11g Release 1 (11.1.1.5.0)
Part Number E16689-01
Contents
Previous
Next
|
Oracle® Fusion
Applications Security Guide 11g Release 1 (11.1.1.5.0) Part Number E16689-01 |
Contents |
Previous |
Next |
This chapter contains the following:
Security Components: How They Fit Together
Regulatory Frameworks in Oracle Fusion Applications Security: How They Are Applied
Security Standards: How They Are Applied
Security Principles: How They Are Applied
Security Products: How They Are Applied
Security Processes: How They Are Applied
Secured Oracle Fusion Applications Deployments: Points To Consider
Users are granted access to various resources using Oracle Identity Management (OIM) and Authorization Policy Manager (APM). Integration with Governance, Risk, and Compliance Controls (GRCC) supports segregation of duties (SOD).
Oracle Fusion entitlement management secures access to all three tiers at the service-oriented architecture (SOA) layer, which is supported by Oracle Platform Security Services (OPSS). That means that rather than having every application with its own entitlement layer, access is managed as a centralized service shared by all applications.
The figure shows elements of Oracle Fusion Applications security and supporting structures in the Web, application, middle, and data tiers.
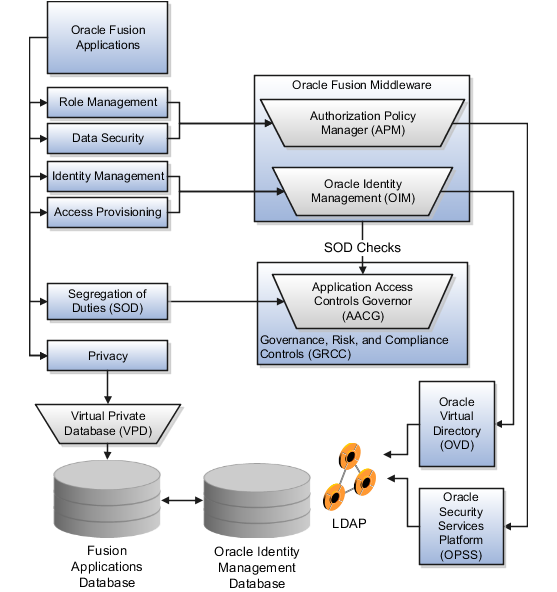
The following components of an Oracle Fusion Applications deployment participate in security.
|
Component |
Does what? |
|---|---|
|
Oracle HTTP Server (OHS) |
Takes all incoming HTTP requests |
|
Oracle Access Manager (OAM) |
Performs single sign on (SSO) |
|
Web Gate (OAM component) |
Intercepts requests and checks for user credentials |
|
Web Pass (OAM Web server plug-in) |
Passes information between the Web server and OAM's Identity Server |
|
OAM Policy Manager |
Supports managing single sign on (SSO), and URL-based authentication and authorization policies |
|
Oracle Identity Management (OIM) |
Handles user provisioning |
|
Oracle Web Services Manager (OWSM) |
Provides infrastructure for Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) and Web services security |
|
OWSM Agent |
Enforces SOA and Web services security |
|
OWSM Policy Manager |
Supports setting up policy configuration for SOA and Web services security |
|
Oracle Platform Security Services (OPSS) |
Provides framework to manage policies, identity, and audit services across the enterprise |
|
Oracle Virtual Directory (OVD) |
Virtualizes data sources in Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) stores |
|
Identity Governance Framework (IGF) |
Manipulates users, groups, and policies in LDAP |
|
Authorization Policy Management (APM) |
Supports managing authorization policies |
|
Enterprise Manager (EM) |
Supports managing deployed components, services, and applications |
|
Oracle Virtual Private Database (VPD) |
Protects personally identifiable information (PII) attributes in the database from unauthorized access by privileged users such as database administrators (DBA) |
Note
OAM policies have no relationship with OPSS policies.
Oracle Fusion Applications accesses policies through the services of WebLogic Servers. OPSS populates the Java authorization (JAZN) file with policies for transfer to Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) and distribution to applications using WebLogic services.
The components of the Oracle Fusion Applications security approach span all tiers of a deployment technology stack.
Data
Middleware
Applications
Web
Installation typically sets up Oracle Fusion Applications in predefined WebLogic Server (WLS) domains. that correspond to product families, such as Financials or Human Capital Management (HCM). A WLS domain is a group of servers working together in the middle tier to serve the Java Platform, Enterprise Edition (Java EE) applications in the applications tier with the data in the database of the data tier.
In the data tier the database manages the data for Oracle Fusion Applications. Data security policies are stored in Oracle Fusion Data Security (FND_GRANTS). Function security policies are stored in the LDAP policy store.
