3 Setting Up Your System for GUI/VAT Processing for Taiwan
This chapter contains the following topics:
-
Section 3.6, "Setting Up Tax Account Mapping for Declaration Sites"
-
Section 3.7, "Associating Format Codes and Programs to Document Types"
-
Section 3.8, "Setting Up GUI/VAT Number Prefixes for Input Tax"
-
Section 3.10, "Specifying the GUI/VAT Number Segments Used by Programs"
-
Section 3.11, "Setting Up GUI/VAT General Ledger Account Mapping"
-
Section 3.12, "Setting Up a GUI/VAT User/Declaration Site Mapping"
-
Section 3.13, "Setting Up the GUI/VAT Tax Type Mapping for Taiwan"
-
Section 3.17, "Setting Up Processing Options and Versions to Work with GUI/VAT Transactions"
-
Section 3.18, "Setting Up Document Type Additional Information for e-GUI (Release 9.1 Update)"
3.1 Understanding Setup for GUI/VAT Transactions
You must set up the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system before you can process and report on transactions for which you must pay VAT. These sections describe some of the Taiwan-specific and standard software setup.
3.1.1 Setting Up Declaration Sites
Set up this information for declaration sites:
| Task | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Set up UDC 75T/DS. You must complete this task.
See GUI/VAT Declaration Site (75T/DS). You use other UDC tables to specify information about the declaration site. |
You use the UDC values when you set up the relationship between companies and declaration sites. You also use the UDC values whenever you specify a declaration site in other Taiwan-specific programs. |
| Set up declaration sites as companies and associate declaration sites to a company. You must complete this task. | The system requires a valid company/declaration site combination to enter GUI information. |
| Set up declaration periods. You must complete this task. | The system uses the declaration periods to determine which transactions belong to a reporting period. You also use the declaration periods when you associate GUI numbers with a declaration site. |
| Set up each declaration site as a headquarters unit or an individual unit. You must complete this task. | When you set up declaration sites, you specify whether the system creates GUI records for different types of transactions.
Additionally, if a declaration site is a headquarters unit, the system prints a summary report when you run the GUI/VAT Usage Detail List program (R75T004U) for the declaration site. If the declaration site is an individual unit, the system prints a detailed report when you run the GUI/VAT Usage Detail List program. |
| Specify the users who are authorized to create GUI transactions for a declaration site. This task is optional. | You specify the users who are authorized to create transactions for a declaration site to limit who can generate a GUI. |
| Specify the tax accounts to use for each declaration site. You must complete this task. | You specify the tax account to use in the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne standard software by associating AAIs with business units. However, declaration sites are not set up as business units, so you must specify the tax account to use for each company and declaration site combination. The system uses the information that you set up to determine the AAI to use for tax processing. |
| Associate GUI numbers with a declaration site. You must complete this task.
See Specifying the GUI/VAT Number Segments Used by Programs. |
GUI numbers must be assigned sequentially by number and transaction date. When you associate GUI numbers with a declaration site, the system automatically retrieves the next available number for a transaction when you run the GUI/VAT Creation From Multi-AR program (R75T004S) or GUI/VAT Creation From Multi-SO program (R75T004O) in final mode. The system also uses the association between the GUI numbers and declaration site when you manually assign a GUI number to a record. |
See Declaration Sites.
3.1.2 Setting Up GUI Numbering
You must perform several tasks to complete the setup for GUI numbers. The tasks are:
| Task | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Set up next numbers. | Set up a next numbering scheme for system 75T (Taiwan) on the first line of the Set Up Next Numbers by System form in the Next Numbers program (P0002).
The system uses the next numbering scheme to assign a unique value to each record in the F75T005T table. The unique value will cause the system to launch the GUI/VAT Transaction program after you use the standard software to enter information. If you do not set up the next numbering scheme, the system does not launch the GUI/VAT Transaction program for all eligible transactions. |
| Set up GUI prefixes.
You must complete this task. |
You set up GUI prefixes for input tax. The system uses the information that you set up to verify that the prefix is a valid prefix. |
| Set up GUI/VAT sales numbers and segments.
You must complete this task. |
You set up the range of numbers to use for output tax in the GUI sales number register. After you enter the range, you must make the range active before you can work with the numbers.
Activate the sales number register, which enables you to divide the sales number register into segments. Then, segment the number range into smaller parts to make the parts available for use for different formats and declaration periods. |
| Specify the GUI/VAT number segment to use with different types of transactions.
You must complete this task. See Specifying the GUI/VAT Number Segments Used by Programs. |
Specify the segments that the system uses to assign GUI numbers for the types of transactions that you process. The system uses the number segments to assign numbers when you run the batch process to assign GUI numbers, and enables you to search for the next number to assign when you manually assign numbers. |
| Disassemble a GUI/VAT sales number register segment.
This task is optional. |
Divide active segments into smaller segments. |
See GUI Numbers.
|
Note: Before a system user can generate transactions using the numbers that you setup, the user must be set up with the same authorization code for the declaration site as you assign to the number segment. |
This process flow shows the setup that must occur for GUI numbering.
Figure 3-1 GUI Numbering Setup Process Flow
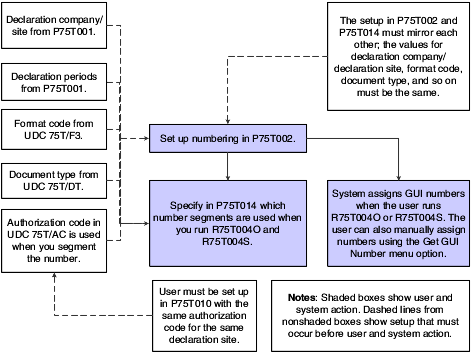
Description of ''Figure 3-1 GUI Numbering Setup Process Flow''
3.1.3 Setting Up Transactions
You set up this information for use in sales order, procurement, accounts payable, accounts receivable, and journal entry transactions:
| Task | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Set up authorization codes. You must complete this task to limit who can generate GUI information. | The system uses authorization codes to determine if a user is authorized to generate GUIs for transaction types for a specific declaration site. After you set up authorization codes, you assign the codes to declaration sites, GUI/VAT number segments, and users. |
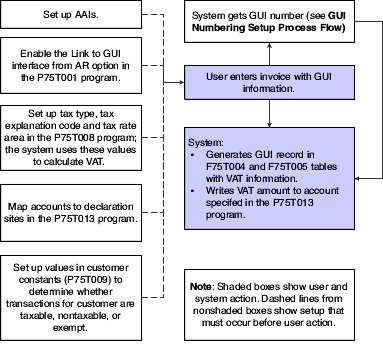
| Link GUI creation to declaration sites. You must complete this task to access the Taiwan-specific forms for entering GUI information when you enter sales orders, invoices, vouchers, and journal entries. You activate the link when you set up declaration sites in the GUI/VAT Declaration Site program. | When you set up declaration sites, you can set values to create GUI records when you enter sales orders, invoices, vouchers, or journal entries. When you specify Y (yes) to generate GUI records and your user display preference is set to TW (Taiwan), the system displays an additional form on which you enter the GUI information after you enter the standard information for sales orders, invoices, vouchers, and journal entries. |
| Associate tax types to tax explanation codes and tax rate areas. | The system uses the tax type that you set up as a default value when you enter the Taiwan-specific information that is required for transactions to which GUI/VAT applies. |
| Associate format codes to document types and specify the standard software program that you use to enter the standard information for the document type/format code combination.
See Associating Format Codes and Programs to Document Types. |
You set up the association between format codes and document types so that the system retrieves the format code when you enter a transaction for the document type.
You specify the standard program that you use to enter standard information for a document type/format code because it is possible, in some instances, to use different standard programs. For example, you might use either the Standard Voucher Entry program (P0411) or the Journal Entries with VAT program (P09106) to enter transactions for imported goods (document type IMP). |
| Set up corresponding versions of the standard software transaction entry programs and the Taiwan-specific programs, and specify the version of the standard software transaction program to use to enter Taiwan transactions.
See Setting Up Processing Options and Versions to Work with GUI/VAT Transactions. |
The standard software transaction entry programs, such as the Standard Invoice Entry (P03B2002) program, automatically launch a version of the GUI/VAT Transaction program (P75T004) when your system is set up to process Taiwan transactions. The system launches the version of the GUI/VAT Transaction program that corresponds to the version of the standard software entry program.
You must also set up the PO GUI/VAT Transaction (P75T003) program with a corresponding version. |
3.1.4 Setting Up Customers
You set up default information for customers in customer constants.
See Setting Up Customer Constants for Taiwan.
In addition to setting up the customer constants for Taiwan, these factors apply to the processing of customer records:
-
The Invoice Consolidation option on the Billing Information form in the Customer Master Information program (P03013) must be turned off because invoice consolidation causes multiple sales order numbers to be matched to one invoice number, which you cannot do for Taiwanese transactions.
-
The Summarize AR Entries by Invoice processing option in the Update Customer Sales program (R42800) must be blank because this option causes related sales order lines to be summarized into one invoice, which you cannot do for Taiwanese transactions.
Consider setting up a generic customer master record that you can use for sales for which you do not print a GUI for a customer. For example, you might have numerous small, cash sales for which you do not print a GUI. You can report these transactions using one invoice for a range of GUI numbers.
3.1.5 Setting Up Suppliers
You use the GUI/VAT Supplier Constants program (P75T0091) to set up the information that you must associate to your suppliers when you process transactions in Taiwan.
If you import goods, you must set up the customs authority as a supplier so that you can specify the tax rate area to use for imported goods. Additionally, you must set up a tax rate area for imported goods, and set up the GUI/VAT Cat. Code 7 - Supplier (75T/C7) UDC table for VAT prepayment transactions.
See GUI/VAT Cat. Code 7–9 - Supplier (75T/C7–75T/C9).
Consider setting up a generic supplier master record that you can use for transactions for which you do not need to report all of the purchase details. For example, if you have numerous miscellaneous purchases, you might report a range of GUI transactions using one invoice generated for a generic supplier.
3.1.6 Setting Up Accounts
You must specify the accounts used for tax processing. The setup for accounts includes these tasks:
| Task | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Specify the general ledger accounts that you use for input and output tax. | During the GL distribution step of transaction entry, the system distributes input tax to the debit account that you specify, and distributes output tax to the credit account that you specify. |
| Associate tax accounts to declaration sites. | In the standard software, the system determines the tax account to use based on the AAI setup for a company/business unit combination. In Taiwan, you must associate the tax accounts to the declaration sites so that the system can determine the AAI to use when processing the tax. |
This process flow shows the account setup that must occur before you process transactions with VAT.
3.1.7 Setting Up System Users
If a system user cannot enter GUI transactions or cannot access the correct forms, verify that:
-
The Localization Country Code field in the User Profile Revisions program (P0092) is TW (Taiwan).
-
The user is set up as an authorized user for the declaration site and transaction type in the GUI/VAT User/Declaration Site Mapping program (P75T010).
The authorization code for the user, declaration site, and segment numbers must be the same.
3.1.8 Setting Up the Standard JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Software
You set up the standard software with the companies, accounts, AAIs, tax rate areas, and other components that you use to process GUI/VAT transactions, in addition to the Taiwan-specific functionality that you set up in Taiwan-specific programs.
You must set up a tax rate area in the Tax Rate/Areas (P40008) program to use for Taiwan import tax. The system uses the tax rate area when you specify that the customs authority is the supplier. You enter the name of the tax rate area for import tax in the GUI/VAT Cat. Code 7 - Supplier (75T/C7) UDC table. This UDC table must contain a code that matches the name of the tax rate/area for Taiwan import tax. For example, you might set up a tax rate/area for Taiwan import tax called F28. You would also set up the code F28 in UDC (75T/C7) and specify F28 in the GUI/VAT Supplier Constants for the Custom's Authority. Then, when you enter a Taiwan import tax transaction with the Custom's Authority as the supplier, the system retrieves the F28 code from the GUI/VAT Supplier Constants and uses it to retrieve the F28 tax rate/area.
3.2 Setting Up User-Defined Codes for GUI/VAT
This section discusses how to set up UDCs for Taiwan and GUI/VAT processing.
Many fields throughout the system accept only user-defined codes. You can customize the system by setting up user-defined codes that meet the specific needs of the business environment.
|
Important: User-defined codes are central to JD Edwards EnterpriseOne systems. You should be thoroughly familiar with user-defined codes before you change them.Also, many user-defined codes for Taiwan are hard-coded and are essential to the correct functioning of the system. Do not change or delete these codes. |
3.2.1 Authorization Code (75T/AC)
You set up authorization codes in the 75T/AC UDC table to control the allocation of GUI number segments. When you set up a user to declaration site mapping in the GUI/VAT User/Declaration Site Mapping program (P75T010), you can specify an authorization code for the user. Then you can assign authorization codes to GUI number segments in the GUI/VAT Number Register - Sales program (P75T002). Only users whose user to declaration site mapping has the same authorization code as a GUI number segment are able to successfully assign GUI numbers from that GUI number segment.
3.2.2 GUI/VAT Account Dr/Cr Flag (75T/AF)
You use the GUI/VAT account debit/credit flag to specify whether an account is a debit account (input tax) or credit account (output tax) in the GUI/VAT GL Account Mapping program (P75T012).
These codes must exist in the GUI/VAT Account Dr/Cr Flag UDC table:
| Codes | Description 01 | Description 02 | Hard-Coded |
|---|---|---|---|
| C | Credit | Sales (Output) Tax | Y |
| D | Debit | Purchase (Input) Tax | Y |
3.2.3 GUI/VAT Cat. Code 1 – 3 Segment (75T/C1 – 75T/C3)
You use GUI/VAT category codes for segments (75T/C1-C3) to classify GUI number segments and the transactions for which they are used. You can use category codes for data selection when running reports. You assign default category codes to GUI number segments in the GUI/VAT Number Register - Sales program (P75T002).
3.2.4 GUI/VAT Cat. Code 4 – 6 - Customer (75T/C4 – 75T/C6)
You use GUI/VAT category codes for customers (75T/C4-C6) to classify customers and their transactions. You can use category codes for data selection when running reports. You assign default category codes to customers in the GUI/VAT Customer Constants program (P75T009).
3.2.5 GUI/VAT Cat. Code 7–9 - Supplier (75T/C7–75T/C9)
You use GUI/VAT category codes for suppliers (75T/C7-C9) to classify suppliers and their transactions. You can use category codes for data selection when running reports. You assign default category codes to suppliers in the GUI/VAT Supplier Constants program (P75T0091).
GUI/VAT Cat. Code 7 - Supplier (75T/C7) is reserved for customs authorities and customs declaration agencies for VAT prepayment transactions (transactions with GUI document type VPD and format code 28).
