| Oracle® Real User Experience Insight Installation Guide Release 6.5.1 for Linux x86-64 Part Number E18052-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Real User Experience Insight Installation Guide Release 6.5.1 for Linux x86-64 Part Number E18052-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
This chapter describes the procedure for installing all required components prior to installing RUEI. The installation of the RUEI software itself is described in Chapter 4, "Installing the RUEI Software".
Note:
It is assumed throughout this guide that the installation is performed as theroot user, unless indicated otherwise.If the Linux DVD is mounted automatically, the content is located in the directory /media/Enterprise Linux dvd 20090908 (the date depends on the downloaded version of the DVD). If the DVD is not automatically mounted, use the following commands to mount it:
mkdir -p /mnt/dvd mount /dev/dvd /mnt/dvd
Note:
In the rest of this chapter it is assumed the Linux operating system DVD is mounted on/mnt/dvd.Besides the base operating system, you do not need to install any additional RPM packages. You should proceed directly to Chapter 4, "Installing the RUEI Software".
Note the procedure described in this section is only required for a Reporter system with a local database.
Install all prerequisites for the Oracle database using the following commands:
cd /mnt/dvd/Server rpm -Uhv kernel-headers-2.6.18-*.el5.x86_64.rpm \elfutils-libelf-devel-0.137-*.el5.x86_64.rpm \elfutils-libelf-devel-static-0.137-*.el5.x86_64.rpm \glibc-devel-2.5-* \ glibc-headers-2.5-*.x86_64.rpm \gcc-4.1.2-*.el5.x86_64.rpm \ gcc-c++-4.1.2-*.el5.x86_64.rpm \libstdc++-devel-4.1.2-*.el5.x86_64.rpm \ libgomp-4.4.0-*.el5.x86_64.rpm \libaio-devel-0.3.106-*.x86_64.rpm \ sysstat-7.0.2-*.el5.x86_64.rpm
Issue the following command to install all prerequisites for the Reporter:
rpm -Uhv httpd-2.2.3-*.el5.x86_64.rpm \ apr-1.2.7-11.*.x86_64.rpm \ apr-util-1.2.7-*.x86_64.rpm \ php-5.1.6-*.x86_64.rpm \ mod_ssl-2.2.3-*.el5.x86_64.rpm \ distcache-1.4.5-*.x86_64.rpm \ php-common-5.1.6-*.x86_64.rpm \ php-cli-5.1.6-*.x86_64.rpm \ php-mbstring-5.1.6-*.x86_64.rpm \ php-ldap-5.1.6-*.x86_64.rpm \ gmp-4.1.4-*.el5.x86_64.rpm \ postgresql-libs-8.1.11-*.el5_1.1.x86_64.rpm \ lm_sensors-2.10.7-*.el5.x86_64.rpm \ net-snmp-5.3.2.2-*.el5.x86_64.rpm \ net-snmp-utils-5.3.2.2-*.el5.x86_64.rpm \ perl-XML-Twig-3.26-*.fc6.noarch.rpm \ perl-XML-Parser-2.34-*.x86_64.rpm
Issue the following the commands to install all optional fonts. Alternatively, install the multi-byte character sets necessary to meet your NLS requirements.
rpm -Uhv fonts-*
Continue with the rest of the installation procedure from Creating the Database User Accounts and Groups.
As an alternative to manual installation, you can use a Yum repository to install the required RPMs. This requires a working Yum repository. For information on Yum repositories, see http://linux.duke.edu/projects/yum/. Install the necessary Oracle database packages using the following commands:
yum -y install gccyum -y install gcc-c++yum -y install compat-libstdc++-33yum -y install libstdc++-develyum -y install elfutils-libelf-develyum -y install glibc-devel yum -y install libaio-devel yum -y install sysstat
Install the necessary Reporter packages using the following commands:
yum -y install perl-URI yum -y install perl-XML-Twig yum -y install net-snmp-utils yum -y install sendmail-cf yum -y install httpd yum -y install mod_ssl yum -y install php yum -y install php-mbstring yum -y install php-ldap yum -y install bitstream-vera-fonts yum -y install librsvg2 yum -y install xorg-x11-xinit yum -y install fonts-*
This section describes the procedure for installing the Oracle database. This section can be skipped if you preparing a Reporter server with a remote database or a Collector system. Continue with the installation procedure at Chapter 4, "Installing the RUEI Software".
