2 Introduction to Oracle Access Manager Integrations
This chapter introduces the integrations between Oracle Access Manager and other components of the Oracle Identity Management suite, including interaction flows among the components, high level requirements for each integration, and related information:
Note:
Integration procedures are described elsewhere in this document. See Section 2.1, "Summary of Integrations"-
Enabling Identity Administration with Oracle Identity Manager
-
Integrating with Oracle Adaptive Access Manager for Native Authentication
-
Integrating Oracle Access Manager with Oracle Identity Federation
-
Integrating Oracle Identity Manager, Oracle Access Manager, and Oracle Adaptive Access Manager
2.1 Summary of Integrations
Table 2-1 lists the identity management integrations described in this document.
Table 2-1 Summary of Oracle Access Manager Integrations
| Integration | Components | Additional Information |
|---|---|---|
|
Oracle Identity Manager Oracle Access Manager |
Section 2.2, "Enabling Identity Administration with Oracle Identity Manager" |
|
|
Oracle Identity Manager Oracle Access Manager |
Section 2.3, "Enabling Single Sign-On for Oracle Identity Manager" |
|
|
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager Oracle Access Manager |
Chapter 5, "Integrating Oracle Access Manager and Oracle Adaptive Access Manager" |
|
|
Oracle Identity Navigator Oracle Access Manager |
||
|
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager Oracle Access Manager |
Chapter 5, "Integrating Oracle Access Manager and Oracle Adaptive Access Manager" |
|
|
Oracle Access Manager Oracle Identity Federation |
||
|
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager Oracle Access Manager Oracle Identity Manager |
2.2 Enabling Identity Administration with Oracle Identity Manager
In this release, Oracle Identity Manager provides identity administration services for Oracle Fusion Middleware.
Integration enables you to manage identities with Oracle Identity Manager and control access to resources with Oracle Access Manager. You can then implement single sign-on for other identity management components and perform additional integrations with suite components, as explained later in this chapter.
The prerequisites for integrating with Oracle Identity Manager are:
-
installing the necessary components/suites, which include: RCU, Oracle WebLogic Server, the IAM Suite, and SOA Suite
-
creating schemas for Oracle Identity Manager and SOA Suite
-
installing and configuring Oracle Internet Directory and Oracle Virtual Directory
-
uploading the password schemas to Oracle Internet Directory
After meeting the prerequisites, the basic integration steps are as follows:
-
Create the Oracle WebLogic Server domains for Oracle Access Manager and Oracle Identity Manager/Oracle SOA Suite respectively.
-
Install Oracle HTTP Server 11g.
-
Configure Oracle Access Manager 11g to point to Oracle Internet Directory rather than to the default embedded LDAP.
For integration details, see:
2.3 Enabling Single Sign-On for Oracle Identity Manager
You can configure Oracle Access Manager to protect Oracle Identity Manager URLs.
2.3.1 Prerequisites
The prerequisites are as follows:
-
Ensure that the components required for the integration have been installed:
-
Oracle WebLogic Server
-
Oracle Identity Navigator
-
Oracle Access Manager
-
Oracle Identity Manager
Note:
Oracle Access Manager may be installed before Oracle Identity Manager and other IdM components, or it may be installed at the same time as other components. -
-
Ensure that the following servers are running:
-
Oracle WebLogic Server
-
Oracle Access Manager Administration Server
-
Oracle Access Manager and Oracle Identity Manager managed servers
-
2.3.2 Configuration
For implementation details, see Configuring Single Sign-on for Administration Consoles in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Enterprise Deployment Guide for Oracle Identity Management.
2.4 Enabling Single Sign-On for Oracle Adaptive Access Manager
You can configure Oracle Access Manager to SSO-enable the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager administration console URL (/oaam_admin). In this setup, the OHS proxy for the URL is configured to use 11g WebGate.
With this configuration, users enter their credentials on the Oracle Access Manager login page, and are automatically logged into Oracle Adaptive Access Manager.
For configuration details, see Section 5.1, "Protecting the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager Console".
2.5 Integrating with Oracle Adaptive Access Manager for Native Authentication
In the native integration, Oracle Access Manager leverages Oracle Adaptive Access Manager to provide pre-and post-authentication services for Oracle Access Manager logins.
For details, see Section 5.3, "Native Integration".
2.6 Enabling Single Sign-On for Oracle Identity Navigator
Oracle Identity Navigator provides an administrative portal to Oracle Identity Management components.
