1 Introducing Oracle Infrastructure Web Services
This chapter introduces Oracle Infrastructure Web services and describes the standards supported.
Overview of Oracle Infrastructure Web Services
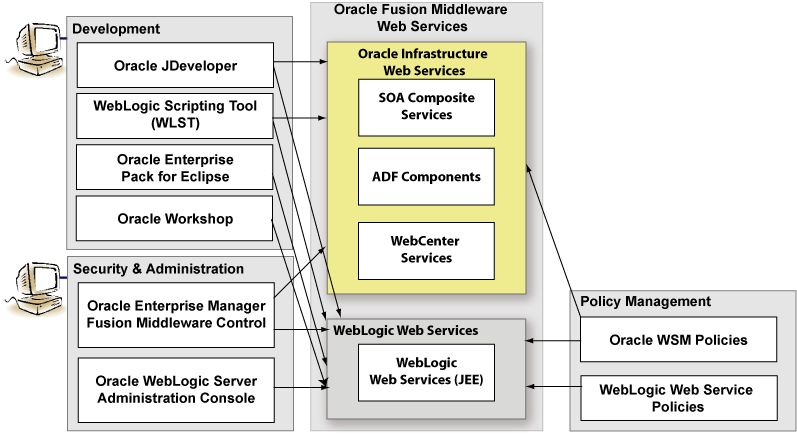
In Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g, there are two categories of Web services to support the development, security, and administration of the following types of Web services:
-
Oracle Infrastructure Web services—SOA, ADF, and Web Center services
-
WebLogic Web services (Java EE Web services)
The following figure illustrates the two Web services categories. Oracle Infrastructure Web services are highlighted (in yellow) in the figure.
Note:
For more information about the full set of components shown in the figure, including the development; security and administration; and policy management tools, see Introducing Web Services.This chapter describes concepts for developing Oracle Infrastructure Web services. For more information about WebLogic Web services, see Introducing WebLogic Web Services for Oracle WebLogic Server.
Types of Oracle Infrastructure Web Services and Clients
Table 1-1 summarizes the types of Oracle Infrastructure Web services supported in Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g.
Table 1-1 Oracle Infrastructure Web Services
| Web Service | Description |
|---|---|
|
SOA service components |
SOA composite applications include SOA service components. SOA service components are the basic building blocks of SOA applications, implementing a part of the overall business logic functionality. The following SOA service components can be managed using Oracle WSM:
For more information about developing SOA service components, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Developer's Guide for Oracle SOA Suite. You can deploy SOA service components to the Oracle Fusion Middleware environment. |
|
SOA service binding components |
SOA Service binding components provide the outside world with an entry point to the SOA composite application. The WSDL file of the service advertises its capabilities to external applications. These capabilities are used for contacting the SOA composite application components. For more information, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Developer's Guide for Oracle SOA Suite. |
|
ADF Business Components |
ADF Business Components simplify the development, delivery, and customization of business applications for the Java EE platform by providing a library of reusable components and supporting design time facilities in Oracle JDeveloper. Using ADF Business Components, developers are not required to write the application infrastructure code required by the typical Java EE application to perform the following tasks:
Additionally, Oracle JDeveloper facilities expose ADF Business Component application modules that encapsulate built-in data manipulation operations and custom methods as Web services so that a service-enabled application module can be consumed across modules of the deploy Fusion Web application. For more information, see "Integrating Service-Enabled Application Modules" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework. |
|
WebCenter services |
WebCenter services expose Web 2.0 technologies for social networking and personal productivity, such as Wiki, RSS, and blogs. WebCenter provides a set of features and services (for example, portlets, customization, and content integration) that you can selectively add to your application. For more information about developing WebCenter services, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Developer's Guide for Oracle WebCenter. |
Table 1-2 summarizes the types of Oracle Infrastructure Web service clients supported in Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g.
Table 1-2 Oracle Infrastructure Web Service Clients
| Web Service Client | Description |
|---|---|
|
SOA reference binding components |
SOA reference binding components connect the SOA composite application to external partners. For more information about developing SOA reference binding components, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Developer's Guide for Oracle SOA Suite. |
|
ADF Web applications |
ADF Web applications can invoke a service, such as a WebLogic Web service, a SOA composite application, or a service-enabled ADF application module. For more information, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Developer's Guide for Oracle SOA Suite. In addition, ADF Web applications can work with Web services in the user interface using a Web service data control. For more information about generating service-enabled application modules, calling a Web service from an ADF application module, or creating Web service data controls, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework. |
|
WebCenter portlets |
WebCenter portlets enable you to surface WebCenter services. For more information about developing WebCenter portlets, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Developer's Guide for Oracle WebCenter. |
Supported Standards
The following table summarizes the Oracle Infrastructure Web service specifications that are part of the Oracle implementation, organized by high-level feature.
Oracle considers interoperability of Web services platforms to be more important than providing support for all possible edge cases of the Web services specifications. Oracle complies with the following specifications from the Web Services Interoperability Organization and considers them to be the baseline for Web services interoperability:
-
Basic Profile 1.1 and 1.0:
http://www.ws-i.org/Profiles/BasicProfile-1.1-2004-08-24.html -
Basic Security Profile 1.0:
http://www.ws-i.org/Profiles/BasicSecurityProfile-1.0.html -
WS-I Attachments Profile 1.0:
http://www.ws-i.org/Profiles/AttachmentsProfile-1.0.html
Note:
For more information about Oracle Infrastructure Web service security standards, see "Web Services Security Standards" in Security and Administrator's Guide for Web Services.Table 1-3 Specifications Supported by Oracle Infrastructure Web Services
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
|
Programming model (based on metadata annotations) and runtime architecture |
Web Services Metadata Exchange (WS-MetadataExchange) 1.1—Part of the WS-Federation roadmap which allows retrieval of metadata about a Web service endpoint. For more information, see Web Services Metadata Exchange (WS-MetadataExchange) specification at |
|
Web service description |
|
|
Data exchange between Web service and requesting client |
|
|
Security |
|
|
Reliable communication |
|
|
Atomic transactions |
Web Services Atomic Transaction—Defines the Atomic Transaction coordination type that is to be used with the extensible coordination framework described in the Web Services Coordination specification. The WS-AtomicTransaction and WS-Coordination specifications define an extensible framework for coordinating distributed activities among a set of participants. For more information, see: |
|
Advertisement (registration and discovery) |
|
Related Documentation
The following table summarizes the documentation that is related to Oracle Infrastructure Web services development, security, and administration.
Table 1-4 Related Documentation
| Document | Description |
|---|---|
|
Oracle Fusion Middleware Introducing Web Services |
This document. Provides an introduction to Web services for Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g. |
|
Describes how to secure and administer Web services. |
|
|
Describes how to build custom assertions for Oracle Web Services Manager (Oracle WSM). |
|
|
Oracle Fusion Middleware Interoperability Guide for Oracle Web Services Manager |
Describes how to implement the most common Oracle WSM interoperability scenarios. |
|
Oracle Fusion Middleware Developer's Guide for Oracle SOA Suite |
Describes how to develop SOA composite services. |
|
Oracle Fusion Middleware Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework |
Describes how to develop ADF components. |
|
Oracle Fusion Middleware Developer's Guide for Oracle WebCenter |
Describes how to develop WebCenter services. |
|
"Developing with Web Services" in the "Designing and Developing Applications" section of the Oracle JDeveloper online help |
Describes how to develop Web services and attach policies using Oracle JDeveloper. |
|
Explains how to use Workshop to write and manage source code and design with sophisticated visual tools and Java frameworks. |