This UDC table must contain a code that matches the name of the tax rate/area for Taiwan import tax. For example, you might set up a tax rate/area for Taiwan import tax called F28. You would also set up the code F28 in UDC (75T/C7) and specify F28 in the GUI/VAT Supplier Constants for the Custom's Authority. Then when you enter a Taiwan import tax transaction with the Custom's Authority as the supplier, the system retrieves the F28 code from the GUI/VAT Supplier Constants and uses it to retrieve the F28 tax rate/area.
|
Note: The documentation for entering a Taiwan import tax transaction refers to code F28. If you use a code other than F28 for Taiwan import tax, substitute the code that you use. |
3.2.6 GUI/VAT Customer Type (75T/CT)
You use the GUI/VAT customer type code to specify whether the customer is a domestic company, a domestic individual, or a foreign customer when you set up that customer in the GUI/VAT Customer Constants program (P75T009). The customer type controls how taxes are calculated for that customer.
These codes must exist in the GUI/VAT Customer Type UDC table:
| Codes | Description 01 | Hard-Coded |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Domestic Company | Y |
| 2 | Domestic Individual Person | Y |
| 3 | Foreign Customer | Y |
3.2.7 Deduction Code (75T/DC)
You use deduction codes to specify whether a purchased item is tax deductible. You enter a deduction code when you set up suppliers in the GUI/VAT Supplier Constants program (P75T0091).
These codes must exist in the Deduction Code UDC table:
| Codes | Description 01 | Description 02 | Hard-Coded |
|---|---|---|---|
| . | Sales Doc / Other Doc With Tax | . | Y |
| 1 | Deductible Goods / Expense | For PUR | Y |
| 2 | Deductible Fixed Asset | For PUR | Y |
3.2.8 Deduction Usage (75T/DD)
You use deduction usage codes to specify the usage of an item for which a zero-tax rate applies. You select a code from this UDC table when you work with sales order transactions in the GUI/VAT Transaction program (P75T004) and when you set up customer constants in the GUI/VAT Customer Constants program (P75T009).
These codes must exist in the Deduction Usage UDC table:
| Codes | Description 01 | Hard-Coded |
|---|---|---|
| (blank) | (blank) | Y |
| 1 | Machine Equipment | Y |
| 2 | Raw Material | Y |
| 3 | Part Material | Y |
| 4 | Fuel | Y |
| 5 | Semi-Finished Goods | Y |
3.2.9 GUI/VAT Data Generation Method (75T/DG)
The system uses the GUI/VAT data generation method code to identify the method by which the GUI/VAT data is generated. The system writes the code to the GUI/VAT Transaction Detail table (F75T005) and uses the values in the tax reports. You do not enter this code in any of the programs.
These codes must exist in the GUI/VAT Data Generation Method UDC table:
| Codes | Description 01 | Hard-Coded |
|---|---|---|
| (blank) | (blank) | N |
| MAN | By Manual Key In | Y |
| POS | Inbound From POS | Y |
| SYS | From Other System Module | Y |
| UBE | Created From UBE | Y |
3.2.10 GUI/VAT Declaration Type (75T/DL)
You use GUI/VAT declaration type codes when you set up a declaration site to specify the type of declaration that the declaration site submits. These codes must exist in the GUI/VAT Declaration Type UDC table:
| Codes | Description 01 | Hard-Coded |
|---|---|---|
| 401 | Only Taxable | Y |
| 403 | Taxable, Tax-Exempt, Special Tax | Y |
3.2.11 GUI/VAT Declaration Site (75T/DS)
You set up GUI/VAT declaration site codes to identify the sites for which you declare VAT. You should set up the most commonly used declaration site by using a blank code and then set up as many other declaration sites as necessary, as shown in this example:
| Codes | Description 01 | Hard-Coded |
|---|---|---|
| (blank) | Default Site | Y |
| 16801 | Oracle Taiwan Pte Ltd | N |
3.2.12 GUI/VAT Document Type (75T/DT)
You use GUI/VAT document types to classify GUI/VAT documents. You use the Description 02 field to specify the transaction types to which the document types correspond. You enter a code from this UDC table when you set up declaration sites and when you work with transactions for which VAT applies.
|
Note: Although the system enables you to change the values in the Description 02 field, you should not change them. |
The GUI/VAT Transaction Type (75T/TT) UDC table uses the same codes in the Description 02 field as are used in the 75T/DT UDC table.
These codes must exist in the GUI/VAT Document Type (75T/DT) UDC table:
| Codes | Description 01 | Description 02 | Hard-Coded |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALW | Returns & Allowances | SAL, PUR | Y |
| GUI | GUI | SAL, PUR | Y |
| IMP | Import Document | IGD, FSV (Format Code = None) | Y |
| INV | Commercial Invoice | SAL | Y |
| OTR | Other Document With VAT | PUR | Y |
| SRC | Sales Receipt | SAL | Y |
| VPD | VAT Payment Document | PUR (Format Code = 28) | Y |
3.2.13 GUI/VAT Declaration Unit (75T/DU)
You specify a declaration unit type when you set up declaration sites. The system uses the value that you specify to determine whether the system generates a summary (headquarters) or detailed (individual) report when you run the GUI/VAT Usage Detail List program (R75T004U). You set up only one declaration site for a company as a headquarters unit.
These codes must exist in the GUI/VAT Declaration Unit UDC table:
| Codes | Description 01 | Hard-Coded |
|---|---|---|
| HQ | Headquarters | Y |
| IU | Individual Unit | Y |
3.2.14 GUI/VAT Ex. Declare Type (75T/EP)
You use GUI/VAT export declaration type codes to identify the declaration type of an export when you enter information about exports in the GUI/VAT Transactions (P75T004) program.
These codes must exist in the GUI/VAT Ex. Declare Type UDC table:
| Codes | Hard-Coded |
|---|---|
| . | Y |
| B1 | Y |
| B2 | Y |
| B8 | Y |
| B9 | Y |
| D1 | Y |
| D3 | Y |
| D4 | Y |
| D5 | Y |
| D9 | Y |
| E2 | Y |
| E3 | Y |
| E6 | Y |
| E7 | Y |
| G3 | Y |
| G5 | Y |
| P1 | Y |
| P2 | Y |
| P5 | Y |
| P6 | Y |
3.2.15 Exportation Method (75T/EX)
You use exportation method codes to specify how goods were exported when you work with transactions in the GUI/VAT Transaction program. The system includes the code in the GUI/VAT Zero Tax Rate Sales Amount List report (R75T004T).
These codes must exist in the Exportation Method UDC table:
| Codes | Description 01 | Hard-Coded |
|---|---|---|
| . | . | Y |
| 1 | Export of goods. | Y |
| 2 | Services related to exports; or services supplied within the territory of the Republic of China (R.O.C.), but used in foreign countries. | Y |
| 3 | Goods sold to outbound or transit passengers by the tax-free shops that are set up according to the law. | Y |
| 4 | The sale of machinery and equipment, materials, supplies, fuel, and unfinished goods to export enterprises inside the duty-free export processing zone, to enterprises inside the Science-based Industrial Park, or to bonded factories or bonded warehouses supervised by the customs house. | Y |
| 5 | International transportation; foreign transport enterprises engaged in international transportation within the territory of the R.O.C. qualify for the zero tax rate, provided that reciprocal treatment, or exemption from similar taxes, is given to the international transport enterprises of the R.O.C. by the foreign country in which it is incorporated. | Y |
| 6 | Vessels and aircraft used in international transportation, and deep sea fishing boats. | Y |
| 7 | Sales of goods and maintenance services to vessels and aircraft that are used for international transportation and deep sea fishing boats. | Y |
3.2.16 GUI/VAT Format Code - Purchase (75T/F2)
You use GUI/VAT format code - purchase codes to specify the type of GUI documents issued for purchase transactions. You assign format codes to suppliers when you set up the constants for suppliers. You use the Description 02 field to specify the transaction types to which the format codes correspond.
GUI/VAT Transaction Type (75T/TT) uses the same codes in the Description 02 field of UDC (75T/F2).
These codes must exist in the GUI/VAT Format Code - Purchase UDC table:
| Codes | Description 01 | Description 02 | Hard-Coded |
|---|---|---|---|
| . | Import Goods / Foreign Service | FSV / IGD | Y |
| 21 | Triplicate GUI / Computer GUI | PUR | Y |
| 22 | Other Doc With Tax Amount | PUR | Y |
| 23 | Triplicate Purchase Return / Allowance | PUR | Y |
| 24 | Duplicate Purchase. Return / Allowance | PUR | Y |
| 25 | Triplicate Cash Register GUI | PUR | Y |
| 26 | Summary Triplicate Computer GUI With Tax | PUR (Tax Below TWD $500) | Y |
| 27 | Summary Other Doc With Tax | PUR (Tax Below TWD $500) | Y |
| 28 | VAT Payment Document | PUR (from Customs) | Y |
3.2.17 GUI/VAT Format Code - Sales (75T/F3)
You use GUI/VAT format code - sales codes to specify the type of GUI documents that are issued for sales transactions. You assign the format codes when you set up customer constants.
These codes must exist in the GUI/VAT Format Code - Sales UDC table:
| Codes | Description 01 | Description 02 | Hard-Coded |
|---|---|---|---|
| 31 | Triplicate GUI / Computer GUI | . | Y |
| 32 | Dup. / Dup. Cash Register GUI | . | Y |
| 33 | Tri. Sales Return / Allowance | . | Y |
| 34 | Dup. Sales Return / Allowance | . | Y |
| 35 | Triplicate Cash Register GUI | . | Y |
| 36 | GUI-Exempt | . | Y |
| 37 | Special Tax: Sales | . | Y |
| 38 | Special Tax: Return, Allowance | . | Y |
| 99 | Sales Receipt | Does not apply to media declaration | Y |
3.2.18 GUI/VAT Format Code (75T/FC)
You use GUI/VAT format code to specify the type of GUI documents that you issue for transactions. You use the Description 02 field to specify the transaction types to which the format codes correspond.
You use the values in the GUI/VAT Format Code UDC table when you associate a document type and format code to a JD Edwards EnterpriseOne program in the GUI/VAT Document Type Format Code Setup program (P75T011). The system uses the document type and format code as default values in the programs.
GUI/VAT Transaction Type (75T/TT) uses the same codes in the Description 02 field of UDC (75T/FC).
These codes must exist in the GUI/VAT Format Code UDC table:
| Codes | Description 01 | Description 02 | Hard-Coded |
|---|---|---|---|
| . | Import Goods / Foreign Service | FSV / IGD | Y |
| 21 | Triplicate GUI / Computer GUI | PUR | Y |
| 22 | Other Doc With Tax Amount | PUR | Y |
| 23 | Triplicate Purchase Return / Allowance | PUR | Y |
| 24 | Duplicate Purchase Return / Allowance | PUR | Y |
| 25 | Triplicate Cash Register GUI | PUR | Y |
| 26 | Summary Triplicate / Computer GUI With Tax | PUR (Tax Below TWD 500) | Y |
| 27 | Summary Other Doc With Tax | PUR (Tax Below TWD 500) | Y |
| 28 | VAT Payment Document | PUR (from Customs) | Y |
| 31 | Triplicate / Computer GUI | SAL | Y |
| 32 | Duplicate. / Duplicate Cash Register | SAL | Y |
| 33 | Triplicate Sales Return / Allowance | SAL | Y |
| 34 | Duplicate Sales Return / Allowance | SAL | Y |
| 35 | Triplicate Cash Register | SAL | Y |
| 36 | GUI-Exempt | SAL | Y |
| 37 | Special Tax: Sales | SAL | Y |
| 38 | Special Tax: Return, Allowance | SAL | Y |
| 99 | Sales Receipt | SAL | Y |
3.2.19 GUI/VAT Import Item Type (75T/II)
You use GUI/VAT import item type codes to classify the imported item when the transaction type is IGD (import goods) or FSV (purchase foreign services). You enter a value from this UDC table when you work with imported goods in the GUI/VAT Transaction program.
These codes must exist in the GUI/VAT Import Item Type UDC table:
| Codes | Description 01 | Description 02 | Hard-Coded |
|---|---|---|---|
| . | . | . | Y |
| 1 | Fixed Asset (obsolete) | For IGD | Y |
| 2 | Other Goods (obsolete) | For IGD | Y |
| 3 | Tax-Exempt Goods | For IGD and Report 403 Only | Y |
| 4 | Foreign Service | For FSV | Y |
3.2.20 GUI/VAT Proof Document Name (75T/PD)
You use GUI/VAT proof document name codes to specify the name of the document that proves that an exported item did not go through customs. You use this code when you enter information for exported items. The system includes the code in the GUI/VAT Zero Tax Rate Sales Amount List report (R75T004T).
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system provides some hard-coded values, and you can add additional values. Examples of hard-coded and nonhard-coded values are:
| Codes | Description 01 | Hard-Coded |
|---|---|---|
| . | . | Y |
| BOE | Exchange Memo | Y |
| DFE | Declaration For Exportation | Y |
| DHL | DHL | N |
| FEDEX | Federal Express | N |
| GRT | Guarantee Report | N |
| GUI | Deduction Copy of GUI | Y |
3.2.21 GUI/VAT Prepayment Status (75T/PS)
You use GUI/VAT prepayment status codes to specify whether a sales transaction has been prepaid, and if so, whether the item has been delivered.
These codes must exist in the GUI/VAT Prepayment Status UDC table:
| Codes | Description 01 | Hard-Coded |
|---|---|---|
| . | . | Y |
| 0 | No prepayment | Y |
| 1 | Prepayment, not delivered | Y |
| 2 | Prepayment, delivered | Y |
3.2.22 GUI/VAT Purchase Item Type (75T/PT)
You use GUI/VAT purchase item type codes to classify items when entering a purchase transaction. You assign a code from this UDC table to suppliers when you set up supplier constants.
These codes must exist in the GUI/VAT Purchase Item Type UDC table:
| Codes | Description 01 | Description 02 | Hard-Coded |
|---|---|---|---|
| . | . | . | Y |
| 1 | Goods And Expense | For PUR, Deduction Code = 1 | Y |
| 2 | Fixed Asset | For PUR, Deduction Code = 2 | Y |
3.2.23 GUI/VAT Purchase Usage - 403 (75T/PU)
You use GUI/VAT purchase usage - 403 codes to specify how a purchased item will be used. You assign a code from this UDC table to suppliers when you set up supplier constants.