You can protect the Oracle Identity Navigator URL by SSO-enabling the Oracle Identity Navigator Administration Console using the WNA authentication scheme.
For integration details, see Chapter 3, "Integrating with Oracle Identity Navigator".
2.7 Integrating Oracle Access Manager with Oracle Identity Federation
You can configure Oracle Access Manager as an authentication engine for Oracle Identity Federation.
For integration details, see Chapter 4, "Integrating Oracle Identity Federation".
2.8 Integrating Oracle Identity Manager, Oracle Access Manager, and Oracle Adaptive Access Manager
This section describes various identity and password administration scenarios supported through IdM integration, and the processing flow for each integration.
For the integration procedure, see Chapter 6, "Integrating Oracle Access Manager, Oracle Adaptive Access Manager, and Oracle Identity Manager"
2.8.1 Introduction and Benefits
This section provides an overview of integration of Oracle Access Manager with Oracle Identity Manager and Oracle Adaptive Access Manager.
2.8.1.1 How Oracle Access Manager Leverages Oracle Identity Manager and Oracle Adaptive Access Manager
In 11g Release 1 (11.1.1), Oracle Access Manager does not provide its own identity service; instead, Oracle Access Manager:
-
consumes identity services provided by Oracle Identity Manager, LDAP directories, and other sources
-
integrates with Oracle Identity Manager and Oracle Adaptive Access Manager to deliver a range of secure password collection functionality to Oracle Access Manager protected applications.
2.8.1.2 Benefits of the Integration
In the three-way Oracle Access Manager-Oracle Identity Manager-Oracle Adaptive Access Manager deployment, these Oracle Adaptive Access Manager and Oracle Identity Manager secure password collection features are added to Oracle Access Manager protected applications:
2.8.1.3 Dependency of Components in the Integration
The following components can be integrated separately:
-
Oracle Access Manager and Oracle Adaptive Access Manager
-
Oracle Identity Manager and Oracle Adaptive Access Manager
However, note the following dependency:
-
When integrating Oracle Access Manager and Oracle Adaptive Access Manager, it is not necessary to involve Oracle Identity Manager.
-
When integrating Oracle Adaptive Access Manager and Oracle Identity Manager, it is also necessary to integrate with Oracle Access Manager.
2.8.2 Deployment Options for Strong Authentication
The combination of Oracle Access Manager and Oracle Adaptive Access Manager enables fine control over the authentication process and provides full capabilities of pre- and post-authentication checking against Oracle Adaptive Access Manager policies.
In the context of this integration, Oracle Access Manager acts as the authenticating and authorizing module, while Oracle Adaptive Access Manager provides the rich strong authenticators and performs the risk and fraud analysis.
2.8.2.1 About Native and Advanced Integration
There are two ways that Oracle Access Manager can leverage the strong authentication capabilities of Oracle Adaptive Access Manager:
-
Native Integration with Oracle Adaptive Access Manager
Oracle Access Manager users wishing to add basic login security, including Knowledge Based Authentication (KBA), may use the native integration option. This option does not require you to deploy a separate Oracle Adaptive Access Manager server (the functionality is accessed through native Oracle Adaptive Access Manager calls), so the footprint is reduced.
The native integration does not provide access to more advanced features such as One-Time Password (OTP) through SMS, email, voice, or IM. The native integration is not customizable beyond basic screen branding.
-
Advanced Integration with Oracle Adaptive Access Manager
This option provides advanced features and customization beyond that available with native integration. Leveraging the Java Napp library, the integration of Oracle Access Manager and Oracle Adaptive Access Manager requires a full Oracle Adaptive Access Manager deployment.
For implementation details, see Chapter 5, "Integrating Oracle Access Manager and Oracle Adaptive Access Manager".
2.8.2.2 Component Interactions
The flow of interactions between the components is as follows:
-
A user tries to access a resource protected by Oracle Access Manager.
-
The Oracle Access Manager WebGate intercepts the (unauthenticated) request and redirects the user to the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager server.
-
The Oracle Adaptive Access Manager Server presents the user with the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager username page.
-
The user submits his username on the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager username page.
-
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager fingerprints the user device and runs pre-authentication rules to determine if the user should be allowed to proceed to the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager password page.