Oracle Internet Directory serves as an LDAP store. If your enterprise is using a different LDAP store, use Oracle Virtual Directory to connect to your LDAP store.
In the middle tier, the WLS contains the business components and user interface faces of the Application Development Framework (ADF) instances that run Oracle Fusion Applications. The middle tier also contains other essential components of an Oracle Fusion Applications deployment that are relevant to security.
Enterprise Scheduler Services for executing processes
Web Center for managing tags, Watchlists, and Oracle Fusion Search
Service Oriented Architecture for managing Web services
Content Management Server of Universal Content Management (UCM) for managing documents and attachments
Oracle Identity Manager (OIM) for user provisioning
Oracle Access Manager (OAM) for authentication and authorization
Oracle Business Intelligence Foundation Suite for Oracle Applications (OBIFA) and BI Publisher for analytics and reports
All of these components use OPSS to communicate with the applications and Web tiers. OPSS controls abstractions of the pages and widgets that appear in Oracle Fusion applications
Authorization Policy Management defines entitlements using OPSS. LDAP such as Oracle Internet Directory repositories store job roles and users. Oracle Identity Management manages job roles and users.
In the applications tier, Enterprise Manager handles the functional setup and features of your deployment.
In the Web tier, WebCache, the HTTP Server, and load balancers manage client interactions.
The following components must be present at setup and runtime.
Oracle Database
Oracle Text
PL/SQL
SQL*Loader
Oracle Data Integrator (ODI)
Oracle Database Enterprise Edition
Oracle Identity Management
Identity Governance Framework (IGF)
WebLogic Server and selected subcomponents
Application Development Framework (ADF)
ADF Data Visualizations (DVT)
Groovy (in ADF business components (ADFbc))
Java Architecture for XML Binding (JAXB)
Java API for XML Web Services (JAX-WS)
Java Transaction API (JTA)
Service Component Architecture (SCA)
SOA Suite and business process management (BPM) Suite selected components
Approval Management System (AMX)
Business Process Execution Language (BPEL)
Business Rules
Oracle Enterprise Scheduler
Events Delivery Network (EDN)
Oracle Content Server (using Web Center Framework) with full Universal Content Management suite
Oracle Human Workflow
Oracle Mediator
Oracle Web Services Manager (OWSM)
Web Center Framework
Oracle Single Sign-On Server
Oracle Virtual Directory
Oracle Business Intelligence Foundation Suite for Oracle Applications (OBIFA) selected components
BI Publisher, including Marketing Segmentation Server
Oracle BI Answers
Oracle BI Dashboards
Oracle BI Delivers
Oracle BI Presentation Server
Oracle BI Server
Other components
Extended Spread Sheet Database (ESSbase)
Oracle Real-Time Decisions (RTD)
Enterprise Crawl and Search Framework (ECSF)
Any LDAP server (such as, but not limited to, Oracle Internet Directory (OID)).
Note
OID is the LDAP that supports provisioning by default, but Oracle Fusion Applications supports third-party servers directly.
For more information about security in the middle tier, see the Oracle Fusion Middleware Security Overview and the Oracle Fusion Middleware Security and Administrator's Guide for Web Services.
Access components safeguard against unauthorized use at all levels of an Oracle Fusion Applications deployment infrastructure.
Users and provisioning components illustrate how access components interact in an Oracle Fusion Applications deployment.
Access components support securing all types of users.
Internal users on trusted devices
Remotely located users on trusted devices
Partners
Web site users
The following graphic shows Oracle Fusion Applications running on the Web services of Oracle Fusion Middleware and subjecting internal and external users to authentication and authorization as defined by the security policies and identities stored in a Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) store. Access to sensitive data is further protected by safeguards such as Oracle Database Vault and Oracle Virtual Directory.
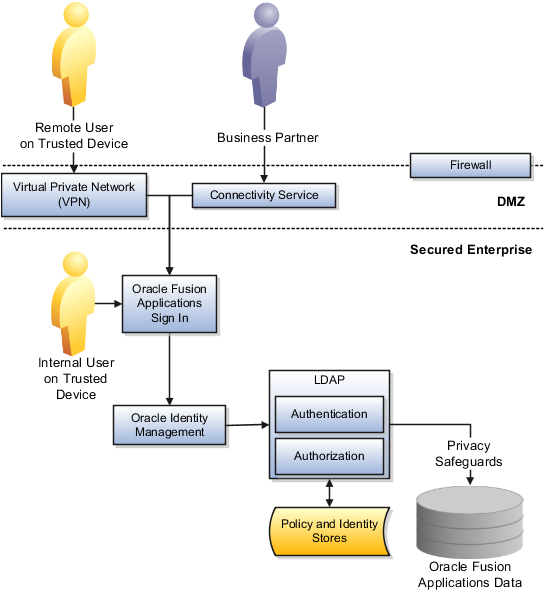
Note
Non-repudiation is handled either through audit trails within Oracle Fusion Applications or through Oracle Web Services Management (OWSM) support for signatures using WebServer security.