These codes must exist in the GUI/VAT Purchase Usage - 403 UDC table:
| Codes | Description 01 | Description 02 | Hard-Coded |
|---|---|---|---|
| . | . | . | Y |
| PU1 | Only For Taxable Business | For Report 403 Only | Y |
| PU2 | Only For Tax-Exempt Business | For Report 403 Only | Y |
| PU3 | For Taxable / Tax-Exempt | For Report 403 Only | Y |
3.2.24 GUI/VAT Revenue Type (75T/RT)
You use GUI/VAT revenue type codes to classify sales transactions according to the type of revenue that they generate. You use a code from this UDC table when you set up GUI number segments. This UDC is not hard-coded.
This table shows examples of the types of codes that you might include:
| Codes | Description 01 | Hard-Coded |
|---|---|---|
| . | . | N |
| R01 | Sales Revenue | N |
| R02 | Commission Revenue | N |
| R03 | Sold Fixed Assets | N |
| R04 | Other Revenue | N |
3.2.25 GUI/VAT Summary Note (75T/SN)
You use GUI/VAT summary note codes to specify whether a transaction is a summary transaction. If a transaction is not a summary transaction, the values in the GUI/VAT No. From and GUI/VAT No. To fields are the same. If a transaction is a summary transaction, the values in the GUI/VAT No. From and GUI/VAT No. To fields might be different.
These codes must exist in the GUI/VAT Summary Note UDC table:
| Codes | Description 01 | Hard-Coded |
|---|---|---|
| . | Not Summary Record | Y |
| A | Summary Record | Y |
3.2.26 GUI/VAT Special Tax Type (75T/SP)
You use GUI/VAT special tax type codes to specify a special tax that is applied to the transaction. You assign the special tax type code to customers the customer constants. The values in the Description 02 field are for information purposes only. The system does not use the percentages in the Description 02 field in calculations.
These codes must exist in the GUI/VAT Special Tax Type UDC table:
| Codes | Description 01 | Description 02 | Hard-Coded |
|---|---|---|---|
| . | Tax-exempt / Non-special Tax | . | Y |
| 1 | Special Food, Beverage Service | 25 percent Providing Hostesses | Y |
| 2 | Special Food, Beverage Service | 15 percent Providing Show Programs | Y |
| 3 | Banking, Authorized Business | 2 percent | Y |
| 4 | Reinsurance Premiums | 1 percent | Y |
| 5 | Banking, Nonauthorized Business | 5 percent | Y |
3.2.27 GUI/VAT Sales Item Type (75T/ST)
You use GUI/VAT sales item type codes to specify whether the item sold is land or another fixed asset. You assign the sales item type codes to customers in the customer constants.
These codes must exist in the GUI/VAT Sales Item Type UDC table:
| Codes | Description 01 | Hard-Coded |
|---|---|---|
| (blank) | General Sales | Y |
| 1 | Land | Y |
| 2 | Other Fixed Asset | Y |
3.2.28 Tax Refund Method (75T/TR)
You use tax refund method codes on the 401 or 403 report to specify how a refunded tax amount should be returned to you. You assign the tax refund method to declaration sites in the GUI/VAT Declaration Site program (P75T001).
These codes must exist in the Tax Refund Method UDC table:
| Codes | Description 01 | Hard-Coded |
|---|---|---|
| . | . | Y |
| BK | Return To Cash In Bank | Y |
| CH | Take A Check | Y |
3.2.29 GUI/VAT Transaction Type (75T/TT)
You use GUI/VAT transaction types to specify whether a transaction is a sale, a purchase, a foreign services purchase, or an import.
These codes must exist in the GUI/VAT Transaction Type UDC table:
| Codes | Description 01 | Hard-Coded |
|---|---|---|
| FSV | Purchase Foreign Services | Y |
| IGD | Import Goods | Y |
| PUR | Purchases (Input) | Y |
| SAL | Sales (Output) | Y |
3.2.30 GUI/VAT Tax Type (75T/TX)
You use GUI/VAT tax type codes to specify the tax type for the transaction that is listed on the government uniform invoice (GUI). These codes must exist in the GUI/VAT Tax Type UDC table:
| Codes | Description 01 | Description 02 | Hard-Coded |
|---|---|---|---|
| (blank) | . | For Trans. Type IGD, FSV Only | Y |
| 1 | Taxable (General/Special) | . | Y |
| 2 | Zero Tax Rate | . | Y |
| 3 | Tax-Exempt | . | Y |
| D | Unused | . | Y |
| F | (Void | Y |
3.2.31 Void Reason Code (75T/VR)
Set up values in this UDC table to provide reasons for voiding a GUI/VAT transactions. You specify the void reason code when you void transactions in the GUI/VAT Transaction Revisions program. The system uses the values that you assign to a voided transactions when you report information about voided GUI numbers.
Examples of values are:
| Codes | Description |
|---|---|
| BD | Bad debt |
| DA | Disputed amount |
| DM | Damaged goods |
| WO | Write off |
3.2.32 GUI/VAT Zero Tax Rate Item Type (75T/ZT)
You use GUI/VAT zero tax rate item type codes to specify whether a zero-tax-rate item has passed through customs. You assign a code to customers in the customer constants, and use the values when you enter certain transactions.
These codes must exist in the GUI/VAT Zero Tax Rate Item Type UDC table:
| Codes | Description 01 | Hard-Coded |
|---|---|---|
| . | Non Zero Tax Rate Sales | Y |
| ZNC | Export Not Through Customs | Y |
| ZTC | Export Through Customs | Y |
3.2.33 e-GUI Mode (75T/EM) (Release 9.1 Update)
e-GUI modes are defined by the Taiwan Tax Authority to identify the e-GUI processing modes between the seller, buyer and the Taiwan e-GUI platform. You must update the e-GUI mode in the GUI/VAT Customer Constants program (P75T009).
The four types of e-GUI modes are B2B-Exchange; B2B Non-Exchange; B2C and B2G. For each e-GUI mode, the Taiwan Tax Authority has defined different integration interfaces and processes. The value for these e-GUI modes must exist in the e-GUI Mode UDC table:
| Codes | Description 01 |
|---|---|
| . | Blank |
| 01 | B2B-Exchange |
| 02 | B2B Non-Exchange |
| 03 | B2C |
| 04 | B2G |
3.2.34 e-GUI Transaction Type (75T/ET)
You enter values from this UDC table when you add additional information for document types to support e-GUI processing. You use the values in this UDC table to select the type of e-GUI transaction to process when you run the e-GUI Extract Invoice Data program (R75T031).
The values for the 75T/ET UDC table are not hard-coded. Some examples of the user-defined codes are:
| Codes | Description 01 |
|---|---|
| 02 | Credit Memo issued by seller |
| 07 | e-GUI with general tax rate |
| 08 | e-GUI with specific tax rate |
3.3 Setting Up AAIs for GUI/VAT
This section discusses how to set up AAIs for Taiwan.
You must set up these Financial AAIs to process GUI/VAT information for Taiwan:
-
GTxxxx
Journal Entry with VAT (for input and output tax corresponding to the GL offset codes set up in the tax rate area).
-
RB
Receivables bank.
-
RC
Receivables trade.
-
RT
VAT for accounts receivable.
-
RD1
Drafts receivable.
-
RD2
Drafts remitted.
-
RD3
Drafts remitted for discount.
-
RD4
Contingent liability.
-
RD5
Void/non-sufficient funds.
-
PB
Payables bank.
-
PC
Payables trade.
-
PT
VAT for accounts payable.
You must also set up these Distribution AAIs to process GUI/VAT information for Taiwan:
-
4220
Cost of goods sold (COGS) - SOC.
-
4230
Revenue - SOS.
-
4240
Inventory - SOI.
-
4310
Inventory - OPI.
-
4320
Received not vouchered - OPR.
-
4340
Exchange rate - OPX.
-
4122
Inventory - TRI.
-
4124
Expense or COGS - TRO.
3.4 Setting Up GUI/VAT Declaration Sites
This section provides an overview of GUI/VAT declaration sites, lists a prerequisite, and discusses how to add declaration sites.
3.4.1 Understanding GUI/VAT Declaration Sites
You use the GUI/VAT Declaration Site program (P75T001) to set up declaration sites. Declaration sites are locations that issue GUIs and report VAT. Each declaration site can be associated with one company only in the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system. However, a company can have multiple declaration sites.
The system saves the data that you enter for declaration sites to the GUI/VAT Declaration Site table (F75T001). The system reads the data in the F75T001 table when you enter GUI information and print GUIs and when you run reports.
When you set up GUI/VAT declaration sites, you establish this information:
(Release 9.1 Update) The Business Administration Number (BAN) of the seller is required to be listed in the e-GUI. To determine the BAN of the seller involved in the transactions, you must associate the declaration site with the business unit. You can associate one or more Business units with a single declaration site. However, you can associate a business unit with only one declaration site.
The information entered for declaration site and business unit mapping is stored in the Declaration Site Business Unit Mapping table (F75T032). The system retrieves the information from the F75T032 table when you run the e-GUI Taiwan report.
3.4.2 Prerequisite
Set up a list of the GUI/VAT declaration sites in UDC (75T/DS).
3.4.3 Form Used to Add Declaration Sites
| Form Name | FormID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Work With GUI/VAT Declaration Site | W75T001A | GUI/VAT System Setup (G75T141), GUI/VAT Declaration Site. | Review and select existing declaration sites. |
| GUI/VAT Declaration Site | W75T001B | Click Add on the Work With GUI/VAT Declaration Site form. | Associate a declaration site to a company and specify information about the declaration site. |
| Work with Declaration Site Business Unit Setup Revision | W75T032B | On the Work With GUI/VAT Declaration Site form, select a declaration record, and then select Define Business Unit from the Row menu. | Associate one or more business units to the declaration site. |
3.4.4 Adding Declaration Sites
Access the GUI/VAT Declaration Site form.
3.4.4.1 Basic
Access the Basic tab.
Figure 3-3 GUI/VAT Declaration Site form, Basic tab
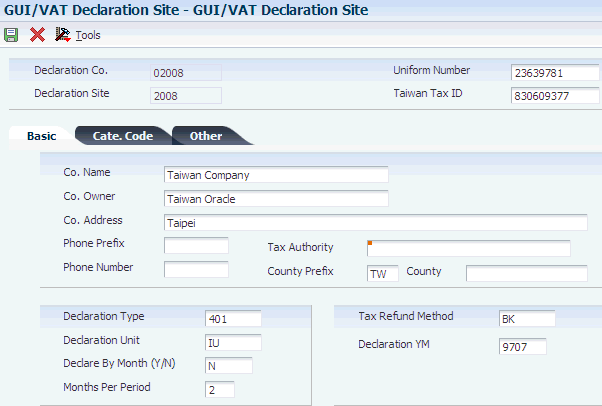
Description of ''Figure 3-3 GUI/VAT Declaration Site form, Basic tab''
- Declaration Co. (declaration company)
-
Enter the company code of the reporting company. The company code must exist in the Company Constants table (F0010).
- Declaration Site
-
Enter a code that exists in the GUI/VAT Declaration Site (75T/DS) UDC table to identify the site for which the VAT is declared.
- Uniform Number
-
Enter the Uniform Number of the Taiwanese company.
- Taiwan Tax ID
-
Enter the tax ID of the company.
- Co. Name (company name)
-
Enter the name of the reporting company as you want it to appear on reports. You can enter up to 40 characters.
You must complete this field.
- Co. Owner (company owner)
-
Enter the company or person to whom billing or correspondence is addressed.
You must complete this field.
- Co. Address (company address)
-
Enter the address of the reporting company. You can enter up to 80 characters.
- Phone Prefix
-
Enter the first segment of a telephone number.
- Phone Number
-
Enter a number without the prefix or special characters, such as hyphens or periods, that makes up the telephone number for an entity.
- Tax Authorities
-
Enter the address book number of the tax authority to whom you send tax payments.
- County Prefix
-
Enter the prefix for the county in which the declaration site exists.
- County
-
Enter the county in which the declaration site exists.
- Declaration Type
-
Enter a value that exists in the GUI/VAT Declaration Type (75T/DL) UDC table to identify the declaration type of a GUI/VAT. Values are:
401: Taxable only
403: Taxable, tax-exempt, or special tax
You must complete this field.
- Declaration Unit
-
Enter a value that exists in the GUI/VAT Declaration Unit (75T/DU) UDC table to specify the type of declaration unit. Values are:
HQ: Headquarters
IU: Individual unit
You must complete this field.
- Declare By Month (Y/N)
-
Enter a value to specify whether the VAT declaration is by month. Values are:
Y: Month.
N: Period.
You must complete this field.
- Months Per Period
-
Enter the number of months in a declaration period.
If you entered N in the Declare By Month field, you must complete this field.
- Tax Refund Method
-
Enter a value that exists in the Tax Refund Method (75T/TR) UDC table to specify the tax refund method. Values are:
BK: Deposit in bank
CH: Check
- Declaration YM (declaration year and month)
-
Enter the Taiwanese calendar year and month of the GUI/VAT declaration.
You must set up declaration periods before completing the Declaration YM field. After creating a declaration site record, set up declaration periods for that declaration site, and then return to the GUI/VAT Declaration Site form and specify the current declaration period in the Declaration YM field.
3.4.4.2 Cate. Code (category code)
Access the Cate. Code tab.
Figure 3-4 GUI/VAT Declaration Site form, Cate. Code tab
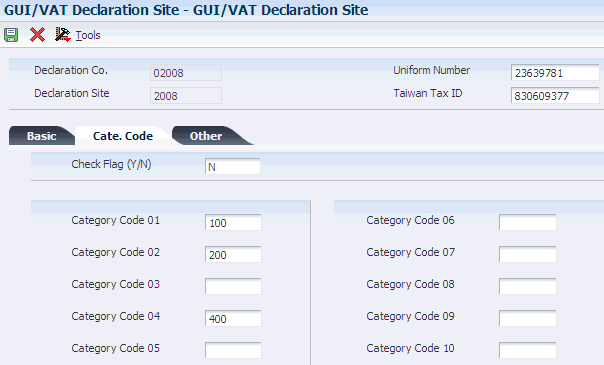
Description of ''Figure 3-4 GUI/VAT Declaration Site form, Cate. Code tab''
- Check Flag (Y/N)
-
Specify whether the system verifies that the category codes that are assigned to the declaration site are valid codes in the Customer Master by Line of Business table (F03012). Values are:
Y: The system validates category codes 1 - 10.
N: The system does not validate category codes.
- Category Code 01 thru Category Code 10
-
Enter a value that exists in the address book category codes. For example, for Category Code 01, enter a value that exists in UDC table 01/01, which is address book category code 01. You can use the category code information for data selection when you generate reports.