Device fingerprinting is a mechanism to recognize the devices a user logs in with, whether it is a desktop computer, laptop computer, PDA, cell phone, kiosk, or other Web-enabled device.
-
If the user is allowed to proceed, the virtual authentication device rules are run during the Authentication Pad checkpoint. These rules determine which virtual authenticator to display in the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager password page.
If the user has registered with Oracle Adaptive Access Manager, the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager Server displays the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager password page with either the personalized TextPad or KeyPad.
If the user has not registered, Oracle Adaptive Access Manager displays the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager password page with the Generic TextPad.
-
The user submits his password on the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager password page.
-
The credentials collected from Oracle Adaptive Access Manager is verified against the identity store using the Oracle Access Manager NAP API. After validation on the Oracle Access Manager side, Oracle Adaptive Access Manager runs the post-authentication rules.
-
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager interacts with the user to establish identity to perform the desired action. Oracle Adaptive Access Manager determines the user's risk score and executes any actions (for example, KBA or OTP) or alerts that are specified in the policy.
-
If the user is not registered, he may be asked to go through registration, for example, KBA or OTP.
Registration is required depending on security requirements, which specify whether the registration is mandatory or optional.
-
If authentication is successful and the user has the appropriate profile registered, Oracle Adaptive Access Manager sets the Oracle Access Manager cookie and redirects the user to the redirect URL.
2.8.3 Deployment Options for Password Management
You can implement password management features for Oracle Access Manager-protected applications by integrating Oracle Access Manager, Oracle Identity Manager, and Oracle Adaptive Access Manager.
This section explains the deployment options. The next section, Section 2.8.4, "Password Management Scenarios", describes the scenarios that are supported by each deployment, and the flow that achieves each scenario.
In the context of password management, Oracle Access Manager works in two different deployment modes:
-
Oracle Access Manager and Oracle Identity Manager integrated for authentication and password management.
For details of the processing flow, see Oracle Access Manager Integrated with Oracle Identity Manager
For implementation details, see Integration Between OIM and OAM in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation Guide for Oracle Identity Management.
-
Oracle Access Manager, Oracle Identity Manager, and Oracle Adaptive Access Manager integrated for authentication, password management, fraud detection and additional capabilities.
For details of the processing flow, see Oracle Access Manager, Oracle Adaptive Access Manager, and Oracle Identity Manager Integrated
For implementation details, see Chapter 6, "Integrating Oracle Access Manager, Oracle Adaptive Access Manager, and Oracle Identity Manager".
2.8.3.1 Oracle Access Manager Integrated with Oracle Identity Manager
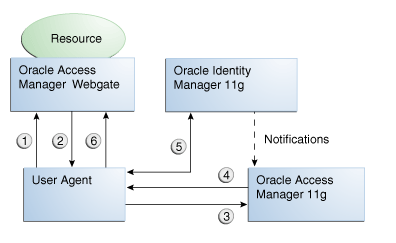
Figure 2-1 shows how password management is achieved when Oracle Access Manager and Oracle Identity Manager are integrated.
The flow of interactions between the components is as follows:
-
A user tries to access a resource protected by Oracle Access Manager.
-
The Oracle Access Manager WebGate intercepts the (unauthenticated) request.
-
WebGate redirects the user to the Oracle Access Manager login service, which performs validation checks.
-
If Oracle Access Manager finds any password management trigger conditions, such as password expiry, it redirects users to Oracle Identity Manager.
-
Oracle Identity Manager interacts with the user to establish the user's identity and carry out the appropriate action, such as resetting the password.
-
Oracle Access Manager logs the user in by means of auto-login, and redirects the user to the OAM-protected resource which the user was trying to access in Step 1.
2.8.3.2 Oracle Access Manager, Oracle Adaptive Access Manager, and Oracle Identity Manager Integrated
The integration between Oracle Adaptive Access Manager and Oracle Identity Manager allows the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager challenge questions to be used, at the same time using Oracle Identity Manager for password validation, storage and propagation.This integration leverages:
-
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager for fraud prevention
-
Oracle Access Manager password propagation to targets.
Figure 2-2 shows how password management is achieved when Oracle Access Manager, Oracle Adaptive Access Manager, and Oracle Identity Manager are integrated.