Provisioning components additionally safeguard against unauthorized access.
The following diagram shows Oracle Fusion Applications provisioning and reconciliation for accounts, roles, and HR and Oracle Fusion Trading Community Model identity. User and account provisioning uses Oracle Virtual Directory. Oracle Internet Directory is an LDAP repository.
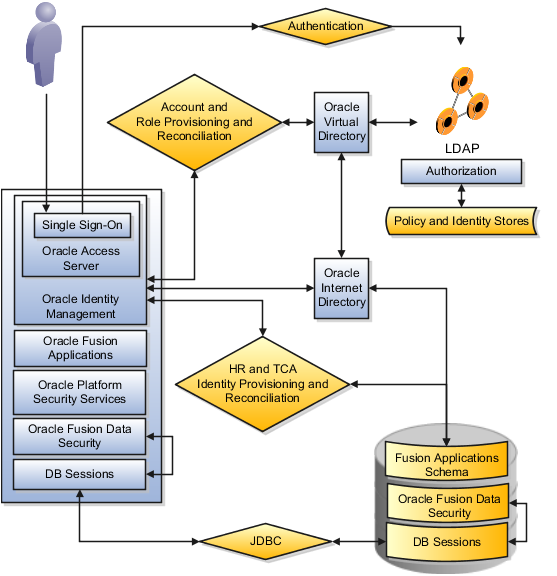
Oracle Fusion Applications security supports compliance with security regulations.
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) standard RBAC (role-based access control) enables efficient compliance with regulations. For specific regulations, features such as personally identifiable information (PII) protections, encryption, and segregation of duties controls provide compliance support.
Various features of Oracle Fusion Applications security and the Governance, Risk, and Compliance Controls (GRCC) suite of products support compliance with security regulations.
Oracle Fusion Applications products adhere to or support compliance with the following mandates.
|
Regulation |
Addressed in Oracle Fusion Applications |
|---|---|
|
Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) |
Oracle Virtual Private Database (VPD), encryption, and masking to protect clones of production data |
|
Sarbanes - Oxley Act (SOX) |
Segregation of duties controls |
|
State regulations such as California SB 1386 |
VPD, encryption, and masking to protect clones of production data |
|
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) |
VPD, encryption, and masking to protect clones of production data |
|
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) |
VPD, encryption, and masking to protect clones of production data |
|
EU Data Protection Directive |
VPD, encryption, and masking to protect clones of production data |
Oracle Fusion Applications protects PII with VPD, Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) and encryption APIs. Oracle Fusion Applications masks production data using Oracle Data Masking. Network security provides encryption in transit. Oracle Application Access Control Governor provides segregation of duties protections.
Administrators manage, remediate, and enforce user access policies to ensure effective segregation of duties using GRC integrated with Identity Management products to prevent segregation of duties control violations before they occur, and ensure user access provisioning that complies with the segregation of duties policies.
Segregation of duties ensure that no single individual has control over two or more phases of a business transaction or operation. Oracle Fusion Applications use a single segregation of duties control system, the Application Access Controls Governor (AACG).
For information on managing segregation of duties, see the Oracle Application Access Controls Governor Implementation Guide and Oracle Application Access Controls Governor User's Guide.
Security standards and tools used to secure Oracle Fusion Applications during implementation and when deployed deliver an integrated security approach.
The following standards and tools support security across Oracle Fusion Applications
Role-based access control (RBAC)
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)
Java Authentication and Authorization Service (JAAS)
These standards are complied with during Oracle Fusion Applications certification.
Security standards and tools in the Oracle Fusion Applications environment prohibit unauthorized access without requiring settings to be changed manually.
The role-based access control (RBAC) standard is applied to Oracle Fusion Applications function and data security to enforce user access based on the role of the user within the organization rather than just the user's individual identity.
Security administration organizes access entitlement by roles to reflect business policies
Role hierarchies and constraints express security polices
Authorization constraints, such as segregation of duties (SOD), prevent information misuse
The effectiveness of the standard is limited by roles too broadly defined with duties and provisioned to users for whom some of those duties may not be appropriate. The Oracle Fusion Applications security reference implementation provides a full range of fine grained role definitions.
