Overview
This chapter describes Oracle Inventory Optimization and its benefits. It also provides an overview of how Oracle Inventory Optimization works and its input and output data.
This chapter covers the following topics:
- Overview of Oracle Inventory Optimization
- Stochastic Optimization Technology
- Business Process
- Key Inventory Decisions
- Input
- Output
- BIS Key Performance Indicators
Overview of Oracle Inventory Optimization
Oracle Inventory Optimization is a comprehensive Internet-based inventory planning solution that enables you to determine when and where to hold your inventories across the supply chain to achieve the desired customer service levels. You can factor in criteria such as demand variability and supply lead time variability when you make your inventory decisions. It is a strategic planning tool that can help you address the following key business issues:
-
How can I improve customer service while reducing inventory?
-
Where do I position my inventories?
-
How can I manage demand and supply variability?
-
-
What service levels can I achieve given specific budgets and other constraints?
The following are the key capabilities of Oracle Inventory Optimization:
-
Oracle Inventory Optimization uses stochastic optimization technology that enables you to factor in the multilevel supply chain network and interdependence of demand variability and supply lead time variability when generating time-phased safety stock recommendations.
-
Oracle Inventory Optimization enables you to evaluate multiple inventory planning scenarios and graphically compare the results. The planning scenarios for example can include different sets of customer service levels, budget constraints, and capacity constraints.
-
Oracle Inventory Optimization is integrated with Oracle's E-Business Suite and Advanced Planning products including Oracle Advanced Supply Chain Planning and Oracle Demand Planning. This enables collaboration between these applications. For example, the safety stock recommendations of Oracle Inventory Optimization can be automatically fed into Oracle Advanced Supply Chain Planning to drive tactical supply chain planning decisions.
Stochastic Optimization Technology
Stochastic optimization is a technique for prudent decision-making under uncertainty. Stochastic optimization considers:
-
Factors that you are trying to maximize or minimize. For example, you would want to maximize service level and profit and minimize cost.
-
Factors that you have under control. For example the investment on inventory when there are no budget constraints.
-
The limiting factors of your plan such as service level and budget constraints.
Oracle Inventory Optimization uses this technology to help you manage the uncertainty inherent to your business decisions. Based on your requirements and objectives, you can determine the optimal inventory stocking levels and other operational policies.
Oracle Inventory Optimization enables you to:
-
Determine the optimal inventory levels across the supply chain, which improves customer service while lowering inventory investment.
-
Consider uncertainty in demand and supply.
-
Manage variability and risk.
-
Evaluate cost and risk trade-off.
-
See a graphical representation of your strategic inventory plan.
-
Plan telescoping time horizons.
-
Provide accurate inputs to tactical plans.
-
Manage key performance indicators (KPIs) and drive continuous improvement.
Business Process
The following diagram describes the business process flow for Oracle Inventory Optimization:
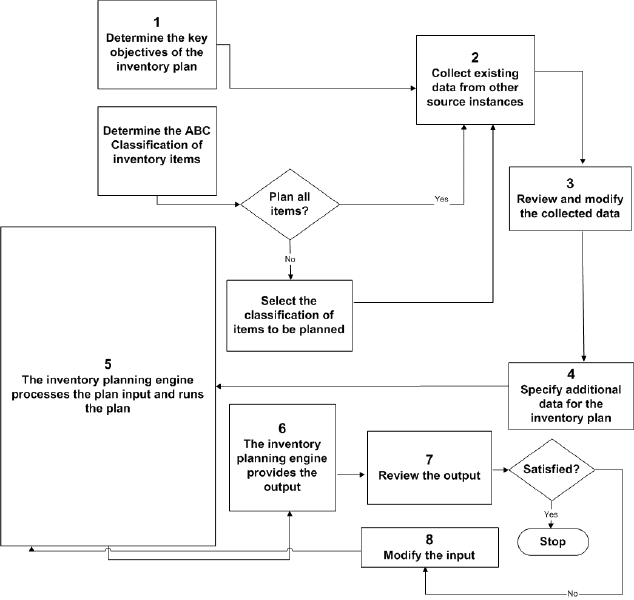
The following steps summarize the business process flow depicted in the diagram:
-
Determine the key objective of the inventory plan by linking to Corporate Balanced Scorecard.