Figure 2-2 Integrating Oracle Access Manager, Oracle Adaptive Access Manager, and Oracle Identity Manager for Password Management
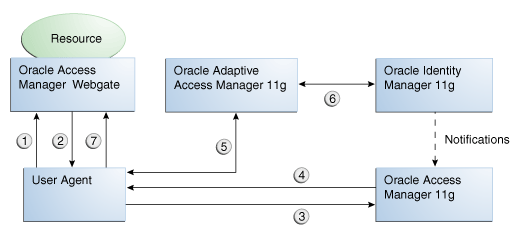
The flow of interactions between the components is as follows:
-
A user tries to access a resource protected by Oracle Access Manager.
-
The Oracle Access Manager WebGate intercepts the (unauthenticated) request and redirects the user login service, which presents the user with the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager username page.
-
The user is redirected to the Oracle Access Manager server. After validation,
-
The server checks if any password management triggering conditions are in effect. If a trigger condition (say, an expired password) is found, the Oracle Access Manager login service redirects the user to the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager server.
-
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager interacts with the user to establish identity.
Interaction with Oracle Adaptive Access Manager proceeds as follows:
-
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager fingerprints the user device (a desktop computer, laptop computer, PDA, cell phone, kiosk, or other web enabled device) and runs pre-authentication rules to determine if the user should be allowed to proceed to the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager password page.
-
If the user is allowed to proceed, the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager Server displays the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager password page with the strong authenticator specified by the virtual authentication device rules.
-
If the user forgot his password, he can use the "Forgot your password" link and go through the "Forgot Password" flow.
-
The user submits his password on the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager password page.
-
The credentials collected from Oracle Adaptive Access Manager are verified against the identity store by Oracle Access Manager. After validation on the Oracle Access Manager side, Oracle Adaptive Access Manager will run the post-authentication rules.
-
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager interacts with the user to establish identity in order to perform the desired action. Oracle Adaptive Access Manager determines the user's risk score and executes any actions (for example, KBA or OTP) or alerts that are specified in the policy.
-
An unregistered user is asked to go through registration (Challenge Registration Flow), for example, KBA or OTP profile registration.
-
-
During credential processing, Oracle Adaptive Access Manager retrieves the password syntax and lifecycle policies from Oracle Identity Manager. Oracle Adaptive Access Manager enforces these policies while processing the trigger action.
After the operation is complete, Oracle Adaptive Access Manager notifies Oracle Access Manager over a back channel.
-
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager auto-logs the user into Oracle Access Manager and redirects the user to the Oracle Access Manager-protected resource in step 1, using an authenticated request.
2.8.4 Password Management Scenarios
Common management scenarios supported by these deployment modes include:
2.8.4.1 Self-Registration
In this scenario, the user does not have an account but tries to access an Oracle Access Manager -protected resource. An Oracle Access Manager 11g Webgate intercepts the request, detects that the user is not authenticated, and redirects the user to the Oracle Access Manager Credential Collector (or 10g authenticating webgate), which shows the Oracle Access Manager Login page containing a "Register New Account" Link.
On selecting this link, the user is securely redirected to Oracle Identity Manager Self Registration URL. Oracle Identity Manager interacts with the user to provision his account.
The Welcome Page is an unprotected page from which the self-registration/account creation can be initiated. This page contains two links, in addition to any introductory text or branding information. The links are:
-
Register New Account - This is an unprotected URL to the corresponding application's registration wizard
-
Login - This is a protected URL which serves as the landing page to which the user is directed after successfully completing the login
Note:
Any application protected by a single sign-on system with the self-registration requirement is expected to support a landing page. The options are:-
Self-registration using the link on the OAM login page
This is the most common option and is covered here.
-
Self-registration using anonymous pages in other applications
If the application dictates that the user be automatically logged in at the end of the registration process, it can implement this by using the Oracle Platform Security Services APIs.
See Also:
Oracle Fusion Middleware Security Overview for more information about Oracle Platform Security Services.The account creation flow is as follows:
-
The user (using his browser) accesses the application's welcome page, which contains a Register New Account link.
-
The user clicks the Register New Account link, which takes the user to a custom self-registration page provided by the application.
-
The user interacts with the application to self-register.
-
On completion, the application performs an auto-login for the user.
The protected application is expected to send an SPML request to Oracle Identity Manager to create the user. After this, the application could choose to do one of the following:
-
The application may choose not to auto-login the user. The application redirects the user to the protected landing page URL. Oracle Access Manager then shows the login page and takes the user through the login flow.
