.maintain |
Flag that specifies whether the session should be maintained. Note: This property is not available for asynchronous Web service Callback clients. |
|
Stop Chunking |
oracle.webservices.donotChunk |
Flag that specifies whether chunking is enabled for client requests. |
|
Chunking Size (bytes) |
oracle.webservices.chunkSize |
Size of the request chunk in bytes. |
|
HTTP Read Timeout (ms) |
oracle.webservices.httpReadTimeout |
Length of the request read timeout in milliseconds. |
|
HTTP Connection Timeout (ms) |
oracle.webservices.httpConnTimeout |
Length of the request connection timeout in milliseconds. |
|
HTTP User Name |
(javax.xml.ws.security.auth.username) oracle.webservices.auth.username |
Authenticated HTTP user name. |
|
HTTP User Password |
(javax.xml.ws.security.auth.password) oracle.webservices.auth.password |
Authenticated HTTP user password. |
|
Preemptive |
oracle.webservices.preemptiveBasicAuth |
Flag that specifies whether security will be sent with the request without being challenged. |
|
Proxy Host |
oracle.webservices.proxyHost |
URL of proxy to which client will send the request. |
|
Proxy Port |
oracle.webservices.proxyPort |
Port number of the proxy. |
|
Proxy User Name |
oracle.webservices.proxyUsername |
Valid user name to access the proxy. |
|
Proxy User Password |
oracle.webservices.proxyPassword |
Valid password to access the proxy. |
|
Proxy Realm |
oracle.webservices.proxyAuthRealm |
Realm used by the proxy. |
|
Proxy Authentication Type |
oracle.webservices.proxyAuthType |
Authentication type used by the proxy. |
The following sections describe how to configure Web service clients using Fusion Middleware Control and WLST.
Using Fusion Middleware Control
The following procedures describe how to configure SOA reference, ADF DC, WebCenter, and asynchronous Web service Callback clients.
Configuring SOA References
The following procedure describes how to configure a SOA reference.
-
View the SOA reference, as described in "Viewing SOA References".
-
Click the Configuration tab.
-
Set the configuration values as required. Refer to Table 6-2.
-
Click Apply.
Configuring ADF DC Web Service Clients
The following procedure describes how to configure an ADF DC Web service client.
-
View the ADF DC Web service client, as described in "Viewing ADF DC Web Service Clients".
-
Click the Configuration tab.
-
Set the configuration values as required. Refer to Table 6-2.
-
Click Apply.
-
Restart the application that uses the Web service.
Configuring Asynchronous Web Service Callback Clients
The following procedure describes how to configure an asynchronous Web service Callback client. Callback clients are used only by asynchronous Web services to return the response to the caller. For more information, see "Developing Asynchronous Web Services" in Concepts Guide for Oracle Infrastructure Web Services.
To configure an asynchronous Web service Callback client:
-
Navigate to the endpoint for the asynchronous Web service, as described in "Viewing the Details for a Web Service Port".
-
Click Callback Client in the upper right portion of the endpoint page.
-
Click the Configuration tab.
-
Set the configuration values as required. Refer to Table 6-2.
-
Click Apply.
Using WLST
Use the following procedure to configure the Web service client port using WLST:
-
Connect to the running instance of WebLogic Server to which the application is deployed as described in "Accessing the Web Services Custom WLST Commands".
-
Use the
listWebServiceClientsWLST command to display a list of the Web service clients in your application as described in "Viewing Web Service Clients". -
Use the
listWebServiceClientPortscommand to display the port name and endpoint URL for a Web service client.listWebServiceClientPorts(application,moduleOrCompName,moduleType,serviceRefName)
For example, to display the port for the service reference
client:wls:/wls-domain/serverConfig> listWebServiceClientPorts('/base_domain/AdminServer/application1#V2.0', 'test1','wsconn','client') HelloWorld_pt
-
Use the
listWebServiceClientStubPropertiescommand to view the configuration details for a Web service client port.listWebServiceClientStubProperties(application, moduleOrCompName, moduleType, serviceRefName,portInfoName)
For example, to view the configuration details for the
HelloWorld_pt:wls:/wls-domain/serverConfig> listWebServiceClientPorts('/base_domain/AdminServer/application1#V2.0', 'test1','wsconn','client','HelloWorld_pt') keystore.recipient.alias=A1 saml.issuer.name=B1 user.roles.include=C1
Alternatively, you can set the
detailargument totruein thelistWebServiceClientscommand to view the configuration details for the port as shown in "Using WLST" in "Viewing Web Service Clients". -
Do one of the following:
-
Use the
setWebServiceClientStubPropertycommand to set or change a single stub property of a Web service client port. Specify the property to be set or changed using thepropNameandpropValuearguments. To remove a property, specify a blank value for thepropValueargument.setWebServiceClientStubProperty(application,moduleOrCompName,moduleType, serviceRefName,portInfoName,propName,[propValue])
For example, to change the
keystore.recipient.alias tooraclefor theHelloWorld_pt, use the following command:wls:/wls-domain/serverConfig> setWebServiceClientStubProperty('/base_domain/AdminServer/application1#V2.0', 'test1','wsconn','client','HelloWorld_pt','keystore.recipient.alias','oracle')
-
Use the
setWebServiceClientStubPropertiescommand to configure the set of properties of a Web service client port. Specify the properties to be set or changed using thepropertiesargument.setWebServiceClientStubProperties(application, moduleOrCompName, moduleType, serviceRefName, portInfoName, properties)
This command configures or resets all of the stub properties for the Oracle WSM client security policy attached to the client. Each property that you list in the command is set to the value you specify. If a property that was previously set is not explicitly specified in this command, it is reset to the default for the property. If no default exists, the property is removed.
For more information about the client properties that you can set, see Table 6-2, "Configuration Properties for Web Service Clients". When specifying these properties, use the format shown in the Property Name column.
You can also set the properties described in "Attaching Client Policies Permitting Overrides".
-
-
For ADF and WebCenter applications, restart the Web service application. You do not need to restart a SOA composite.
For more information about these WLST commands and their arguments, see "Web Services Custom WLST Commands" in Oracle Fusion Middleware WebLogic Scripting Tool Command Reference.