3.4.4.3 Other
Access the Other tab.
Figure 3-5 GUI/VAT Declaration Site form, Other tab
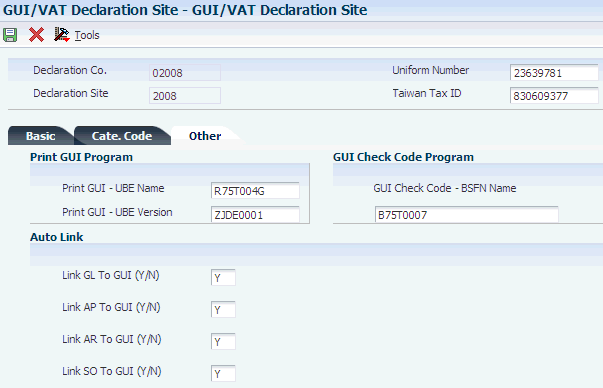
Description of ''Figure 3-5 GUI/VAT Declaration Site form, Other tab''
- Print GUI - UBE Name
-
Enter the program number of the program that you use to print the GUI document. For example, if you use the GUI/VAT Computer GUI Print Sample program, enter R75T004G.
Note:
Only the GUI/VAT Computer GUI Print Sample program and the GUI/VAT Computer GUI Print - Sample 1 program (R75T004G1) print the GUI in the required format. - Print GUI - UBE Version
-
Enter the version name of the program that you specified in the Print GUI - UBE Name field. For example, you might enter ZJDE0001.
- GUI Check Code - BSFN Name
-
If you want to use your own custom program to validate the uniform number instead of the validation routine supplied in the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne software, enter the name of your custom business function. You must enter the function name using the standard ANSI C naming conventions.
- Link GL To GUI (Y/N)
-
Specify whether the system creates a GUI record during the creation of a journal entry for the declaration company. Values are:
Y: Link. The system displays a Taiwan-specific form on which you enter GUI/VAT information after you use the Journal Entry with VAT program (P09106) program to enter the standard information.
N: Do not link. The system does not display the Taiwan-specific form.
- Link AP To GUI (Y/N)
-
Specify whether the system creates a GUI record during the creation of a voucher for the declaration company. Values are:
Y: Link. The system displays a Taiwan-specific form on which you enter GUI/VAT information after you use the Standard Voucher Entry program (P0411) to enter the standard information.
N: Do not link. The system does not display the Taiwan-specific form.
- Link AR To GUI (Y/N)and Link SO To GUI (Y/N)
-
Specify whether the system creates a GUI record during the creation of an invoice for the declaration company. Values are:
Y: Link. The system displays a Taiwan-specific form on which you enter GUI/VAT information after you use the Standard Invoice Entry program (P03B2002) to enter the standard information.
N: Do not link. The system does not display the Taiwan-specific form.
3.5 Setting Up GUI/VAT Declaration Periods
This section provides an overview of declaration periods and discusses how to set up declaration periods.
3.5.1 Understanding Declaration Periods
You use the GUI/VAT Declaration Site program to set up declaration periods to specify the declaration site's schedule for submitting tax declarations. You must set up declaration periods for each declaration site. When you specify that a declaration site reports by period instead of by month, you set up the periods for sales, sales return, purchase, and purchase return transactions. The system uses the declaration periods for reporting, and you use them when you set up the sales number register.
You submit declarations by calendar month and year, not by the company's fiscal period and year. Typically, a year is divided into six or twelve declaration periods (six periods if you submit declarations every two months, or twelve periods if you submit declarations monthly).
You must declare output (sales) tax within two months following the sales transaction. For example, if you submit declarations every two months, output tax for sales transactions that took place in January must be declared in the first declaration period (January and February). If you submit declarations monthly, output tax for sales transactions that occurred in place in January can be declared in either the first declaration period (January) or the second declaration period (February).
You typically declare input (purchase) tax within four months, based on the supplier's invoice date. However, you can apply for a special grant to override this restriction.
You complete the date fields on the GUI/VAT Declaration Period Revisions form for each declaration period during the year. Enter dates in the format YYMM, where YY is the 2-digit Taiwan calendar year (the international calendar year minus 1911), and MM is the 2-digit number of the month. For example, enter 9909 for September 2010.
3.5.2 Forms Used to Set Up Declaration Periods
| Form Name | FormID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Work With GUI/VAT Declaration Period | W75T001PA | GUI/VAT System Setup (G75T141), GUI/VAT Declaration Site.
On the Work With GUI/VAT Declaration Site form, select a record and select Period Setup from the Row menu. |
Access the Work With GUI/VAT Declaration Period form. |
| GUI/VAT Declaration Period Revisions | W75T001PB | Click Add on the Work With GUI/VAT Declaration Period form. | Set up declaration periods. |
3.5.3 Setting Up Declaration Periods
Access the GUI/VAT Declaration Period Revisions form.
Figure 3-6 GUI/VAT Declaration Period Revisions form.
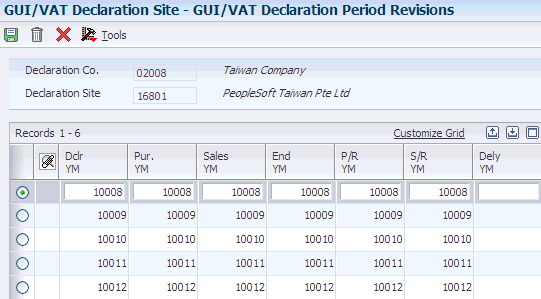
Description of ''Figure 3-6 GUI/VAT Declaration Period Revisions form.''
- Dclr YM (year and month of VAT declaration)
-
Enter the Taiwanese calendar year and month of the GUI/VAT declaration.
- Pur. YM (year and month for purchase documents)
-
Enter the year and month that begins the range of dates for the purchase documents.
- Sales YM (year and month for sales documents)
-
Enter the year and month that begins the range of dates for the sales documents.
- End YM (year and month end range of dates)
-
Enter the year and month that ends the range of dates for the sales or purchase documents.
- P/R YM (year and month for purchase returns)
-
Enter the year and month that begins the range of dates for the purchase return or allowance documents.
- S/R YM (year and month for sales returns)
-
Enter the year and month that begins the range of dates for the sales return or allowance documents.
- Delay YM (year and month of delayed declaration)
-
Enter the Taiwan calendar year and month of the delayed declaration for purchase tax.
3.6 Setting Up Tax Account Mapping for Declaration Sites
This section provides an overview of tax account mapping for declaration sites and lists the forms used to map tax accounts to declaration sites.
3.6.1 Understanding Tax Account Mapping for Declaration Sites
In the standard JD Edwards EnterpriseOne software, you associate AAIs to business units to determine the tax accounts to which tax amounts are written. You use the Declaration Site Tax Account Mapping program (P75T013) to map accounts to a company/declaration site combination. You must map all of the accounts that are associated with the AAIs and DMAAIs in your system. For example, you must create records in the Declaration Site Tax Account Mapping program for AAIs RTxxxx, PTxxxx, and GTxxxx. You select an account that exists for the company to which the declaration site is associated.
|
Note: The accounts in the Account Master table (F0901) are set up by a combination of company and business unit. If the company to which the declaration site belongs has numerous business units, select the account for the business unit that you use for tax reporting. In many cases, this business unit will be the main, or headquarters, business unit. |
When you enter transactions in Taiwan, the system verifies that the tax account that you associated with a declaration site is associated with an AAI in the Automatic Accounting Instructions program (P0012). The system uses that AAI to write amounts to the tax account that you specify in the Declaration Site Tax Account Mapping program.
The system writes the data about the relationship between the tax account and the declaration site to the Declaration Site Tax Account Mapping table (F75T013).
3.6.2 Forms Used to Map Tax Accounts to Declaration Sites
3.7 Associating Format Codes and Programs to Document Types
This section provides an overview of format codes for document types and discusses how to associate format codes to document types.
3.7.1 Understanding Format Codes for Document Types
The Taiwanese government requires that you use specific formats for various transactions. Instead of entering the format code for each transaction, you can set up associations between the document types and format codes. Then, when you enter a transaction for a particular document type, the system retrieves the format code for the document type.
You use the GUI/VAT Document Type Format Code Setup program (P75T011) to specify the default values for formats and document types that the system uses when you enter invoices, vouchers, or journal entries. You can set up the default values for these programs:
The system does not launch the Taiwan-specific form after you enter an invoice, voucher, or journal entry unless you set up the entry program in the GUI/VAT Document Type Format Code Setup program.
3.7.2 Forms Used to Associate Formats and Programs to Document Types
| Form Name | FormID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Work with GUI/VAT Document Type Format Code Setup | W75T011A | GUI/VAT System Setup (G75T141), GUI/VAT Document Type Format Code Setup | Review and select existing associations. |
| GUI/VAT Document Type Format Code Setup Revision | W75T011B | Click Add on the Work with GUI/VAT Document Type Format Code Setup form. | Enter the document type and format code to use as default values for each transaction entry program that you use. |
3.7.3 Associating Formats to Document Types
Access the GUI/VAT Document Type Format Code Setup Revision form.
Figure 3-7 GUI/VAT Document Type Format Code Setup Revision form
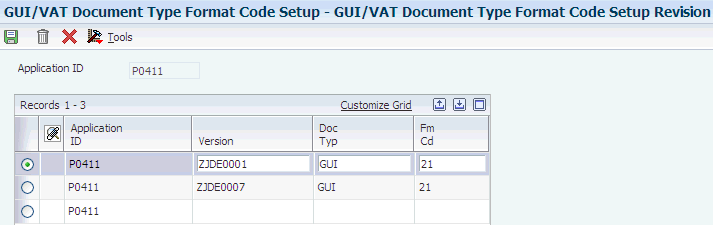
Description of ''Figure 3-7 GUI/VAT Document Type Format Code Setup Revision form''
- Application ID
-
Enter the application ID of the transaction entry program for which you set up the association between the document type and format code.
- Version
-
Enter the version of the application that you specified in the Application ID field.
You must set up corresponding versions for the application that you specify in the PO GUI/VAT Transaction (P75T003) program. For example, if you set up version XYZ for the Standard Voucher Entry program (P0411), a version XYZ must also exist for the PO GUI/VAT Transaction (P75T003) program. When you enter transactions using version XYZ of the Standard Voucher Entry program, the system launches version XYZ of the GUI/VAT Transaction program so that you can enter GUI information.
- Doc Typ (document type)
-
Enter a value that exists in the GUI/VAT Document Type (75T/DT) UDC table to specify the document type for which you set up the association.
You must specify the same document type in this field as you set up in the corresponding versions for the PO GUI/VAT Transaction (P75T003) program. For example, if you specify document type IMP in this field, the document type in the processing options for the corresponding version of the PO GUI/VAT Transaction (P75T003) program must also be IMP.
- Fm Cd (format code)
-
Enter a value that exists in the GUI/VAT Format Code (75T/FC) UDC table to specify the format code to associate to the document type that you entered in the Doc Typ field.
3.8 Setting Up GUI/VAT Number Prefixes for Input Tax
This section provides an overview of GUI/VAT number prefixes for input tax and discusses how to associate GUI/VAT number prefixes with format codes.
3.8.1 Understanding GUI/VAT Number Prefixes for Input Tax
Input tax is the tax that you pay on your purchases. When you process vouchers or journal entries for your purchases, the system must validate that the GUI/VAT prefix that your supplier used for the transaction is a valid prefix for the transaction date and format.
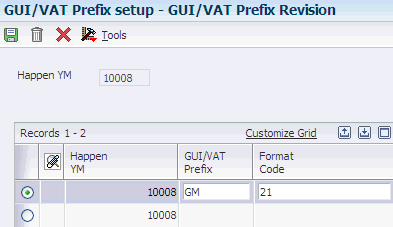
You use the GUI/VAT Prefix Setup program (P75T006) to set up associations between GUI/VAT prefixes and the format codes that you use for purchase transactions. You set up the associations for each year and month for which you process transactions (Happen Year). The Taiwanese government publishes the set of GUI/VAT prefixes annually.
The system uses the associations that you set up to validate that the GUI/VAT prefix is valid for the format type and transaction date of the transaction. If the association is not valid, the system does not enable you to proceed with the transaction. The system performs the validation when you use these programs:
-
Standard Voucher Entry (P0411)
-
Speed Voucher Entry (P0411SV)
-
Journal Entry (P0911)
-
Journal Entries with VAT (P09106)
The system saves the data for the associations to the GUI/VAT Prefix Setup table (F75T006).
3.8.2 Forms Used to Associate GUI/VAT Number Prefixes with Format Codes
| Form Name | FormID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Work With GUI/VAT Prefix | W75T006C | GUI/VAT System Setup (G75T41), GUI/VAT Prefix setup | Review and select existing records. |
| GUI/VAT Prefix Revision | W75T006E | Click Add on the Work With GUI/VAT Prefix form. | Associate a GUI/VAT prefix number with a format code. |
3.8.3 Associating GUI/VAT Number Prefixes with Format Codes
Access the GUI/VAT Prefix Revision form.
- Happen YM (happen year and month)
-
Enter the Taiwanese year and month of transactions for which you set up the association.
- GUI/VAT Prefix
-
Enter the two-character GUI/VAT prefix for which you set up the association.
- Format Code
-
Enter a value that exists in the GUI/VAT Format Code - Purchase (75T/F2) UDC table to specify the GUI format code for which you create the association to the prefix. Values for input tax are:
Blank: blank
21: Triplicate GUI / Computer GUI
22: Other Doc With Tax Amount
23: Triplicate Purchase Return / Allowance
24: Duplicate Purchase Return / Allowance
25: Triplicate Cash Register GUI
26: Summary Triplicate / Computer GUI With Tax
27: Summary Other Doc With Tax
28: VAT Payment Document
31: Triplicate / Computer GUI
3.9 Setting Up the GUI/VAT Sales Number Register
This section provides an overview of the GUI/VAT sales number register, lists a prerequisite, and discusses how to:
-
Add numbers to the GUI/VAT sales number register.
-
Segment GUI/VAT sales numbers.
3.9.1 Understanding the GUI/VAT Sales Number Register
GUIs must be numbered sequentially by transaction date. To assure that numbers are assigned sequentially by date, you set up the sales number register in the GUI/VAT Number Register - Sales program (P75T002). When you set up a GUI/VAT sales number register:
-
Add the sales number register, which includes specifying the range of GUI numbers.
-
Activate the sales number register, which gives you the ability to divide the sales number register into segments.
-
Segment the numbers that you added into smaller units that you can use for different GUI types, formats, and date ranges.