Download Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1.0.6.0) Standard Edition, Standard Edition One, and Enterprise Edition from the Oracle database home page (http://www.oracle.com/technology/software/products/database/index.html).
The procedure for installing the Oracle database is fully described in the product documentation. This section presents a summary of that procedure.
The information in this guide is based on the Oracle Database 11g for Linux x86-64 Quick Installation Guide. It is recommended that you download and review it. It is available from the Oracle Database Documentation Library (http://download.oracle.com/docs/cd/B28359_01/install.111/b32285/toc.htm).
Note:
The Oracle database's maximum memory usage is set by theMEMORY_TARGET parameter. By default, this is set to 40% of the available server RAM. For example, in a system with 16 GB RAM, it is set to approximately 6.4 GB. Note that if extra RAM is added to the server system to increase performance, it is not made available to the Oracle database until the MEMORY_TARGET parameter is manually increased.
Information about automatic memory management is available from the Oracle Database Documentation Library (http://download.oracle.com/docs/cd/B28359_01/server.111/b28310/memory003.htm#ADMIN11200).
Create two groups (dba and oinstall) with the following commands:
/usr/sbin/groupadd dba/usr/sbin/groupadd oinstall
Create the oracle user, and specify oinstall as the primary group and dba as the secondary group, with the following command:
/usr/sbin/useradd -g oinstall -G dba oracle
Set the oracle user password with the following command:
passwd oracle
Modify the /etc/sysctl.conf file to satisfy the Oracle installer's requirements by adding the following lines:
kernel.sem = 250 32000 100 128net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 1024 65000net.core.rmem_default = 4194304net.core.rmem_max = 4194304net.core.wmem_default = 262144net.core.wmem_max = 262144fs.file-max = 6553600
Make these changes effective immediately with the following command:
/sbin/sysctl -p
To improve the performance of the software, you must increase the shell limits for the oracle user. Add the following lines to the /etc/security/limits.conf file:
oracle soft nproc 2047oracle hard nproc 16384oracle soft nofile 1024oracle hard nofile 65536
If not already present, add the following lines to the /etc/pam.d/login file:
session required /lib64/security/pam_limits.sosession required pam_limits.so
Depending on the oracle user's default shell, you need to make changes to it. For the Bourne, Bash, or Korn shell, add the following lines to the bottom of the /etc/profile file:
if [ $USER = "oracle" ]; then if [ $SHELL = "/bin/ksh" ]; then ulimit -p 16384 ulimit -n 65536 else ulimit -u 16384 -n 65536 fifi
For information about other shells, you should refer to the Oracle Database 11g Release 1 for Linux x86-64 Quick Installation Guide available at the following location:
http://download.oracle.com/docs/cd/B28359_01/install.111/b32285/toc.htm
Throughout this guide it is assumed that the directory /u01/app is the root of the Oracle installation. This is specified in the ORACLE_BASE environment variable.
Enter the following command to display information about all mounted file systems:
df -k
This command displays information about all the file systems mounted on the system, including:
The physical device name.
The total amount, used amount, and available amount of disk space.
The mount point directory for that file system.
Create the necessary subdirectories in the mount point directory that you identified and set the appropriate owner, group, and permissions for them using commands similar to the following:
mkdir -p /u01/appchown -R oracle:oinstall /u01/appchmod -R 775 /u01/app
Logon to the system as the oracle user.