LDAP provides an Oracle Fusion Applications deployment with lookup and communications services on the identity and policy stores.
Java Authentication and Authorization Service (JAAS) is a standard interface used for integrating with internal and third party sources for authentication and authorization, including LDAP and Single Sign On.
Oracle Platform Security Services (OPSS) provides tools and services for recording, reorganizing, and reviewing features of Oracle Fusion Applications security:
Users across Oracle Fusion Applications
Enterprise roles that are provisioned to users
Application roles that each application provides to fulfill an enterprise role
Entitlement that is granted to application roles
Access to services, web pages, and individual widgets
Understanding how Oracle Fusion applies common security principles may be helpful in planning your Oracle Fusion Applications deployment.
Oracle Fusion Applications applies the following standard security principles:
Least privilege
Segregation of duties
Containment and no write down
Transparency
Assured revocation
Defense in depth
Adherence to these principles enhances Oracle Fusion Applications security.
Note
Changes and custom implementations required by your enterprise may reverse the protections provided by these principles.
Oracle Fusion Applications applies security privileges using a specific implementation of features and various supporting tools.
Oracle Fusion Applications roles carry only required privileges. Application roles define duties that entitle access to only the functions and data necessary for performing the defined tasks of that duty.
Oracle Fusion Applications checks duty roles for segregation of duties policy violations measured against content and the risks defined in the Oracle Application Access Controls Governor (AACG) and against content according to best available security guidelines. User and role provisioning respects the segregation of duties policies.
Secured information cannot move from more to less secure stores, such as the unsecured search index, data warehouse, or a test database. Oracle Fusion Applications enforces security policies consistently across tools, access methods, and the entire information life cycle from data at rest and in transit to clones and backups.
Oracle Fusion Applications does not write sensitive information from an environment that applies restrictions to gain access to that sensitive information to one that does not. For example, Oracle Fusion Applications does not write personally identifiable information that is sensitive and private, such as national identifiers or home contact details, from Human Capital Management (HCM) to the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) stores. This policy extends to attachments.
Function, data, and segregation of duties security policies are readable in plain language wherever policies are viewed or managed. Oracle Fusion Applications provides view access to implemented roles and security policies through Oracle Identity Management (OIM) and Authorization Policy Manager (APM), as well as security reference manuals and business analysis consoles.
In addition, the following optional products provide additional transparency and are certified for use with Oracle Fusion Applications:
Oracle Database Vault
Enterprise Manager Data Masking
Revoking one security policy revokes all implementations of that policy across all tools in production.
Personnel, technology, and operations are secured with multiple layers of defense across the life cycle of the information in motion, while at rest, and when accessed or used. In Oracle Fusion Applications, segregation of duties, authentication and password security, encryption, and logging and auditing are mechanisms of redundant defense that enforce protection. A comprehensive defense-in-depth approach to protecting private and sensitive data includes securing sensitive data at rest or stored in database files and their backups, as well as in transit.
The following products provide defense in depth.
|
Defense |
Product certified for use with Oracle Fusion Applications |
Installed? |
Details |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Monitoring |
Oracle Audit Vault |
Optional |
Collects data and provides insight into who did what to which data when, including privileged users such as database administrators (DBA) |
|
Access control |
Oracle Database Vault |
Optional |
Prevents highly privileged users (DBA) from accessing application data |
|
Oracle Identity Management |
Yes |
|
|
Authorization Policy Manager |
Yes |
|
|
Virtual Private Database |
Yes |
|
|
Encryption and Masking |
Oracle Advanced Security |
Optional |
Protects stored, confidential data with encryption keys external to the database |
|
Transparent Data Encryption |
Optional |
|
|
Oracle Data Masking |
Optional |
Converts nonproduction data irreversibly, but optionally in formats that enable applications to function without error |
The figure shows the products that provide defense in depth with access control, encryption, masking, and monitoring.
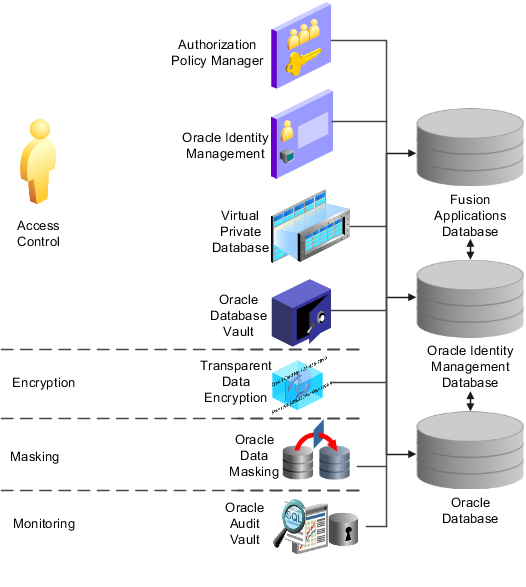
Products used to secure implementations and deployments of Oracle Fusion Applications include function and data access management through vaulting, encryption or masking, and controls.