3.9.1.1 Activating and Deactivating Records
You can make a sales number register active or inactive by choosing the record and using the Active Inactive option on the Row menu. If an active sales number register has not been segmented, select Active Inactive from the Row menu to deactivate the number. If the sales number register has been segmented, select Force Inactive from the Row menu to deactivate the number. A sales number register must have a status of Active before you can work with it.
3.9.1.2 Segmenting the Records
A company might have multiple declaration sites (branch offices) in different counties or cities in Taiwan. Each declaration site must report tax to its respective local tax authority. Thus, the company has to segment the allotted GUI number range for use by each declaration site.
When you set up GUI/VAT sales number register segments, you specify the range of GUI numbers to include in each segment. The system uses the segment information to keep track of the last-used GUI number so that GUI numbers are assigned in sequence.
You can assign category codes to sales number register segments to classify the transactions according to the sales number register segment that is used to generate the GUI number. For example, you might allocate a specific sales number register segment for special sales or sales from a specific sales counter. Assigning a category code that identifies the special purpose enables you to identify the sales number register segment while entering the transaction and to later use data selection to report on those transactions.
After you divide a sales number register into segments, you activate the segments to make the GUI numbers that are specified in the segments available for assignment to sales transactions.
You can segment only sales number registers that are active. You can activate a GUI/VAT sales number register segment by choosing an inactive segment on the Work With GUI/VAT Sales Number Segment form and choosing Active Inactive from the Row menu.
You can deactivate a sales number register segment by choosing an active segment on the Work With GUI/VAT Sales Number Segment form and choosing Active Inactive from the Row menu. You can deactivate a sales number register segment only if none of the GUI numbers in the segment has been assigned to transactions.
3.9.1.3 Disassembling Segments
You can disassemble an inactive sales number register segment to divide it into smaller segments. For example, if a segment covers a range of 150 GUI numbers, you can disassemble it, putting 50 GUI numbers in one segment and 100 GUI numbers in the other segment.
When you disassemble a segment, the system creates two segments in place of the segment that you disassembled, with the number of GUI numbers that you specified in the second segment and the remaining GUI numbers in the first segment. For example, if you disassembled a 150-number segment, specifying 50 numbers for the second segment, the system creates one segment with 50 numbers and one segment with 100 numbers in place of the original 150-number segment. Each segment must contain a multiple of 50 GUI numbers.
You cannot disassemble a segment if any of the numbers have been assigned to transactions.
3.9.2 Prerequisite
Before you begin this task, set up declaration sites and declaration periods. The system uses the declaration periods to determine the effective date of the GUI numbers when you enter a value in the Declaration Y/M field.
3.9.3 Forms Used to Set Up the Sales Number Register
| Form Name | FormID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| GUI/VAT Sales Number Register Revisions | W75T002B | GUI/VAT System Setup (G75T141), GUI/VAT Number Register - Sales.
Click Add on the Work With GUI/VAT Sales Number Register form. |
Add a GUI/VAT sales number register. |
| Work With GUI/VAT Sales Number Register | W75T002A | On the Work With GUI/VAT Sales Number Register form, select an active or inactive sales number register in the detail area, and then select Active Inactive from the Row menu.
The system changes the value in the AI (GUI Register Active Flag) field and changes the color of the field. |
Activate or deactivate a GUI/VAT sales number register. |
| GUI/VAT Sales Number Segment Revisions | W75T002D | Select a record on the Work With GUI/VAT Sales Number Segment form and click Select. | Segment GUI/VAT sales numbers. |
| GUI/VAT Segment Disassembly | W75T002G | On the Work With GUI/VAT Sales Number Segment form, select an inactive segment in the detail area, and then select Disassemble from the Row menu. | Disassemble an inactive sales number register segment. |
3.9.4 Adding a GUI/VAT Sales Number Register
Access the GUI/VAT Sales Number Register Revisions form.
Figure 3-9 GUI/VAT Sales Number Register Revisions form
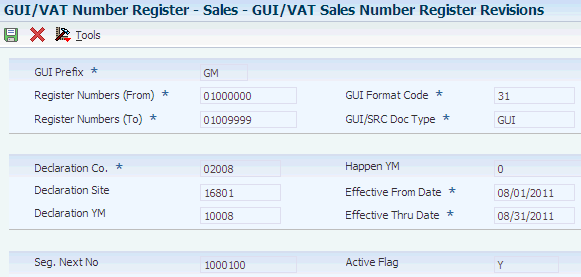
Description of ''Figure 3-9 GUI/VAT Sales Number Register Revisions form''
- GUI Prefix
-
Enter the prefix for the GUI numbers that you obtained from the government.
- Register Numbers (From)
-
Enter the beginning number of a range of receipt register numbers. A valid register number has eight digits.
- Register Range
-
Enter the total number of the range. For example, if the range of numbers is 20000000 through 20005000, enter 5000. The number that you enter must be a multiple of 50.
You must complete this field.
- GUI Format Code
-
Enter a code that specifies the GUI format code for the transaction. The code that you enter must exist in the GUI/VAT Format Code (75T/F3) UDC table. Values are:
Blank: Blank
31: Triplicate GUI / Computer GUI
32: Duplicate / Duplicate Cash Register GUI
33: Triplicate Sales Return / Allowance
34: Duplicate Sales Return / Allowance
35: Triplicate Cash Register GUI
36: GUI-Exempt
37: Special Tax: Sales
38: Special Tax: Return, Allowance
99: Sales Receipt
The system completes the GUI/SRC Doc Type field based on the value that you specify in the GUI Format Code field.
- Declaration Co. (declaration company)
-
Enter the declaration company for which you set up the numbering. The company must exist in the Company Names & Numbers program (P0010).
- Declaration Site
-
Enter a code that identifies the site for which the VAT is declared. The code that you enter must exist in the GUI/VAT Declaration Site (75T/DS) UDC table, and must be associated with the declaration company in the GUI/VAT Declaration Site program.
- Declaration YM (year and month of VAT declaration)
-
Enter the Taiwanese calendar year and month of the GUI/VAT declaration. The value that you enter must exist as a reporting period in the GUI/VAT Declaration Site table (F75T001) for the declaration site that you specify. You set up reporting periods from which you select the declaration year/month in the GUI/VAT Declaration Site program.
The system completes the Effective From Date and Effective Thru Date fields based on the value that you specify in the Declaration YM field.
- Happen YM (year and month that tax document happened)
-
Enter the Taiwanese calendar year and month of the GUI/VAT transaction. This field is optional.
Complete this field to set up the segment numbering by month for additional control. Enter the date in the format YYMM, where YY is the two-digit Taiwan calendar year (the international calendar year minus 1911), and MM is the two-digit number of the month. For example, enter 9809 for September 2009.
- Effective From Date
-
The system completes this field with the beginning date of the declaration period.
- Effective Thru Date
-
The system completes this field with the ending date of the declaration period.
3.9.5 Segmenting GUI/VAT Sales Numbers
Access the GUI/VAT Sales Number Segment Revisions form.
Figure 3-10 GUI/VAT Sales Number Segment Revisions form
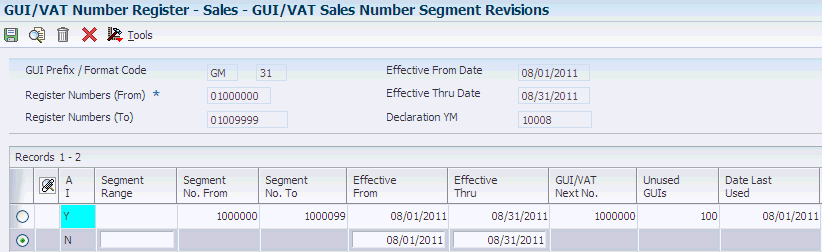
Description of ''Figure 3-10 GUI/VAT Sales Number Segment Revisions form''
- Segment Range
-
Enter the number of unused GUI numbers to add to the segment. The range must be a multiple of 50.
- Segment No. From (segment number from)
-
The system completes this field based on the value that you entered in the Segment Range field.
- Segment No. To (segment number to)
-
The system completes this field based on the value that you entered in the Segment Range field.
- Effective From
-
The system completes this field with the start date of the declaration period.
- Effective Thru
-
The system completes this field with the ending date of the declaration period.
- GUI/VAT Next No. (GUI/VAT next number)
-
The system completes this field based on the value that you entered in the Segment Range field. The value does not appear until you exit the detail line.
- Unused GUIs
-
The system completes this field based on the value that you entered in the Segment Range field. The value does not appear until you exit the detail line.
The value in this field changes as you assign the numbers to transactions.
- Date Last Used
-
When you initially set up the segments, the system completes this field with the start date of the declaration period. The value does not appear until you exit the detail line.
The value in this field changes to the most recent transaction date as you use the numbers.
- Auth Code (authorization code)
-
Enter a value that exists in the Authorization Code (75T/AC) UDC table to limit the use of the number segment to users who are assigned the same authorization code for the same declaration site.
- Rev Typ (revenue type)
-
Enter a value that exists in the GUI/VAT Revenue Type (75T/RT) UDC table to specify the revenue type of a sales transaction. You can use this field to limit the types of transactions to which the numbers are assigned.
- CC 1 thru CC3 (category code 1 thru category code 3)
-
Enter a value that exists in UDC table 75T/C1, 75T/C2, or 75T/C3 to classify the GUI/VAT number segment.
3.10 Specifying the GUI/VAT Number Segments Used by Programs
This section provides an overview of how the system uses the GUI/VAT number segments, lists a prerequisite, and discusses how to:
-
Set processing options for GUI/VAT Number Segment (Batch) Setup (P75T014).
-
Specify the GUI/VAT number segments used by a document type/format code combination.
3.10.1 Understanding How the System Uses the GUI/VAT Number Segments
You specify in the GUI/VAT Number (Batch) Setup program (P75T014) the segment to use for a combination of:
-
Declaration company
-
Declaration site
-
Authorization code
-
Declaration year and month
-
GUI document type
-
GUI format code
-
Tax type
When you run the programs that assign GUI/VAT numbers, the system compares the values for the transactions to the values that you set up in the GUI/VAT Number (Batch) Setup program and uses the next number from the segment that is specified in the GUI/VAT Number (Batch) Setup program when it creates the GUI record.
The system uses the segments that you assign when you run these programs in final mode:
-
GUI/VAT Creation From Multi-AR (R75T004S).
-
GUI/VAT Creation From Multi-SO (R75T004O).
-
GUI/VAT Creation From Selected AR (P75T004R).
The system calls the GUI/VAT Creation From Multi-AR program when you use the GUI/VAT Creation From Selected AR program to generate GUI information.
-
GUI/VAT Creation From Selected SO (P75T004O).
The system calls the GUI/VAT Creation From Multi-SO program when you use the GUI/VAT Creation From Selected SO program to generate GUI information.
-
GUI/VAT Creation From Selected SO History (P75T004H)
The system calls the GUI/VAT Creation From Multi-SO program when you use the GUI/VAT Creation From Selected SO History program to generate GUI information.
-
GUI/VAT SO History Enquiry (P75T4219)
The system calls the GUI/VAT Creation From Multi-SO program when you use the GUI/VAT SO History Enquiry program to generate GUI information.
-
GUI/VAT SO Inquiry (P75T4211).
The system calls the GUI/VAT Creation From Multi-SO program when you use the GUI/VAT SO Inquiry program to generate GUI information.
3.10.2 Prerequisite
Before you begin the task in this section, set up number segments in the GUI/VAT Number Register - Sales program, and activate the segments that you want to use.
3.10.3 Forms Used to Specify the GUI/VAT Number Segment Used by a Document Type / Format Code Combination
| Form Name | FormID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Work With GUI/VAT Number Segment (Batch) | W75T014A | GUI/VAT Daily Processing (G75T110), GUI/VAT Number Segment (Batch) Setup. | Review existing segment assignments. |
| GUI/VAT Number Segment (Batch) Revision | W75T014B | Click Add on the Work With GUI/VAT Number Segment (Batch) from.
Complete the required fields, and select Select Segment from the Form menu. |
Assign a segment to use with the batch programs.
Note: You can select only active segments. You make segments active in the GUI/VAT Register Number - Sales program. |
3.10.4 Setting Processing Options for GUI/VAT Number Segment (Batch) Setup (P75T014)
Processing options enable you to specify default values for programs and reports.
3.10.4.1 Default
- Declaration company of GUI/VAT
-
Specify the default company for which you set up a GUI/VAT number segment batch.
- Declaration site of VAT
-
Specify a value that exists in the GUI/VAT Declaration Site (75T/DS) UDC table to specify the default site for which you set up a GUI/VAT number segment batch.
3.10.5 Specifying a GUI/VAT Number Segment Used by a Document Type / Format Code Combination
Access the GUI/VAT Number Segment (Batch) Revision form.
Figure 3-11 GUI/VAT Number Segment (Batch) Revision form
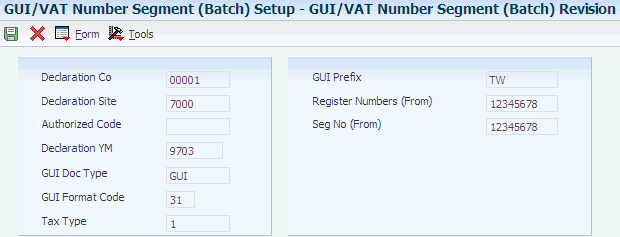
Description of ''Figure 3-11 GUI/VAT Number Segment (Batch) Revision form''
|
Note: To select a new batch for a declaration company and site for which a number segment batch has already been set up, select an existing record on the Work With GUI/VAT Number Segment (Batch) form and click Select. |
The system completes the Declaration Co and Declaration Site fields based on the information that is specified in the processing options of the GUI/VAT Number Segment (Batch) Setup program. You can change them on the GUI/VAT Number Segment (Batch) Revision form, if necessary.
- Authorized Code
-
Enter a value that exists in the Authorized Code (75T/AC) UDC table to limit the use of the assigned number to users who have the same authorization code assigned for the declaration site.
- Declaration YM (year and month of VAT declaration)
-
Enter the Taiwanese calendar year and month of the segment that you want to assign to the batch programs. You must complete this field. The value that you enter must be set up as a declaration period in the GUI/VAT Declaration Site program.
- GUI Doc Type (GUI document type)
-
Enter a value that exists in the GUI/VAT Document Type (75T/DT) UDC table to specify the GUI document type to assign to the segment.
You must complete this field.
- GUI Format Code
-
Enter a code that specifies the GUI format code for the transaction. The code that you enter must exist in the GUI/VAT Format Code (75T/F3) UDC table. You must complete this field.