-
If there is no approval associated with the request, the application can make use of the OPSS APIs to conduct an auto-login to the specific Landing Page URL and respond with a redirect request with that URL (along with the SSO cookie). This takes the user directly to the landing page without bringing up the login page.
-
Auto-login cannot be done if an approval is needed (the application determines which profile to use at the time of SPML request). The application needs to respond with an appropriate page indicating that the request has been submitted.
2.8.4.2 Password Change
The Change Password flow enables users to change their password.
Password Change Flow with Oracle Access Manager and Oracle Identity Manager
In this situation, the user successfully logs into Oracle Access Manager but is required to immediately change the password. The user is not authorized to access protected resources until the password is changed and challenges have been set up.
On successful login, Oracle Access Manager detects if the triggering condition is in effect and redirects the user to the Oracle Identity Manager "Change Password" URL. Oracle Identity Manager facilitates the user password change or challenge set-up and resets the triggering condition.
On completion, Oracle Identity Manager redirects the user to the protected resource.
This situation is triggered in the following cases:
-
The "Change password upon login" flag is on. This occurs:
-
when a new user is created
-
when the administrator resets a user's password
-
-
Password has expired
This flow describes the situation where a user logs in to an Oracle Access Manager-protected application for the first time, and is required to change password before proceeding.
The following describes the Change Password flow:
-
Using a browser, the user tries to access an application URL that is protected by Oracle Access Manager.
-
Oracle Access Manager Webgate (SSO Agent) intercepts the request and redirects the user to the Oracle Access Manager Login Page.
-
The user submits credentials, which are validated by Oracle Access Manager.
-
Oracle Access Manager next determines if any of the First Login trigger conditions are valid. If so, Oracle Access Manager redirects the user to the Oracle Identity Manager Change Password URL.
-
Oracle Access Manager Webgate (SSO Agent) intercepts the request, determines that Oracle Identity Manager is protected by the Anonymous Authentication Policy, and allows the user request to proceed.
-
Oracle Identity Manager interacts with the user to enable the user to change his password. On completion, Oracle Identity Manager updates the attributes that triggered the First Login flow. Oracle Identity Manager then performs a user auto-login.
-
Oracle Identity Manager notifies Oracle Access Manager of the successful first login.
-
Oracle Identity Manager redirects the user to the application URL the user tried to access in step 1.
Password Change Flow - Oracle Access Manager, Oracle Adaptive Access Manager, and Oracle Identity Manager Integrated
In this scenario, the user is at the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager password page and clicks the "Change your password" link.
-
Using a browser, the user tries to access an application URL that is protected by Oracle Access Manager.
-
Oracle Access Manager WebGate intercepts the (unauthenticated) request.
-
Oracle Access Manager WebGate redirects the user to the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager Server and passes a redirect URL.
-
The Oracle Adaptive Access Manager Server presents the user with the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager username page.
-
The user submits his username on the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager username page.
-
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager fingerprints the user device (a desktop computer, laptop computer, PDA, cell phone, kiosk, or other web enabled device) and runs pre-authentication rules to determine if the user should be allowed to proceed to the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager password page.
-
If the user is allowed to proceed, the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager Server displays the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager password page with the strong authenticator specified by the virtual authentication device rules.
-
The user submits his password on the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager password page.
-
During authentication, Oracle Adaptive Access Manager calls the Oracle Access Manager Java APIs to validate the credentials.
-
If authentication is successful and the user has registered questions, but he wants to reset his password, the user clicks the Change Password link.
-
The user is redirected to the Change Password URL of Oracle Adaptive Access Manager, which allows the users to change his password.
-
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager collects the current password and the new password, and confirms the password from the user using its authenticators.
-
Password policy information, dynamically obtained from Oracle Identity Manager, is displayed to guide the user to select the appropriate password.
-
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager makes Oracle Identity Manager calls to update the password in the repository.
-
If the update is successful, Oracle Adaptive Access Manager redirects the user to the resource protected by Oracle Access Manager.
2.8.4.3 Forgot Password
The Forgot Password flow allows the users to reset their password after successfully answering all challenge questions.
Forgot Password Flow for Oracle Access Manager/Oracle Identity Manager Integration
In this scenario, the user is at the Oracle Access Manager Login page and clicks the "Forgot Password" link. Oracle Access Manager redirects the user to the Oracle Identity Manager "Forgot Password" URL, and passes the destination URL to which Oracle Identity Manager must redirect upon a successful password change as a query parameter (backURL).