Add or edit the umask setting in the ~/.bash_profile file to the following:
umask 022
Make the setting active for the current shell by issuing the following command:
. ./.bash_profile
Set the ORACLE_BASE environment variable to define the location of the root of the Oracle directory tree:
export ORACLE_BASE=/u01/app/oracle
Unzip the Oracle database installation zip file. This creates the directory database. Then, run the graphical installer (note this will not run under user root). Ensure that your X Window environment is properly set up. In addition, when logging on remotely with SSH, ensure X forwarding is enabled. Use the following commands:
cd <location of the zip file>unzip linux_11gR1_database.zip./database/runInstaller
Use the installation wizard, and specify the values shown in Figure 3-1.
Note that the Create Starter Database check box should be unchecked.
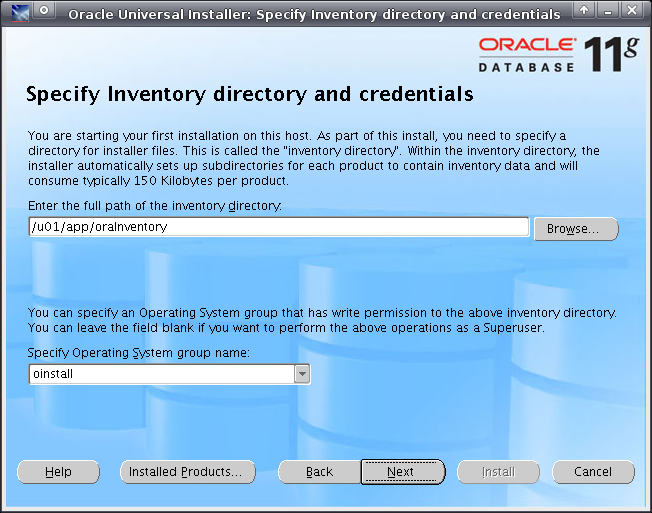
When ready, click Next. Specify the values shown in Figure 3-2. When ready, click Next.
Figure 3-2 Specify Inventory Directory and Credentials
Important:
Any warnings or errors reported during database installation (especially any missing prerequisites) must be resolved before proceeding. See Installing All Requirements Using a Yum Repository (Alternative) and Appendix E, "Troubleshooting" for information about required components.If all dependencies are met, you can click Next.
When installation is almost complete, you are prompted to run two scripts, orainstRoot.sh and root.sh, as root. This is shown in Figure 3-3.
Run the two scripts indicated in Figure 3-3. They should be run in a terminal window as root. You will receive output similar to the following:
/u01/app/oraInventory/orainstRoot.sh Changing permissions of /u01/app/oraInventory to 770.Changing groupname of /u01/app/oraInventory to oinstall.The execution of the script is complete Finished product-specific root actions.
The second script generates the following output:
/u01/app/oracle/product/11.1.0/db_1/root.sh
Running Oracle 11g root.sh script...
The following environment variables are set as:
ORACLE_OWNER= oracle
ORACLE_HOME= /u01/app/oracle/product/11.1.0/db_1
Enter the full pathname of the local bin directory: [/usr/local/bin]:
Copying dbhome to /usr/local/bin ...
Copying oraenv to /usr/local/bin ...
Copying coraenv to /usr/local/bin ...
Creating /etc/oratab file...
Entries will be added to the /etc/oratab file as needed by
Database Configuration Assistant when a database is created
Finished running generic part of root.sh script.
Now product-specific root actions will be performed.
On completion of each script, return the dialog shown in Figure 3-3, and click OK. In the main installer screen, verify that the message "The installation of Oracle database 11g was successful" appears. Click Exit, and confirm by clicking Yes.
Logon as the root user.
Create an /etc/init.d/oracledb script file to start and stop the Oracle database. An example of this initialization script is available in the RUEI installation zip file (/root/RUEI/extra/oracledb) explained in Chapter 4, "Installing the RUEI Software". Note that you will need to modify the settings for the ORACLE_BASE and ORACLE_HOME environment variables shown above if you selected a different installation directory for the Oracle database.
Make the script file executable and use it to start the Oracle database with the following commands:
chmod +x /etc/init.d/oracledb/sbin/chkconfig --add oracledb/sbin/service oracledb start
The Oracle database is now installed, and the database listener should be up and running.