Values are:
31: Triplicate / Computer GUI
32: Duplicate / Duplicate Cash Register GUI
33: Triplicate Sales Return / Allowance
34: Duplicate Sales Return / Allowance
35: Triplicate Cash Register GUI
36: GUI-Exempt
37: Special Tax: Sales
38: Special Tax: Return, Allowance
99: Sales Receipt
- Tax Type
-
Enter a value that exists in the GUI/VAT Tax Type (75T/TX) UDC table to specify the tax type of the transaction.
3.11 Setting Up GUI/VAT General Ledger Account Mapping
This section provides an overview of GUI/VAT general ledger (GL) account mapping and lists the forms used to set up GUI/VAT general ledger account mapping.
3.11.1 Understanding GUI/VAT GL Account Mapping (Release 9.1 Update)
You set up GUI/VAT general ledger account mappings to specify all accounts for which you distribute amounts when you run the Tax Journal Entry program (P09106). During the GL distribution step of transaction entry, the system distributes input tax to the debit account that you specify, and distributes output tax to the credit account that you specify.
You use the GUI/VAT Account Mapping program (P75T012) to specify the accounts to which the system distributes amounts when you run the Tax Journal Entry program (P09106). You must set up in the GUI/VAT Account Mapping program all of the GL posting accounts that are specified in the GTxxxx AAIs. Enter D (debit) in the DC (debit/credit) field for accounts that you use for input tax. Enter C (credit) in the DC (debit/credit) field for accounts that you use for output tax. Do not map offset accounts.
The system saves the account mapping to the GUI/VAT GL Account Mapping table (F75T012).
|
Note: The accounts in the Account Master table (F0901) are set up by a combination of company and business unit. If the company to which the declaration site belongs has numerous business units, select the account for the business unit that you use for tax reporting. In many cases, this business unit will be the main, or headquarters, business unit. |
3.11.2 Forms Used to Set Up GUI/VAT GL Account Mapping
| Form Name | FormID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| GUI/VAT GL Account Mapping Revisions | W75T012B | GUI/VAT System Setup (G75T141), GUI/VAT GL Account Mapping.
Click Add on the Work With GUI/VAT GL Account Mapping form. On the GUI/VAT GL Account Mapping Revisions form, select an empty row in the detail area and select Get Account from the Row menu. |
Set up GUI/VAT GL account mappings. |
3.12 Setting Up a GUI/VAT User/Declaration Site Mapping
This section provides an overview of GUI/VAT user/declaration site mapping and discusses how to set up declaration site mapping.
3.12.1 Understanding GUI/VAT User/Declaration Site Mappings
You set up GUI/VAT user/declaration site mappings to specify the declaration site to which transactions entered by specific users are assigned. If a declaration site is assigned an authorization code in the GUI/VAT Declaration Site program, only users who are assigned the same authorization code can enter GUI information for the declaration site. Likewise, if a GUI number segment is assigned an authorization code, only users who are assigned the same code can assign a number from the segment. Users can generate GUI information for only the transaction type that you specify in the GUI/VAT User/Declaration Site Mapping program (P75T010). If a user needs to generate more than one type of transaction, or works with more than one declaration site, set up multiple records for the user.
When you first map a user to a declaration site, the mapping is inactive. You must change the mapping status to active before the user can enter transactions for the specified declaration site.
3.12.2 Forms Used to Set Up User / Declaration Site Mappings
| Form Name | FormID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Work With GUI/VAT User / Declaration Site Mapping | W75T010A | GUI/VAT System Setup (G75T141), GUI/VAT User / Declaration Site Mapping.
Select Change Status from the Row menu. |
Change the status from active to inactive or from inactive to active. |
| GUI/VAT User / Declaration Site Mapping Revisions | W75T010C | Click Add on the Work With GUI/VAT User / Declaration Site Mapping form. | Set up a GUI/VAT user/declaration site mapping. |
3.12.3 Setting Up User / Declaration Site Mappings
Access the GUI/VAT User / Declaration Site Mapping Revisions form.
Figure 3-12 GUI/VAT User / Declaration Site Mapping Revisions
Description of ''Figure 3-12 GUI/VAT User / Declaration Site Mapping Revisions''
- User ID
-
Enter the user ID as the ID appears in the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system.
- GUI Trans Type (GUI transaction type)
-
Enter a value that exists in the GUI/VAT Transaction Type (75T/TT) UDC table to specify the transaction type for which the user can enter transactions.
- Doc/Order Company (document/order company)
-
Enter the company that is associated with the declaration site for which you set up the mapping.
- Dclr Co (declaration company)
-
Enter the company that is associated with the declaration site for which you set up the mapping.
- Dclr Site (declaration site)
-
Enter a value that exists in the GUI/VAT Declaration Site (75T/DS) UDC table to specify the site for which you set up the mapping.
- Auth Code (authorization code)
-
Enter a value that exists in the Authorization Code (75T/AC) UDC table to generate a link between the user and the GUI number segments for a declaration site.
The same authorization code must be set up for the segment of numbers that you use for the type of transaction that you specified in the GUI Trans Type field. You must also specify the same authorization code in the PO GUI/VAT Transaction (P75T003) and GUI/VAT Transaction (P75T004) programs that you use to generate the GUI record.
3.13 Setting Up the GUI/VAT Tax Type Mapping for Taiwan
This section provides an overview of the setup for GUI/VAT tax type mapping, lists prerequisites, and discusses how to set up a GUI/VAT tax type mapping.
3.13.1 Understanding the Setup for GUI/VAT Tax Type Mapping
You specify in the customer master record for each customer the tax rate area and tax explanation code that apply to the customer. The combination of the tax rate area and tax explanation code determines if the customer is subject to VAT. You must also specify at the transaction level whether a specific transaction for a customer is subject to VAT. You specify whether a transaction is taxable by assigning a tax type to the transaction.
Tax types for Taiwan are:
-
Taxable
-
Zero-rate
-
Exempted
-
Void
You use the GUI/VAT Tax Type Mapping program (P75T008) to associate a tax type to a tax rate area and tax explanation code combination. The system stores the associations in the GUI/VAT Tax Type Mapping table (F75T008). When you enter transactions for a customer, you enter the tax rate area and tax explanation code for the transaction in the standard software for sales orders, invoices, vouchers, and journal entries. The standard software calls the GUI/VAT Transaction program (P75T004), which looks up the associations in the F75T008 table and uses the combination of the tax rate area and tax explanation code to determine a default value for the tax type of the transaction. The system calculates the VAT by using the tax explanation code and tax rate area that you associated with the tax type.
The system writes the tax type to the GUI/VAT Transaction Detail table (F75T004) in the record for the transaction. The system uses the records in the F75T004 table when you run the programs to report taxable, nontaxable, and tax-exempt transactions.
Each GUI can include transactions for only one of the tax types. For example, if a sales order transaction has some items that are taxable and some that are taxed at a zero-tax rate, you must generate two GUIs.
|
Note: You cannot delete a record from the F75T008 table if transactions that use the record exist in the F75T004 table. |
3.13.2 Prerequisites
Before you complete the tasks in this section:
-
Set up the GUI/VAT tax type UDC (75T/TX).
-
Set up the tax rate areas that apply to your business transactions.
-
Set up tax explanation codes.
3.13.3 Forms Used to Set Up GUI/VAT Tax Type Mappings
| Form Name | FormID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Work With GUI/VAT Tax Type Mapping | W75T008A | GUI/VAT System Setup (G75T141), GUI/VAT Tax Type Mapping. | Review and select GUI/VAT tax type mapping records. |
| GUI/VAT Tax Type Mapping Revisions | W75T008B | Click Add on the Work With GUI/VAT Tax Type Mapping form. | Add and revise GUI/VAT tax type mapping records. |
3.13.4 Setting Up a GUI/VAT Tax Type Mapping
Access the GUI/VAT Tax Type Mapping Revisions form.
Figure 3-13 GUI/VAT Tax Type Mapping Revision form
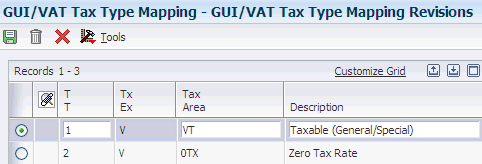
Description of ''Figure 3-13 GUI/VAT Tax Type Mapping Revision form''
- T T (VAT tax type)
-
Enter a value that exists in the GUI/VAT Tax Type (75T/TX) UDC table to specify the tax type of the VAT that you associate with a tax explanation code/tax rate area combination.
Values are:
1: Taxable
2: Zero tax rate
3: Exempt
D: Unused
F: Void
- Tx Ex (tax explanation code)
-
Enter a value that exists in the Tax Explanation Codes (00/EX) UDC table to specify the tax explanation code that you associate with the tax rate area and tax type. The tax explanation code for VAT must be V.
- Tax Area
-
Enter a code that identifies a tax or geographic area that has common tax rates and tax authorities. The system validates the code you enter against the Tax Areas table (F4008). The system uses the tax rate area in conjunction with the tax explanation code and tax rules to calculate tax and GL distribution amounts when you create an invoice or voucher.
3.14 Setting Up Exchange Rates for Taiwan
This section provides an overview of exchange rate setup for Taiwan and discusses how to set up exchange rates for Taiwan.
3.14.1 Understanding Exchange Rate Setup for Taiwan
If you process sales transactions in a currency other than TWD (Taiwan dollars), you must set up your system with the exchange rates provided by the Taiwan Customs Department. The Taiwan Customs Department publishes rates three times a month in this manner:
-
Use the rate published on the 5th day of the month for transactions dated from the 11th through the 20th.
-
Use the rate published on the 15th day of the month for transactions dated from the 21st through the last day of the month.
-
Use the rate published on the 25th day of the month for transactions dated from the 1st through the 10th of the next month.
|
Important: Because government regulations are subject to change, you should consult the current regulations to assure that you use the most current schedule. |
You use the Ten-Days Exchange Rate Setup program (P0015A) to set up exchange rates to convert other currencies to the Taiwanese dollar. You specify the factor that the system uses to convert the currency as the no inverse method. This method is a calculation method that uses the same exchange rate for the multiplier and divisor rates. The no inverse method reduces the rounding differences that can occur when you work with large amounts using the inverse method and reciprocal rate. Any rounding differences that might occur with the no inverse method are usually immaterial.
When you set up an exchange rate for the no inverse method, the system automatically creates a corresponding record in the opposite direction. For example, if you set up an exchange rate record from USD to TWD for the no inverse method and specify conversion method Y for multiplier, the system automatically creates an exchange rate record from TWD to USD with conversion method Z for divisor. The two rates on these exchange rate records are the same - one is the multiplier rate and the other is the divisor rate. The opposite rate on each record is blank because, with no inverse, that rate has no purpose.
You must use a rate type different than blank to setup the Ten-Days Exchange Rates Setup program.
The system saves the effective dates for the exchanges rates in the Currency Exchange Rates table (F0015). Uses the 1st, 11th, or 21st of a month as effective dates.
You must not use the triangulation method when you run the Currency Exchange Rate Entry program to set up exchange rates for Taiwan. If you do so, the system displays an error when you run the Taiwan Ten-Days Exchange Rate program.
The system uses the rates and effective dates when you run the Taiwan Ten-Days Exchange Rate program (R75T1113U) to update sales order records.
3.14.2 Forms Used to Set Up Exchange Rates for Taiwan
| Form Name | FormID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Work with Currency Exchange Rates | W0015AA | GUI/VAT System Setup (G75T141), Ten-Days Exchange Rate Setup | Select existing exchange rate records. |
| Review Currency Exchange Rates | W0015AB | Select a record on the Work with Currency Exchange Rates form and click Select. | Select the record for an effective date to specify the conversion method. |
| Revise Currency Exchange Rates | W0015AC | Select a record on the Review Currency Exchange Rates form and click Select. | Specify the method for the currency conversion. |
3.14.3 Setting Up an Exchange Rate for Taiwan
Access the Revise Currency Exchange Rates form.
Figure 3-14 Revise Currency Exchange Rates form
Description of ''Figure 3-14 Revise Currency Exchange Rates form''
- Currency Code
-
Enter the currency code from which you convert the transaction. The currency code must exist in the Currency Codes table (F0013).
- To Currency Code
-
Enter the currency code to which you convert the transaction. The currency code must exist in the Currency Codes table (F0013).
- Effective Date
-
Enter the effective date of the exchange rate.
- Contract (Addr)
-
Enter a number that identifies an entry in the Address Book system, such as employee, applicant, participant, customer, supplier, tenant, or location. Yo must leave the default value of 0 in this field to apply the rate type to all customers.
- Rate Type
-
Enter a value that exists in the Rate Type (11/RT) UDC table to specify the rate type that you set up. The default rate type is blank, but you change it to a value to setup the Ten-Days Exchange Ratesx Setup program. Examples of values are:
@: Rate change
H: Historical
- Calculation Method
-
Enter the method that the system uses to convert the currency. You must not use the triangulation method while setting up the Ten-Days Exchange Ratesx Setup program.
- Conversion Method (Y/Z)
-
Enter a value that specifies which method to use when converting from one currency to another. Valid values are:
Y: This specifies the multiplier method. In this method, the system multiplies the foreign amount by the multiplier exchange rate to calculate the domestic amount.
Z: This specifies the divisor method. In this method, the system divides the foreign amount by the divisor exchange rate to calculate the domestic amount.
- No inverse Method
-
Enter the factor by which the currency that you specify in the Currency Code From field is multiplied to calculate the currency equivalent to the currency that you specify in the To Currency Code field.
3.15 Setting Up Supplier Constants for Taiwan
This section provides an overview of supplier constants for Taiwan, lists a prerequisite, and discusses how to:
-
Set up supplier constants for Taiwan.
-
Import data for supplier constants for Taiwan.
3.15.1 Understanding Supplier Constants for Taiwan
You set up supplier constants to provide the system with information to use when you create GUIs for that supplier. Supplier constants include information such as the supplier's uniform number, the GUI format to use, and purchase information.
You use the GUI/VAT Supplier Constants program (P75T0091) to add Taiwan-specific information to a supplier record. When you add a supplier record in the Supplier Master Information program (P04012) and the value in the Localization County Code field in the User Profile Revisions program (P0092) is set to TW (Taiwan), the system launches the GUI/VAT Supplier Constants program when you create a supplier record. You can also access the GUI/VAT Supplier Constants program by using the Regional Info option in the Supplier Master Information program or by using a menu option.
You can assign category codes to suppliers to classify purchases according to the type of supplier. Assigning category codes to supplier enables you to use data selection to report on transactions according to the type of supplier. Set up the 75T/C7–75T/C9 UDC tables with the category code information that you want to associate with suppliers.