The following integrated products support security across Oracle Fusion Applications
Oracle Identity Management (OIM)
Oracle Application Access Controls Governor (OAACG)
Oracle Web Services Manager (OWSM)
Oracle HTTP Server
Additional products are available for enhanced protections.
Oracle Audit Vault
Oracle Access Manager
Oracle Role Manager
Oracle Entitlement Server
Oracle Virtual Directory
Oracle Transparent Data Encryption (TDE)
Oracle Database Vault
Security products in the Oracle Fusion Applications technology stack establish prohibitions to unauthorized access without requiring changes to be made in applications.
Business intelligence
Policy and identity stores
Database protections
Optional database vaulting
Optional data encryption and masking
Controls
Monitoring, reporting, and analysis capabilities available through the Oracle Business Intelligence Foundation Suite for Oracle Applications (OBIFA) components of Oracle Fusion Applications support adherence to or compliance with regulations. Reports of roles by product, functional privileges by role, and data security policies by role allow security professionals to modify and adapt their deployment of Oracle Fusion Applications security. Access to BI reports is also under role-based access control.
Oracle Fusion Applications policy and identity stores are implemented using the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) store in Oracle Internet Directory to record and serve Oracle Fusion Applications security with repositories of users, roles, identities, policies, credentials, and other security elements.
Enterprise roles are implemented as LDAP Groups.
The policy store includes function security policies. Policies define security rules in XML and can be viewed and managed using Authorization Policy Manager.
Enterprise roles and role hierarchies of the reference implementation are stored in the identity store and available to the users you add to the identity store for your enterprise. The data security policies of the reference implementation are stored in the policy store. Data security policies reference duty roles to assert exactly what a job or abstract role means.
Vaults serve to protect categories of data from improper access.
A database vault protects sensitive data from highly privileged users such as database administrators (DBA).
An audit vault secures archives of audit data with reports and alerts that notify of access to sensitive information.
A virtual privacy boundary on data protects personally identifiable information (PII) attribute values.
For example, Oracle Database Vault is certified for use with Oracle Fusion Applications. ODV can be used to secure sensitive data that is not PII. If Oracle Fusion Applications is deployed with ODV, the vault can protect credit card information, which reduces the risk of insider threats with separation of duty, multi-factor authorization and command rules. If Oracle Fusion Applications is deployed without ODV, Oracle Database Encryption APIs secure confidential PII attributes such as credit card and bank account numbers with controls at the column level.
Encryption and masking prevents unauthorized access to sensitive data. Oracle Fusion Applications provides protections of sensitive data using encryption APIs to mask fields in production user interfaces
Oracle Fusion Applications is certified for use with the following additional products if they are included in a deployment.
Oracle Transparent Data Encryption (TDE)
Data Masking tools in Oracle Enterprise Manager
Encryption protects data as it is written to the file system against unauthorized access via that file system or on backups and archives. The data can be decrypted by applications when it is retrieved. Transparent Data Encryption enables encrypting data in columns independent of managing encryption keys.
Data masking prevents views of sensitive data. Data masking in Enterprise Manager overwrites sensitive data with randomly generated data in non-production instances such as for development, testing, or diagnostics. This type of masking is irreversible and the sensitive data cannot be reconstituted.
Security controls are policies, audits, and assurances. Security controlling products include the following.
Oracle Identity Management (OIM) centrally controls user accounts and access privileges
Oracle Authorization Policy Manager (APM) manages the security policies that control access based on roles
Oracle Application Access Controls Governor (OAACG) provides the segregation of duties controls library
Oracle Virtual Private Database (VPD) applies security policies at row and column levels in the database
Each of these products, except VPD, provide user interfaces for administering security controls. VPD controls are applied by running scripts against the database.
Processes used to secure Oracle Fusion Applications during implementation and when deployed deliver an integrated security approach.
The following processes support security across Oracle Fusion Applications
Authentication
Federation
Authorization
Provisioning and reconciliation
Content Management
Monitoring and diagnostics
Security processes in the Oracle Fusion Applications environment prohibit unauthorized access without requiring settings to be changed manually.
Authentication manages who is allowed into a network or application. Once in the network or application, an entitlement of privileges manages what may be done.