Oracle Identity Manager asks the user the Challenge questions; upon providing the correct responses, the user is allowed to specify a new password.
On completion, Oracle Identity Manager redirects the user to the protected resource.
The Forgot Password flow is as follows:
-
Using a browser, the user tries to access an application URL that is protected by Oracle Access Manager.
-
The Oracle Access Manager Webgate (SSO Agent) intercepts the request and redirects the user to the Oracle Access Manager Login Page.
-
The user clicks on the Forgot Password link on the Oracle Access Manager Login page, which sends the user to the Oracle Identity Manager Forgot Password URL.
-
Oracle Identity Manager interacts with the user to enable the user to reset the password. On completion, Oracle Identity Manager performs a user auto-login.
-
Oracle Identity Manager redirects the user to the application URL to which access was attempted in step 1.
Forgot Password Flow for Oracle Access Manager/Oracle Identity Manager/Oracle Adaptive Access Manager Integration
With Oracle Adaptive Access Manager and Oracle Identity Manager integration, the forgot password feature is made available as a link from the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager password page. The flow starts when the user is at the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager password page and clicks the "Forgot your password" link.
The flow is as follows:
-
Using a browser, the user tries to access an application URL that is protected by Oracle Access Manager.
-
Oracle Access Manager WebGate intercepts the (unauthenticated) request.
-
Oracle Access Manager WebGate redirects the user to the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager Server.
-
The Oracle Adaptive Access Manager Server presents the user with the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager username page.
-
The user submits his username on the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager username page.
-
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager fingerprints the user device (a desktop computer, laptop computer, PDA, cell phone, kiosk, or other web enabled device) and runs pre-authentication rules to determine if the user should be allowed to proceed to the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager password page.
-
If the user is allowed to proceed, the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager Server displays the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager password page with the strong authenticator specified by the virtual authentication device rules.
-
The user clicks the "Forgot your password" link on the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager password page.
-
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager presents the user with a pre-registered set of challenge questions.
-
The user provides the answers to the challenge questions.
-
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager uses fuzzy logic to validate the answers to challenge questions.
-
If the user provided correct responses, he is redirected to the Password Reset page.
-
Password policy text from Oracle Identity Manager is retrieved by Oracle Adaptive Access Manager by making calls to Oracle Identity Manager, and then shown in the Reset Password page.
-
The user enters the new password.
-
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager calls Oracle Identity Manager to update the repository with the new password.
-
If the update is successful Oracle Adaptive Access Manager redirects the user to the resource protected by Oracle Access Manager.
2.8.4.4 Account Lock and Unlock
Oracle Access Manager keeps track of the login attempts and locks the account when the count exceeds the established limit.
When an account is locked, Oracle Access Manager displays the Help Desk contact information.
When contacted by the end user, the Help Desk unlocks the account using the Oracle Identity Manager administrative console. Oracle Identity Manager notifies Oracle Access Manager about the changes.
When the number of unsuccessful user login attempts exceeds the value specified in the password policy, the user account is locked. Any login attempt after the user account has been locked displays a page that provides information about the account unlocking process, which will need to be customized to reflect the process (Help Desk information or similar) that is followed by your organization.
Note:
Oracle Identity Manager does not support automatic locking of a user account after a specific period has elapsed.The following describes the account locking/unlocking flow:
-
Using a browser, a user tries to access an application URL that is protected by Oracle Access Manager.
-
Oracle Access Manager Webgate (SSO Agent) intercepts the request and redirects the user to the Oracle Access Manager login page.
-
The user submits credentials that fail Oracle Access Manager validation. Oracle Access Manager renders the login page and asks the user to resubmit credentials.
-
The user's unsuccessful login attempts exceed the limit specified by the policy. Oracle Access Manager locks the user account and redirects the user to the Oracle Access Manager Account Lockout URL, which displays Help Desk contact information.
-
The user contacts the Help Desk over the telephone and asks an administrator to unlock the account.
-
Oracle Identity Manager notifies Oracle Access Manager of the account unlock event.
-
The user attempts to access an application URL and this event triggers the normal Oracle Access Manager single sign-on flow.
2.8.4.5 Challenge Setup
The Challenge Setup enables users to register challenge questions and answers.