-
Collect existing data from other source instances. For detailed information about collections, see Oracle Advanced Planning Implementation and User's Guide.
-
Review the data collected by the inventory planning engine and make changes as needed.
-
Specify additional inputs for the inventory plan. The following are the data that you can specify:
-
Service level policy
-
Inventory budget (optional)
-
Supplier lead time variability
-
Safety stock levels
-
Minimum and maximum inventory levels
-
-
The inventory planning engine processes the input and runs the inventory plan.
-
The inventory planning engine reports the results after running the inventory plan.
-
Review the output generated by the inventory planning engine.
-
If the inventory plan is not optimal, make changes to the input. Step 3 through 6 are repeated until the inventory plan is optimal.
For information on what Oracle Inventory Optimization takes as input, see Input.
For information on what Oracle Inventory Optimization provides as output, see Output.
For information on setting up Oracle Inventory Optimization, see Oracle Advanced Planning Implementation and User's Guide.
Key Inventory Decisions
Some of the key factors that can influence your decision factors are:
Service Level Decision Factors
Service level is a measure of satisfying demand through inventory or by the current production schedule to satisfy the customers' requested delivery dates and quantities. The decision on service level may depend on factors such as your business objectives, budget constraints, and targeted profit. For example, profits may rise as you increase the service level. However, increased service level beyond a certain point may not increase the profits because of the relative increase in inventory costs. Therefore, if your service level is driven by profit, you need to determine the most profitable scenario with an acceptable service level.
The service level may also influence your safety stock level and inventory location. For example, if you are targeting a high service level, you may want to reduce the transportation lead time by locating your inventory close to your customers.
Safety Stock Decision Factors
As safety stock can provide a buffer against uncertainty, you may want to consider the variability in demand and supply when you calculate the safety stock level. In many cases, the degree of variability in supply and demand changes over time. You need to consider all possible scenarios when you calculate safety stock.
Inventory Location Decision Factors
The decision on where to locate your inventory can be a trade-off between several factors such as supplier lead times, transportation lead time, manufacturing lead time, and the flexibility of your manufacturing system. For example, when you store safety stock in the form of finished goods, the manufacturing lead time for those finished goods decreases. However, the components and materials used in making those finished goods are committed and you cannot use them to meet unexpected customer requirements. Therefore, if your safety stock is in the form of raw materials, then you may want to locate your inventory close to your manufacturing plant.
Input
Oracle Inventory Optimization takes the following information as input:
-
Demand uncertainty
-
Customer service level for each demand
If the customer service level is specified at a deeper level of granularity, the service level value will apply to all independent demands for that customer.
-
Supplier lead time variation
-
Supply chain network in the form of sourcing rules and bill of distribution
-
List of items to be included in the plan
-
Bills of material including effectivity
-
Routings and key resources for items
-
Capacity constraints
Capacity constraints can be in the form of supplier capacity, transportation capacity, and resource availability or line rates.
-
Cost elements
Cost can include production cost, item cost, carrying cost percentages, purchase cost, transportation cost, and resource cost.
You can establish the following instances as eligible source instances for Oracle Inventory Optimization:
-
Oracle Applications R11 (Discrete or Process Manufacturing)
-
Oracle Applications R11i (Discrete or Process Manufacturing)
-
Oracle Applications R12 (Discrete or Process Manufacturing)
Output
The output of Oracle Inventory Optimization is a time-phased strategic inventory plan. More specifically, output includes the following:
-
Time-phased constrained and unconstrained safety stock levels for each item
You can specify the time-phased constrained safety stock quantities as input to Oracle Advanced Supply Chain Planning in the form of demand plan(s).
-
Recommended service levels
-
Key performance indicators
-
Recommendations and exception messages such as for service level and budget violations
-
Total cost of achieving the target customer service level and the individual cost elements that make up the total cost
BIS Key Performance Indicators
Oracle Inventory Optimization is integrated with Oracle Business Intelligence System's Performance Management System. You can set your organizational objectives using Oracle Business Intelligence System.
You can use key performance indicators to drive continuous improvement in your enterprise. You can set performance targets and exception tolerances by business units or by period and automatically notify the appropriate people when exceptions arise.
Note: Organizational objectives are referred to as Performance Measures in Oracle Business Intelligence System and as key performance indicators in Oracle Inventory Optimization and Oracle Advanced Supply Chain Planning