Authentication works in tandem with managing identities in Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) stores or other user directories to verify that a user is who they say they are. Password security is a primary authentication mechanism. Biometrics could be another. Authentication can be further refined by levels of demilitarized zone (DMZ) or security zones. Authentication is available as an embedded or external process using Java Authentication and Authorization Service (JAAS). For example, JAAS authenticates identities in an LDAP store or through Single Sign On in the Oracle Access Manager of Oracle Identity Management.
A user signs on and establishes an authenticated session to access secured functions, which in turn provides access to data based on entitlement granted to roles that have been provisioned to the user.
Note
Oracle Fusion Applications supports anonymous sessions, weak authentication (remember me), multi-level authentication, and global session identifiers.
The authentication mechanisms used in Oracle Fusion Applications are negotiated by the secure socket layer (SSL). User sign in can be deferred to an external authenticator using Single Sign On in the Oracle Access Manager. Authentication successes and failures are recorded in audits.
Federation enables identities and their relevant roles (entitlement) to be propagated across security domains, within and among multiple organizations.
For example, enterprises implement identity federation within their portals. Acme Inc. and Beta Corp. are business partners. Acme is a national computer parts distributor, and Beta is a computer manufacturer that makes the parts that Acme resells. Beta has several inventory and production applications within its portal, and it wants the employees of Acme to access these applications, so that Acme can operate more efficiently. Using federation, Acme provides identity information that it owns, and Beta authorizes access and serves up applications that it owns. Federation manages the credentials, profiles, and sign ins of each Acme employee that accesses Beta's applications. If an Acme employee quits or is fired and Beta is not told, that ex-employee is automatically locked out of Betas systems as soon as the user leaves Acme Inc.
Authorization is the permission for an entity to perform some action against some resource. For example, a user's enterprise role membership authorizes access to all Oracle Fusion Applications resources needed to enable the user to fulfill the duties described by that job or abstract role. OPSS controls the authorization processes on functions and Oracle Fusion Data Security, as well as in some cases application code, control the authorization processes on data.
Segregation of duties is a type of authorization constraint that defines violations that could result in misuse of information.
Security related provisioning involves provisioning roles and identities or people.
Human approvals secure a task using both grants and roles. Administrators and implementation consultants apply the RBAC standard in Oracle Fusion Applications to the requirements of their enterprise using provisioning tools.
Accounts are created as identities or people in the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) store. Roles are provisioned by making the identity a member of a group that is the requested role. LDAP records and serves Oracle Fusion Applications security with identities, policies, and credentials.
Oracle Fusion Applications notifies the IT security manager of all account requests, role provisioning requests, and grants to ensure role administration is always documented, authorized and auditable. Accounts are created as identities in the LDAP store.
Oracle Fusion Applications use the following tools to handle account and role provisioning with the stores, as well as Human Resources (HR) and Oracle Fusion Trading Community Model identity provisioning with the Oracle Fusion Applications schema.
Oracle Fusion Human Capital Management (HCM)
Oracle Identity Management (OIM)
Provisioning infrastructure and policies include provisioning services, temporary storage of registration data, approval and approval routing, notifications, business logic, and eligibility. Users are provisioned using the LDAP deployed for use by Oracle Fusion Applications.
Granting or revoking object entitlement to a particular user or group of users on an object instance or set of instances extends the base Oracle Fusion Applications security reference implementation without requiring customization of the applications that access the data.
Changes to identity information are reconciled to OIM (LDAP) and thereby reconciled to users. Changes to users are not reconciled to identity information in HR.
Oracle Fusion Applications integrate with the Universal Content Repository of Oracle Universal Content Management (UCM) using LDAP, single sign on, and Web Services to handle attachments. By default a Oracle Fusion Applications deployment grants no access to documents through content management user interfaces. All access is through Oracle Fusion Applications.
Oracle Fusion Applications apply security to files in Universal Content Management (UCM) by calling a file authorization Web Service to determine whether the current user has been granted access to a file. When a user tries to access a file, Oracle Fusion Applications determine whether the user is permitted access and grants access for the duration of the session.
Attached documents are only accessible through Oracle Fusion Applications user interfaces, not through content management user interfaces. Attached documents that contain sensitive information are placed in document categories that require authorization when content is accessed from within Oracle Fusion Applications. Function security rules apply to content management. Access to attachments is determined by access to the owning entity, such as a table, purchase order, agreement, or supplier account, but also to the category.
For example, a role that has access to the purchase order, such as a buyer, can view attachments in the category Note to Buyer and can create, update, and delete attachments in the category Note to Receiver. The receiver of the purchase order and receipts entity can view attachments in the category Note to Buyer and Special Handling Instructions.