F75T0091 (GUI/VAT Supplier Constants) The system saves the Taiwan-specific data that you enter in the GUI/VAT Supplier Constants program to the GUI/VAT Supplier Constants table (F75T0091).
You can enter information for suppliers one at a time, or you can import a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet that contains information for several suppliers.
3.15.1.1 Considerations for Importing Supplier Constants for Taiwan
To import suppliers' constants from a spreadsheet, you must create a spreadsheet that contains the required columns in this order:
-
Supplier Number
-
Supplier Uniform Number
-
GUI Format Code
-
In Bond Flag
-
Deduction Code
-
Purchase Item Type
-
Import Item Type
Note:
Complete the Import Item Type column only if you left the GUI Format Code column blank to specify import goods or foreign service. -
Purchase Usage
-
Category Code 7 - Supplier
-
Category Code 8 - Supplier
-
Category Code 9 - Supplier
-
User Code
-
User Date
-
User Amount
-
User Number
-
User Reference
-
User ID
-
Program ID
-
Work Station ID
-
Date Updated
-
Time of Day
For information about the valid values for each column, see the corresponding fields on the GUI/VAT Supplier Constants Revisions form.
3.15.1.2 Deleting Supplier Records
You can delete the information in the F75T091 table only when no transactions exist for the supplier in the GUI/VAT Transaction Header (F75T004) and GUI/VAT Transaction Detail (F75T005) tables. If no transactions exist for the supplier, the system deletes only the supplier information that exists in the F75T091 table when you delete the record using the delete function in the GUI/VAT Supplier Constants program. If you delete the supplier record from the Supplier Master table (F0401) by deleting the supplier record using the delete function in the Suppler Master Information program, the system also deletes the record from the F75T091 table.
3.15.2 Prerequisite
Set up your suppliers in the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Payable system, specifying a tax explanation code of V and the appropriate tax rate area.
3.15.3 Forms Used to Set Up Supplier Constants for Taiwan
| Form Name | FormID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| GUI/VAT Supplier Constants Revisions | W75T0091A | GUI/VAT System Setup (G75T141), GUI/VAT Supplier Constant.
Click Add on the Work with GUI/VAT Supplier Constants form. Enter a supplier record in the Supplier Master Information program, and then click OK on the Supplier Master Revision form. Select a record on the Work With Supplier Master form in the Supplier Master Information program, and then select Regional Info from the Row menu. Select Regional Info from the Form menu on the Suppler Master Revision form. |
Set up the supplier constants for Taiwan. |
| GUI/VAT Supplier Constants Import | W75T0091C | On the Work With GUI/VAT Supplier Constants form, click Import Data on the Form menu.
On the GUI/VAT Supplier Constants Import form, select Import Grid Data from the Tools menu. |
Import suppliers' constants from a spreadsheet. |
3.15.4 Setting Up Supplier Constants for Taiwan
Access the GUI/VAT Supplier Constants Revisions form.
3.15.4.1 Basic
Access the Basic tab.
Figure 3-15 GUI/VAT Supplier Constants Revisions form, Basic tab
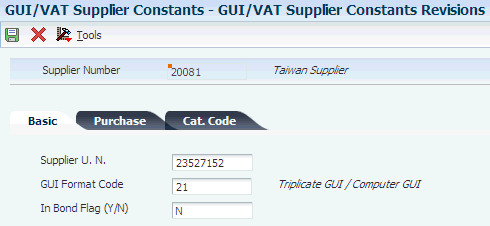
Description of ''Figure 3-15 GUI/VAT Supplier Constants Revisions form, Basic tab''
- Supplier U. N. (supplier uniform number)
-
Enter the uniform number of the vendor company.
- GUI Format Code
-
Enter a value that exists in the GUI/VAT Format Code - Purchase (75T/F2) UDC table to specify the GUI format code for the transaction. Values are:
Blank: Import Goods / Foreign Service
21: Triplicate GUI / Computer GUI
22: Other Doc With Tax Amount
23: Triplicate Purchase Return / Allowance
24: Duplicate Purchase Return / Allowance
25: Triplicate Cash Register GUI
26: Summary Triplicate/Computer GUI With Tax
27: Summary Other Doc With Tax
28: VAT Payment Document
31: Triplicate / Computer GUI
- In Bond Flag (Y/N)
-
Specify whether an item is in bond in a plant or warehouse. Values are:
Y: The item is in bond.
N: The item is not in bond.
3.15.4.2 Purchase
Access the Purchase tab.
Figure 3-16 GUI/VAT Supplier Constants Revisions form, Purchase tab
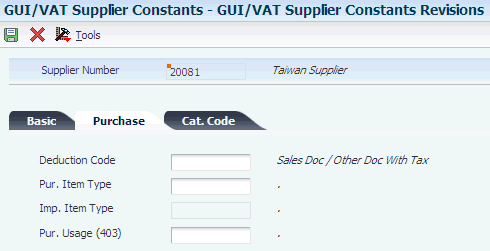
Description of ''Figure 3-16 GUI/VAT Supplier Constants Revisions form, Purchase tab''
- Deduction Code
-
Enter a value that exists in the Deduction Code (75T/DC) UDC table to specify whether a purchased item is deductible. Values are:
Blank: Sales Doc / Other Doc With Tax
1: Deductible Goods / Expense
2: Deductible Fixed Asset
- Pur. Item Type (purchase item type)
-
Enter a value that exists in the GUI/VAT Purchase Item Type (75T/PT) UDC table to specify the type of item that is purchased. Values are:
Blank: Blank
1: Goods And Expense
2: Fixed asset
- Imp. Item Type (import item type)
-
Enter a value that exists in the GUI/VAT Import Item Type (75T/II) UDC table to specify the type of import item when the transaction type is IGD (imported goods). Values are:
Blank: Blank
1: Goods And Expense
2: Other Goods
3: Tax-Exempt Goods
4: Foreign Service
- Pur. Usage (403) (purchase usage 403)
-
Enter a value that exists in the GUI/VAT Purchase Usage - 403 (75T/PU) UDC table to specify how a purchased item will be used. Values are:
Blank: Blank
PU1: Only For taxable business
PU2: Only For tax-exempt business
PU3: For taxable / tax-exempt
3.15.4.3 Cat. Code (category code)
Access the Cat. Code tab.
Figure 3-17 GUI/VAT Supplier Constants Revision form, Cat. Code tab
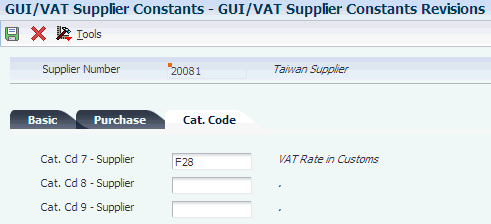
Description of ''Figure 3-17 GUI/VAT Supplier Constants Revision form, Cat. Code tab''
- Cat. Cd 7 - Supplier (category code 7 - supplier)
-
Enter a value that exists in the GUI/VAT Cat. Code 7 - Supplier (75T/C7) UDC table to associate additional information to the supplier.
Use this category code for customs authorities that you set up as a supplier.
See Setting Up Suppliers.
- Cat. Cd 8 - Supplier (category code 8 - supplier)
-
Enter a value that exists in the GUI/VAT Cat. Code 8 - Supplier (75T/C8) UDC table to associate additional information to the supplier.
- Cat. Cd 9 - Supplier (category code 9 - supplier)
-
Enter a value that exists in the GUI/VAT Cat. Code 9 - Supplier (75T/C9) UDC table to associate additional information to the supplier.
3.15.5 Importing Supplier Constants for Taiwan
Access the GUI/VAT Supplier Constants Import form.
To import supplier constants for Taiwan:
-
On the GUI/VAT Supplier Constants Import form, select Import Grid Data from the Form menu.
-
In the header area, define the import file, define the cell range, and define the import location in the grid, and then click Apply.
The system imports the data from the spreadsheet into the GUI/VAT Supplier Constants Import form.
-
Click Continue.
-
Correct any errors that occur in the imported data.
-
Click OK.
3.16 Setting Up Customer Constants for Taiwan
This section provides an overview of customer constants for Taiwan, lists prerequisites, and discusses how to:
-
Enter customer constants for Taiwan manually.
-
Import customer constants for Taiwan.
3.16.1 Understanding Customer Constants for Taiwan
You set up customer constants to supply the system with information to use when creating GUIs for that customer. Customer constants include information such as the customer's uniform number, the GUI format code to use, zero tax rate information, and tax exemption information.
You use the GUI/VAT Customer Constants program (P75T009) to add customer constant information for Taiwan. When you use the Customer Master Information program (P03013) to add a customer, and the value in the Localization County Code field in the User Profile Revisions program (P0092) is set to TW (Taiwan), the system launches the GUI/VAT Customer Constants program when you click OK on the Customer Master Revisions form. You can also access the GUI/VAT Customer Constants program by using the Regional Info option in the Customer Master Information program or by using a menu option.
You can assign category codes to customers to classify sales according to the type of customer. Assigning category codes to customers enables you to use data selection to report on transactions according to the type of customer.
The system saves the data that you enter in the GUI/VAT Customer Constants program to the GUI/VAT Customer Constants table (F75T009).
You can enter information for customers one at a time, or you can import a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet that contains information for several customers.
3.16.1.1 Valid Values for Format Codes (Release 9.1 Update)
When you set up customer constants, you assign each customer a customer type code. You can associate each customer type code with GUI format codes. Each GUI format code has additional value codes that you assign to the customer record. This table lists the format code values that you can assign for each customer type.
| Customer Type Code | GUI Format Codes |
|---|---|
| 1 (Domestic company) | On the Taxable tab, you can enter either 31 or 35 in the GUI Format Code 1 field.
On the Zero Tax Rate tab, enter 36 in the GUI Format Code 2 field if the In Bond Flag field is set to Y (yes). Otherwise, enter 31. On the Tax Exempt tab, you can enter either 31 or 35 in the GUI Format Code 3 field. |
| 2 (Domestic individual) | On the Taxable tab, you can enter either 32 or 35 in the GUI Format Code 1 field.
On the Tax Exempt tab, you can enter either 32 or 35 in the GUI Format Code 3 field. Note that the Zero Tax Rate tab is not used for domestic individuals. |
| 3 (Foreign customer) | On the Zero Tax Rate tab, enter 36 in the GUI Format Code 2 field.
On the Tax Exempt tab, you enter either 36 in the GUI Format Code 3 field. Note that the Taxable tab is not used for foreign customers. |
3.16.1.2 Considerations for Importing Customer Constants for Taiwan
To import customer constants from a spreadsheet, you must create a spreadsheet that contains these columns in the order specified:
-
Customer Number
-
Company
-
GUI Customer Type
-
Customer Uniform Number
-
Sales Item Type
-
Special Tax Item Type
-
Category Code 4 - Customer
-
Category Code 5 - Customer
-
Category Code 6 - Customer
-
GUI Format Code 1
-
GUI Format Code 2
-
Zero Tax Rate Item Type
-
Deduction Usage
-
In Bond Flag
-
GUI Format Code 3
-
User Code
-
User Date
-
User Amount
-
User Number
-
User Reference
-
User ID
-
Program ID
-
Work Station ID
-
Date Updated
-
Time of Day
-
e-GUI Mode
For information about the valid values for each column, see the corresponding fields on the GUI/VAT Customer Constants Revisions form.
The columns that should be completed depend on the value in the CT (Customer Type) column:
-
For a customer type of 1 (Domestic Customer), complete these columns only if the value in the In Bond Flag field is Y:
-
GUI Format Code 2
-
Zero Tax Rate Item Type
-
Usage Description About Deduction Copy
-
-
For a customer type of 2 (Domestic Individual Person), leave these columns blank:
-
Customer Uniform Number
-
GUI Format Code 2
-
Zero Tax Rate Item Type
-
Usage Description About Deduction Copy
-
-
For a customer type of 3 (Foreign Customer), leave these columns blank:
-
Customer Uniform Number
-
GUI Format Code 1
-
Deduction Usage
-
|
Note: Enter N in the In Bond Flag column for customer type 2 and customer type 3. |
3.16.1.3 Deleting Customer Constant Information
You can delete the information in the F75T009 table only when no transactions exist for the customer in the GUI/VAT Transaction Header (F75T004) and GUI/VAT Transaction Detail (F75T005) tables. If no transactions exist for the customer, the system deletes only the customer information that exists in the F75T009 table when you delete the record using the delete function in the GUI/VAT Customer Constants program. If you delete the customer record from the Customer Master by Line of Business table (F03012) by deleting the customer record using the delete function in the Customer Master Information program, the system also deletes the record from the F75T009 table.
3.16.2 Prerequisites
Before you complete the tasks in this section:
-
Set up the customers in the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable system, specifying a tax explanation code of V and the appropriate tax rate area.
-
Verify that the customers are not set up to use invoice consolidation.
3.16.3 Forms Used to Set Up Customer Constants for Taiwan
| Form Name | FormID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Work With GUI/VAT Customer Constants | W75T009A | GUI/VAT System Setup (G75T141), GUI/VAT Customer Constants.
Select Regional Info from the Row menu on the Work with Customer Master form. |
Review existing GUI/VAT customer constants and add new GUI/VAT customer constants. |
| GUI/VAT Customer Constants Revisions | W75T009B | Click Add on the Work With GUI/VAT Customer Constants form.
Daily Processing (G03B10), Customer Master Information. Click Add on the Work With Customer Master form, add customer information on the Customer Master Revision form, and then click OK. Select Regional Info from the Form menu on the Customer Master Revision form. |
Manually enter customer constants for Taiwan. You use this method to enter customer constants one customer at a time. |
| GUI/VAT Customer Constants Import | W75T009C | On the Work With GUI/VAT Customer Constants form, select Import Data from the Form menu. | Import GUI/VAT customer constants from a Microsoft Excel worksheet. |
3.16.4 Entering Customer Constants for Taiwan Manually
Access the GUI/VAT Customer Constants Revisions form.
- GUI Customer Type
-
Enter the code that indicates the type of customer. The code must exist in the GUI/VAT Customer Type (75T/CT) UDC table.
- Company
-
Enter the company for which you set up the customer constants.
3.16.4.1 Common
Select the Common tab.