Challenge Setup Flow for Oracle Access Manager-Oracle Identity Manager Integration
Oracle Access Manager detects and redirects on password trigger conditions:
-
Password Policy is updated to increased the required number of challenges
-
Password Policy is updated to require challenges
When such redirection happens, Oracle Identity Manager checks if the challenge questions are set. If not, it asks the user to set up challenge questions in addition to resetting the password.
The following describes the flow:
Note:
The flow assumes First Login is not required.-
Using a browser, the user tries to access an application URL that is protected by Oracle Access Manager.
-
Oracle Access Manager Webgate (SSO agent) intercepts the request and redirects the user to the Oracle Access Manager Login Page.
-
The user submits credentials, which are validated by Oracle Access Manager. If a password triggering condition is detected, Oracle Access Manager redirects the user to the Oracle Identity Manager Change Password URL.
-
The Oracle Access Manager Webgate (SSO agent) intercepts the request, determines that Oracle Identity Manager is protected by the anonymous authentication policy, and allows the user request to proceed.
-
Oracle Identity Manager interacts with the user to set up the challenges. On completion, Oracle Identity Manager updates the attributes that triggered the Set the Challenges flow.
-
Oracle Identity Manager redirects the user to the application URL that the user attempted to access in step 1.
Challenge Setup Flow for Oracle Access Manager-Oracle Identity Manager-Oracle Adaptive Access Manager Integration
In this scenario, the user is successfully authenticated but is required to register challenge questions. The user is not authorized to access protected resources until the challenges questions have been registered.
Note:
When adding Oracle Adaptive Access Manager to existing Oracle Identity Manager deployments, you will need to forego all the existing questions and answers that are registered in Oracle Identity Manager. Instead, users are asked to register the challenge questions again in Oracle Adaptive Access Manager on the next login.-
Using a browser, the user tries to access an application URL that is protected by Oracle Access Manager.
-
Oracle Access Manager WebGate intercepts the (unauthenticated) request.
-
Oracle Access Manager WebGate redirects the user to the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager Server and passes a redirect URL.
-
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager presents the user with the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager username page.
-
The user submits his username on the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager username page.
-
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager fingerprints the user device (a desktop computer, laptop computer, PDA, cell phone, kiosk, or other web enabled device) and runs pre-authentication rules to determine if the user should be allowed to proceed to the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager password page.
-
If the user is allowed to proceed, the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager Server displays the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager password page with the strong authenticator specified by the virtual authentication device rules.
-
The user submits his password on the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager password page.
-
During authentication, Oracle Adaptive Access Manager calls Oracle Access Manager to validate the credentials.
-
After authentication, Oracle Adaptive Access Manager checks if the user has registered challenge questions.
-
If the user has not registered for challenges, Oracle Adaptive Access Manager interacts with the user to set up the challenges (select challenge questions and register answers and/or set up an OTP profile).
-
If the registration is successful Oracle Adaptive Access Manager redirects the user to the Oracle Access Manager protected resource.
2.8.4.6 Challenge Reset
Challenge Reset enables users to reset their challenge registration. This feature is available when Oracle Access Manager is integrated with Oracle Adaptive Access Manager.
The flow is as follows:
-
Using a browser, the user tries to access an application URL that is protected by Oracle Access Manager.
-
Oracle Access Manager WebGate intercepts the (unauthenticated) request.
-
Oracle Access Manager WebGate redirects the user to the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager Server and passes a redirect URL.
-
The Oracle Adaptive Access Manager Server presents the user with the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager username page.
-
The user submits his username on the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager username page.
-
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager fingerprints the user device (a desktop computer, laptop computer, PDA, cell phone, kiosk, or other web enabled device) and runs pre-authentication rules to determine if the user should be allowed to proceed to the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager password page.
-
If the user is allowed to proceed, the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager Server displays the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager password page with the strong authenticator specified by the virtual authentication device rules.
-
The user submits his password on the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager password page.
-
During authentication, Oracle Adaptive Access Manager calls Oracle Access Manager to validate the credentials.
-
If authentication is successful and the user has questions registered, but he wants to reset his challenge questions, the user clicks the Reset Challenge link.
-
User is redirected to Oracle Adaptive Access Manager where he can reset challenge questions.
-
After resetting the challenge registration, Oracle Adaptive Access Manager prompts the user to register for challenge.
-
If the user did not complete the registration, they are prompted for registration on the next login.