All workers typically have access sufficient for viewing all other workers in a public directory, but workers should not have access to any attachments for the person. Line managers have access to workers that they manage and have access to documents such as performance review notes or anything they choose to upload, but line managers do not have access to things like tax documents or visa documents. HR specialists have access to all people for whom they are responsible and can see everything that the line manager sees, as well as visa documents, but not tax documents. Payroll specialists have access to all people for whom they are responsible and can view the tax documents. Security of person documents is implemented using Document Type security profiles.
You associate attachment categories with an entity using the Manage Attachments Categories task.
Oracle Fusion Applications security works at runtime to prevent and detect embezzlement, such as fraud, and other acts of personal gain at the expense of an enterprise. Tools and tasks that are relevant to detection include analyzing risks carried in segregation of duties violations.
System configuration is relevant to runtime processes. Administrators determine and modify system configuration based on enterprise security requirements and the particulars of their Oracle Fusion Applications deployment using diagnostics.
Considerations in deploying secure Oracle Fusion applications include the following.
Baseline standalone deployment infrastructure
Integrations with other applications
Extended deployment with secured Web services
Secured audits
Oracle Fusion Applications security is designed to control exchanges with third party or non-Fusion deployments.
Oracle Fusion Applications are designed to be deployed as a complete applications platform.
In the absence of integrations with legacy applications or external Web services that allow data to be loaded into Oracle Fusion applications database tables, the design and reference implementation provide standalone security.
Extending a standalone deployment of Oracle Fusion Applications involves adding new entities to the Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) database table or even configuring new attributes through flexfields. Extending Fusion Applications does not include making changes to the behavior of an application unless that change involves adding new data attributes to an existing entity object and adding any new entity objects to an application.
Where Oracle Fusion Applications need to be extended, you may additionally need to install Oracle JDeveloper.
Calling applications use application identities (APPID) to enable the flow of transaction control as it moves across trust boundaries. For example, a user in the Distributed Order Orchestration product may release an order for shipping. The code that runs the Pick Notes is in a different policy store than the code that releases the product for shipment. When the pick note printing program is invoked it is the Oracle Fusion Distributed Order Orchestration Application Development Framework (ADF) that is invoking the program and not the end user.
Oracle Fusion Applications stores application IDs just like individuals, but in a separate branch of the identity store directory.
Before deployment, review the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) identity store to verify the existence of the APPIDs.
Warning
Do not change or remove application identities or their permissions.
The following application identities are predefined.
|
Application Identity Code |
Application Identity Name |
|---|---|
|
|
Application Toolkit User Messaging Service Application Identity |
|
|
Approval Management Service Application Identity |
|
|
Data Role Template Application Identity |
|
|
Oracle Fusion Search Administrator Application Identity (CRM) |
|
|
Business Intelligence Applications Extract Transform and Load Application Identity |
|
|
Oracle Identity Manager Application Identity |
|
|
Oracle Fusion Search Application Identity |
|
|
Applications Development Framework Application Identity (CRM) |
|
|
Applications Development Framework Business Intelligence Application Identity (CRM) |
|
|
Applications Development Framework SOAP Application Identity (CRM) |
|
|
Applications Diagnostic Framework Application Identity (CRM) |
|
|
Enterprise Search and Crawl Framework Application Identity (CRM) |
|
|
Oracle Enterprise Manager Application Identity (CRM) |
|
|
Email Sending Daemon Application Identity (CRM) |
|
|
Enterprise Scheduler Job Application Identity (CRM) |
|
|
Enterprise Scheduler Reporting Application Identity (CRM) |
|
|
Oracle Data Integrator Application Identity (CRM) |
|
|
Oracle Data Integrator Supervisor Application Identity (CRM) |
|
|
Applications Development Framework Self Service Application Identity (CRM) |
|
|
Oracle Fusion Search Application Identity (CRM) |
|
|
Web Services Application Identity (CRM) |
|
|
Applications Development Framework Application Identity (Financials) |
|
|
Employee National Identifiers Application Identity |
|
|
Employee Matching Application Identity (Financials) |
|
|
Document Management Integration Application Identity (Financials) |
|
|
Web Services Application Identity (Financials) |
|
|
Applications Diagnostic Framework Application Identity (FSCM) |
|
|
Enterprise Search and Crawl Framework Application Identity (FSCM) |
|
|
Oracle Enterprise Manager Application Identity (FSCM) |
|
|