Figure 3-18 GUI/VAT Customer Constants Revisions form, Common tab
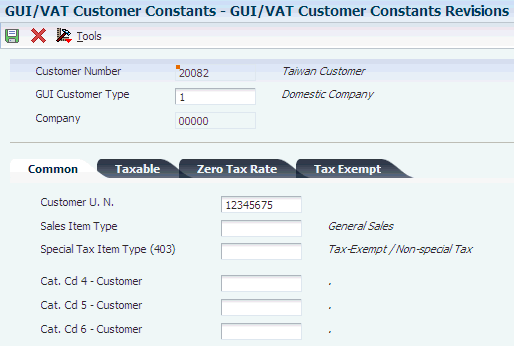
Description of ''Figure 3-18 GUI/VAT Customer Constants Revisions form, Common tab''
- Customer U. N.(customer uniform number)
-
Enter the uniform number of the customer's company.
Complete this field if you specified 1 (domestic company) in the GUI Customer Type field.
- Sales Item Type
-
Enter the code that indicates the type of item sold. The code that you enter must exist in the GUI/VAT Sales Item Type (75T/ST) UDC table.
- Special Tax Item Type (403)
-
Enter the code that identifies the type of special tax item. The code that you enter must exist in the GUI/VAT Special Tax Type (75T/SP) UDC table.
- Cat. Cd 4 - Customer (Category Code 4 - Customer), Cat. Cd 5 - Customer (Category Code 5 - Customer), and Cat. Cd 6 - Customer (Category Code 6 - Customer)
-
Enter a code that classifies the customer. Values are stored in UDC 75T/C4, 75T/C5, and 75T/C6, respectively.
3.16.4.2 Taxable tab
Select the Taxable tab.
Figure 3-19 GUI/VAT Customer Constants Revisions form, Taxable tab
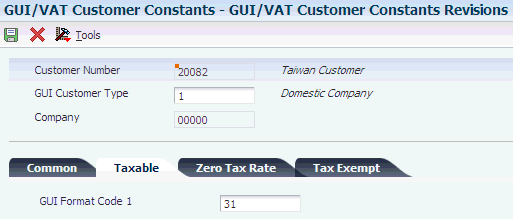
Description of ''Figure 3-19 GUI/VAT Customer Constants Revisions form, Taxable tab''
- GUI Format Code 1
-
Enter the code that specifies the GUI format code for the transaction. The code that you enter must exist in the GUI/VAT Format Code (75T/FC) UDC table.
Complete this field if you specified 1 (Domestic Company) or 2 (Domestic Individual Person) in the GUI Customer Type field.
3.16.4.3 Zero Tax Rate
Select the Zero Tax Rate tab.
Figure 3-20 GUI/VAT Customer Constants Revisions form, Zero Tax Rate tab
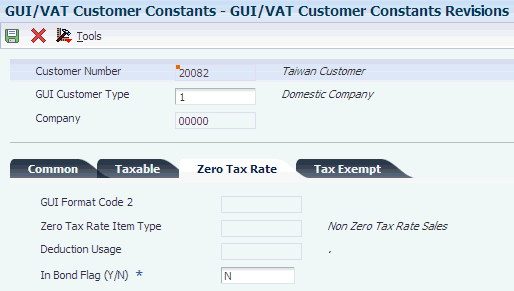
Description of ''Figure 3-20 GUI/VAT Customer Constants Revisions form, Zero Tax Rate tab''
If you specified 3 (Foreign Company) in the GUI Customer Type field, complete the GUI Format Code 2 and Zero Tax Rate Item Type fields.
- GUI Format Code 2
-
Enter the code that indicates the format code for a transaction that has a transaction type of SAL and a tax type of 2. The code that you enter must exist in the GUI/VAT Format Code - Sales (75T/F3) UDC table.
Complete this field if you specified 3 (Foreign Company) in the GUI Customer Type field.
- Zero Tax Rate Item Type
-
Enter the code that indicates whether the zero-tax-rate item has passed through customs. The code that you enter must exist in the GUI/VAT Zero Tax Rate Type (75T/ZT) UDC table.
Complete this field if you specified 3 (Foreign Company) in the GUI Customer Type field.
- Deduction Usage
-
Enter the code that indicates the usage of an item for which a zero tax rate applies. The code that you enter must exist in the Deduction Usage (75T/DD) UDC table.
- In Bond Flag (Y/N)
-
Enter the code that indicates whether an item is in bond in a plant or warehouse. Values are:
Y: The item is in bond.
N: The item is not in bond.
Complete this field if you specified 1 (Domestic Company) in the GUI Customer Type field.
3.16.4.4 Tax Exempt
Select the Tax Exempt tab.
Figure 3-21 GUI/VAT Customer Constants Revisions form, Tax Exempt tab
Description of ''Figure 3-21 GUI/VAT Customer Constants Revisions form, Tax Exempt tab''
- GUI Format Code 3
-
Enter the code that indicates the format code for a transaction with a transaction type of SAL and a tax type of 3. The code that you enter must exist in the GUI/VAT Format Code - Sales (75T/F3) UDC table.
3.16.5 Importing Customer Constants for Taiwan
Access the GUI/VAT Customer Constants Import form.
To import customer constants for Taiwan:
-
On GUI/VAT Customer Constants Import, select Import Grid Data from the Form menu.
-
In the header area, define the import file, define the cell range, and define the import location in the grid, and then click Apply.
The system imports the data from the spreadsheet into the GUI/VAT Customer Constants Import form.
-
Click Continue.
-
Correct any errors that occur in the imported data.
-
Click OK.
3.17 Setting Up Processing Options and Versions to Work with GUI/VAT Transactions
This section provides an overview of corresponding versions for GUI/VAT transactions and discusses how to set processing options for:
-
PO-GUI/VAT Transactions (P75T003).
-
GUI/VAT Transaction (P75T004).
3.17.1 Understanding Corresponding Versions for GUI/VAT Transactions
The GUI/VAT Transactions program (P75T004) has many versions. You use different versions of the GUI/VAT Transactions program (P75T004) when you enter GUI/VAT information after entering invoices, vouchers, and journal entries. The system automatically calls the correct version of the GUI/VAT Transactions (P75T004) program after you enter an invoice, voucher, or journal entry when your system is set up to do so. You can also access different versions of this program from a menu to work with existing GUI records.
Because the GUI/VAT Transactions (P75T004) program is used for several purposes, the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne software for Taiwan provides a supplemental program in which you set up default processing values. You create versions of the PO GUI/VAT Transaction program (P75T003) and set the processing options in each version for the types of transactions that you process. For example, you might create a version of the PO GUI/VAT Transaction (P75T003) program to use when the system calls the GUI/VAT Transactions (P75T004) program after you enter a voucher. If you use version XYZ of the Standard Voucher Entry (P0411) program to enter vouchers for Taiwan, you would create a version XYZ of the PO GUI/VAT Transactions (P75T003) program and set the processing options to process a specific GUI/VAT transaction type.
The standard programs for which you might set up corresponding versions of the PO GUI/VAT Transaction (P75T003) program are:
-
Standard Invoice Entry (P03B2002)
-
Speed Invoice Entry (P03B11SI)
-
Journal Entry (P0911)
-
Journal Entries with VAT (P09106)
-
Standard Voucher Entry (P0411)
-
Speed Voucher Entry (P0411SV)
If you use a standard software program to enter more than one type of GUI/VAT transaction, set up a corresponding version of the entry program and the PO GUI/VAT Transaction (P75T003) program for each GUI/VAT transaction type. For example, you might set up these versions for the Standard Voucher Entry program:
| GUI/VAT Transaction Type | Version of P0411 | Version of P75T003 |
|---|---|---|
| IMP (import) | Import | Import |
| FSV (foreign service) | FService | FService |
|
Note: Before a system user can enter GUI/VAT transactions, the user must be set up to enter the transaction type for the declaration site. You set up the user in the GUI/VAT User/Declaration Site Mapping (P75T010) program. |
You must also set up corresponding versions for the Print Invoice (R42565) and GUI/VAT Create from Multi-SO (R75T004O) programs because the Print Invoice program launches the GUI/VAT Create from Multi-SO program.
3.17.1.1 Example of Corresponding Version Setup
Suppose you need to set up your system to enter GUI/VAT information for sales transactions. Follow these steps to create and setup corresponding versions:
-
Create a version of the Standard Invoice Entry program (P03B2002) to use for transaction type SAL (sales), and set the processing options for the new version.
You can create a version by copying an existing version. You might name the new version with a name that makes it obvious that the version is used for invoices for Taiwan sales transactions. For example, you might name the version Twn-Sales.
-
Create a version of the PO GUI/VAT Transaction program (P75T003) to use for transaction type SAL.
Name the version with the same name that you used for the new version of the Standard Invoice Entry program. In this example, you would name the new version Twn-Sales.
-
Set up the processing options in the PO GUI/VAT Transaction program, setting the value of the Transaction type of GUI/VAT processing option to SAL.
-
Create a record in the GUI/VAT Document Type Format Code Setup program (P75T011) for each GUI/VAT document type/format code combination that you use for transaction type SAL, entering the version name that you assigned to the new version that you created for the Standard Invoice Entry program.
3.17.2 Setting Processing Options for PO-GUI/VAT Transaction (P75T003)
Select GUI/VAT System Setup (G75T141), PO-GUI/VAT Transaction.
3.17.2.1 GUI/VAT
- Declaration Company of GUI/VAT
-
Enter the company for which you set up the default values.
- Declaration Site of GUI/VAT
-
Enter a value that exists in the Declaration Site (75T/DS) UDC table to specify the declaration site for which you set up the default values.
- Authorized Code of GUI/VAT
-
Enter a value that exists in the Authorization Code (75T/AC) UDC table to limit the entry of transactions for the declaration site to users who are assigned the same code.
- Transaction type of GUI/VAT
-
Enter a value that exists in the GUI/VAT Transaction Type (75T/TT) UDC table to specify the type of GUI/VAT transaction for which you set the default values. Examples of values are:
IDG: Import goods
FSV: Foreign service
PUR: Purchase
SAL: Sale
3.17.2.2 Option
- Return / Allowance Amount Check Error Level
-
Specify whether the system issues an error or a warning message if the amount of a return or allowance does not match the original amount. Values are:
1: Error message. The system does not allow you to continue.
2: Warning message. The system displays a warning message but allows you to continue with the transaction.
3: No message. The system does not display a warning or error message and allows you to continue.
- Keep GUI Audit (Y/N)
-
Specify whether the system stores GUI audit information in the GUI/VAT Transaction Header table (F75T004). GUI audit information consists of the Company Key (KCO), Company Key Order Number (KCOO), Document Type (DCT), Order Type (DCTO), Document Voucher Invoice (DOC) and Document Order Invoice (DOCO) fields. The information in these fields establishes a link between the GUI record and the general ledger, accounts receivable, accounts payable, and sales order systems. Values are:
Y: Store GUI audit information. This is the default value.
Note:
If you set this processing option to Y, you must also complete the fields in the Auto Link area in the GUI/VAT Declaration Site program (P75T001).N: Do not to store GUI audit information.
3.17.3 Setting Processing Options for GUI/VAT Transaction (P75T004)
Processing options enable you to specify the default processing for programs and reports.
3.17.3.1 GUI/VAT
- Declaration Company of GUI/VAT
-
Specify the company for which you are filing the GUI/VAT declaration.
- Declaration Site of GUI/VAT
-
Enter a value that exists in the Declaration Site (75T/DS) UDC table to specify the declaration site for which you file the declaration.
- Authorized Code of GUI/VAT
-
Specify the authorization code for the GUI/VAT declaration. Values are stored in UDC (75T/AC).
- Transaction type of GUI/VAT
-
Specify the transaction type of the GUI/VAT declaration. Values are stored in UDC (75T/TT).
3.17.3.2 Option
- Return / Allowance Amount Check Error Level
-
Specify the error level for the system to use when checking the amount of a return or allowance. Values are:
1: Error message
2: Warning message
3: No error checking
- Allow To Modify GUI (Y/N)
-
Specify whether to allow modifications to the GUI. Values are:
Y: Allow.
N: Do not allow. This is the default value.
- Keep GUI Audit (Y/N)
-
Specify whether the system should store GUI audit information in the F75T004 table. GUI audit information consists of Company Key (KCO), Company Key Order Number (KCOO), Document Type (DCT), Order Type (DCTO), Document Voucher Invoice (DOC) and Document Order Invoice (DOCO) fields. The information in these fields establishes a link between GUI and the general ledger, accounts receivable, accounts payable, and sales order systems. Values are:
Y: Store. This is the default value.
N: Do not to store.
3.18 Setting Up Document Type Additional Information for e-GUI (Release 9.1 Update)
You must set up additional information for document types to comply with the e-GUI tax filing requirements for Taiwan. Use the Work With Document Type Additional Info program (P75T033) to add the following information for the document types:
-
e-GUI Transaction Type
-
Format Code
The system updates this information in the Document Type Additional Information Setup table (F75T033).
3.18.1 Forms Used to Set Up Document Type Additional Information for e-GUI
| Form Name | FormID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Work With Document Type Additional Info | W75T033A | e-GUI System Setup (G75T210), Document Type Additional Information Setup. | Access the Work With Document Type Additional Info form. |
| Document Type Additional Info Revision | W75T033B | Click Add on the Work With Document Type Additional Info form. | Set up additional information for a document type. |
3.18.2 Adding a Document Type Additional Information for e-GUI
Access the Document Type Additional Info Revision form and complete these fields.
- Document Type
-
Specify the document type for which you want to add the e-GUI transaction type and the format code.
- e-GUI Transaction Type
-
Specify the e-GUI transaction type of the sales or accounts receivable invoice. This value must exist in the e-GUI Transaction Type UDC table (75T/ET).
- Format Code
-
Specify the e-GUI format code for the transaction. The code must exist in the GUI/VAT Format Code UDC table (75T/FC).
|
Note: The fields Document Type and e-GUI Transaction Type are mandatory when you submit the invoice to the Taiwan Tax Authority for e-GUI tax filing. |
3.19 Disabling Automatic GUI/VAT Creation From Multi-SO Program(R75T004O) during Sales Order Print Process
Currently, the Print Invoices program (R42565) automatically launches the GUI/VAT Creation From Multi-SO program (R75T004O) to print sales invoice. You use the Print Invoices R42565 program (P75T2565) to prevent the R75T004O program from printing a sales invoice. This is a dummy program that you use to set this processing option for the Print Invoices program (R42565).
3.19.1 Setting Up A Processing Option for the Print Invoices R42565 program (P75T2565)
Processing options enable you to specify the default processing for programs and reports.
3.19.1.1 Default
- Disable GUI/VAT Creation From Multi-SO (R75T004O) Automatic Launch
-
Specify whether to enable or disable the GUI/VAT Creation From Multi-SO program (R75T004O). If you set this processing option to disable the R75T004O program, the system will print the sales invoice without c-GUI and related reports. Values are:
Blank: Do not disable
Y: Disable