Oracle Fusion Search Application Identity (FSCM) |
|
|
Applications Diagnostic Framework Application Identity (HCM) |
|
|
Enterprise Search and Crawl Framework Application Identity (HCM) |
|
|
Oracle Enterprise Manager Application Identity (HCM) |
|
|
Enterprise Scheduler Job Application Identity (HCM) |
|
|
Batch Loader Enterprise Scheduler Job Application Identity (HCM) |
|
|
Oracle Data Integrator Application Identity (HCM) |
|
|
Oracle Data Integrator Supervisor Application Identity (HCM) |
|
|
Oracle Fusion Search Application Identity (HCM) |
|
|
Web Services Application Identity (HCM) |
|
|
Service Provisioning Markup Language Interface Application Identity (HCM) |
|
|
Web Center Forum Application Identity |
|
|
Oracle WebCenter Crawl Application Identity |
|
|
Web Services Manager Application Identity |
|
|
Applications Development Framework Application Identity (Procurement) |
|
|
Enterprise Scheduler Job Application Identity (Procurement) |
|
|
Web Services Application Identity (Procurement) |
|
|
Applications Development Framework Application Identity (Projects) |
|
|
Enterprise Scheduler Job Application Identity (Projects) |
|
|
Web Services Application Identity (Projects) |
|
|
Applications Development Framework Application Identity (SCM) |
|
|
Enterprise Scheduler Job Application Identity (SCM) |
|
|
Web Services Application Identity (SCM) |
|
|
Enterprise Scheduler Job Application Identity (Setup) |
As a security guideline, reset application identity passwords periodically during scheduled downtimes. For example, when moving application identities from one environment to another as part of moving an identity store, you must reset the passwords so they are unique to an environment. Reset the APPID passwords using the following command.
Restriction
This command can be run only after the Oracle WebLogic Server installation for the Oracle Fusion Applications domain is set up.
Run the following command to get the list of all the entries for which the passwords need to be set:
Ldapsearch -h ldapHost -p ldapPort -D binddn -w password -b 'cn=appidusers,cn=users,namigncontext' -s sub 'objectclass=orclAppiduser' cn >& reset.txt
ORACLE_HOME/idmtools/bin/appidtool.sh pwdreset -ldapHost tuvwxy0123.us.example.com -ldapPort 3060 -ldapUser cn=orcladmin -wlsHost tuvwxy0123.us.example.com -wlsPort 7001 -wlsUser weblogic -file reset.txt -userBase cn=users,namingcontext
|
Variable |
Refers to the value for: |
|---|---|
|
|
Identity store host |
|
|
Identity store port |
|
|
User name for connecting to the identity store. This user should have the entitlement necessary to reset the APPID passwords. |
|
|
Administration Server on the Oracle Fusion Applications domain |
|
|
Administration Server port on the Oracle Fusion Applications domain |
|
|
The file that contains the list of application identities for which the passwords need to be set |
|
|
The user base under which the application identities exist |
Integrating Oracle Fusion Applications with other applications, including other Oracle Applications product lines, require decisions in the following areas.
Central Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) repository
Data migration
Coordination of Oracle Fusion Applications roles to legacy function security control
For example, coordinate Oracle Fusion Applications roles to responsibilities and menu paths in Oracle eBusiness Suite (EBS) for integration between EBS and Oracle Fusion Applications.
Note
Duty roles are not propagated or synchronized across Oracle Fusion Middleware, where they are considered to be application roles.
When implementing a system-to-system integration with an external system, you may need to identify that system in the identity store in order to grant that system permissions.
If you extend your Oracle Fusion Applications deployment with a Web service that allows external users to load data into database interface tables, consider the following requirements.
Implement authentication
Implement authorization checks; though not required, their absence allows sharing of identities, which removes your ability to audit the access.
Create a regular identity for the external user with the appropriate function and data security access.
For example, create a new duty role with the desired data access entitlement, privilege to submit an Oracle Enterprise Scheduler Service job, and permission to access the Web Service.
For information about securing Web services and task flows when extending applications, see the Oracle Fusion Applications Security Hardening Guide.
Tuning and maintaining Oracle Fusion Applications security includes auditing, managing changes, and handling leaks, threats, and inappropriate access.
Tasks that consume Web services exposed to Enterprise Manager (EM) require specific duty roles to be provisioned to the users performing those tasks. For example, the user connecting to the Web service that EM uses to collect metrics must be provisioned with the FUN_BU_ADMIN_DUTY role.
Avoid provisioning users who are under audit with roles that are entitled to manage audits and audit results. Avoid provisioning users who are under audit with roles that entitle access to protected data the users are otherwise not permitted to access.
Tip
Avoid entitling users who configure audits from being the same users who performed the activities under audit.
For information about elevating access privileges for a scheduled job, see the Oracle Fusion Applications Developer's Guide for Oracle Enterprise Scheduler.