Implementation Considerations
This chapter covers the following topics:
- Implementing Nonconformance and Disposition Solution
- Implementation Roadmap
- Implementation Checklist
Implementing Nonconformance and Disposition Solution
This chapter contains general implementation considerations for the Nonconformance and Disposition solution.
The Nonconformance and Disposition solution is based on a set of related collection plans that store nonconformance and disposition related information. Implementation of the solution templates aid in the process of satisfying the requirements of some international quality standards, listed below:
-
ISO 9000:2000 and QA9000 - 4.13 - Control of Nonconforming Product
-
Code of Federal Regulations - 21CFR820.90 - Nonconforming Product
-
Additional requirements of AS9100 - Clause 8.3 - Control of Nonconforming Product
The nonconformance and disposition records are created, updated, and copied across plans throughout the lifecycle, by various participants within the business process. Notifications are sent to responsible parties to ensure that appropriate actions are taken. Some of the disposition execution can be automated. A predefined list of values is provided to ensure the validity of data.
This implementation guide provides you with the most generic nonconformance and disposition business flow. Your specific nonconformance and disposition business processes can be different from the generic business flow. This solution is flexible and easily extensible, and can be tailored to suit your specific business needs. The following sections describe some of the factors that need to be considered before implementation.
What are the benefits of a transition from a paper based nonconformance and disposition system?
The basic premise of the solution templates provides a central repository for all the nonconformances and dispositions information, within an organization. By implementing the solution templates, you have the following advantages:
-
Remove the paper trail, as well as reduce the maintenance of all paper records
-
Provide a shorter cycle time to review and disposition nonconformances
-
Notify the required personnel in your organization via e-mail alerts and workflow notifications, as well as e-mail alerts to mobile devices
-
Easy retrieval of any nonconformance or disposition information, using the standard query capabilities of Oracle Quality
-
Provide for an easier method of reporting on nonconformances over a period of time or for a specific item or assembly
-
Ease in the extension of the solution templates to capture any additional information elements that need to be recorded and tracked
-
If your organization still requires paper copies of records for compliance purposes, these can be printed using the Oracle Quality Report Writer, or by building custom reports
How will the solution template help your enterprise transition from stand-alone legacy systems?
If you are using different disparate, non-integrated systems to track nonconformances, as mentioned earlier, the solution templates aid to centrally maintain this information, In addition to using Oracle Quality, other integrations available within the e-Business Suite will help you to track nonconformances at different points within the supply chain.
What are the different types of nonconformances logged in your enterprise?
Depending on the type of business and industry you are in, the nonconformances reported in your enterprise might be at different points within the supply chain. To address all the likely functional areas that may generate a nonconformance, the solution has been designed to accept inputs from different sources.
Some functional areas where nonconformance occurs are identified below:
-
Supplier Nonconformance: A supplier reports this type when they find a nonconformance prior to shipping the purchased material or outside processing material to your company. The supplier can use Oracle iSupplier Portal to submit the nonconformance electronically.
-
Receiving Nonconformance: This type is recorded and subsequently dispositioned for purchased material and for material sent to the supplier for any outside processing operations. The nonconformance is usually recorded as a result of receiving inspection.
-
Work In Process Nonconformance: This type is logged during the in-process inspection of a semi-finished assembly, or finished goods inspection prior to moving it to an inventory location.
-
Inventory Nonconformance: This type can be logged during inventory inspection or during cycle/physical count activities.
-
Customer Nonconformance: This type is logged when a customer reports that the products they have received do not meet the specified requirements. This can likely result in a Returned Material Authorization (RMA) that is issued, and the nonconforming material received back by the supplier for further evaluation and disposition.
-
Maintenance Nonconformance: This type of nonconformance is logged to report defects on maintenance equipment used for critical production processes within an organization.
-
Nonconformance logged through mobile devices: Since quality inspections can be performed on mobile devices using Oracle Warehouse Management and Mobile Supply Chain Applications functionalities, it is possible to log nonconformances for receiving or in-process inspection activities via mobile devices.
-
Non-Material Nonconformance: In any organization, it is possible to report nonconformances on process issues, non-compliance to standard operating procedures, quality standards, and other non-material type issues.
Nonconformances logged from all sources are stored in a central repository titled, Nonconformance Master.
Due to the tight integration of Oracle Quality with other modules within the Oracle eBusiness Suite, it is possible to record nonconformances during inspection or other transaction that are currently supported. Please refer to Setup Steps.
What type of data will be captured for nonconformance and disposition?
The Nonconformance and Disposition solution provides data collection capability to capture data for nonconformance, disposition, and associated quality results. Depending on your current business process, as well as your required level of detail, a choice can be made between the three different configurations:
| Configuration | Details and Usage | Parent Plan |
|---|---|---|
| Nonconformance and Disposition (recommended configuration) |
This configuration has all the collection plans and seeded data for implementing Nonconformance and Disposition Management (the master set of the next two configurations) | Template Nonconformance Master Plan |
| Disposition Only | This configuration consists of all collection plans and related seeded data used for Disposition Management only. Use this configuration if your business tracks disposition only and would like to take advantage of the automatic disposition transaction execution capability. |
Template Disposition Header Plan (Disposition Only) |
| Nonconformance Only | This configuration consists of all collection plans and related seeded data used for Nonconformance Management only. Use this configuration if your business does not require a systematic way of tracking disposition. |
Template Nonconformance Master Plan (Nonconformance only) |
Additional data could be captured in user-defined collection elements and added to these collection plans. See: Setup Steps, Step 9.
Alternatively, these elements can be grouped into additional plans and linked to the nonconformance/disposition system. See: Setup Steps, Step 10.
What needs to be done after a configuration is chosen?
Once the decision on which configuration is suited for your enterprise has been made, the next step is to copy the template plans, associated with the specific configuration, to real plans. The template plans have collection elements, actions, and parent-child relationships that have already been defined.
A tool is provided to copy this set of template collection plans to real plans. See: Setup Steps, Step 2. You can choose to copy from the template collection plans, tailor these to your business needs, and make these a reference set of plans for your implementation. See: Considerations Prior to Implementation.
How is the nonconformance and disposition information organized?
All the necessary data elements required for the nonconformance and disposition lifecycle can be captured at different levels in the parent-child collection plan structure. Depending on the granularity of information that your business process requires you to capture, the different levels might or might not be applicable to you.
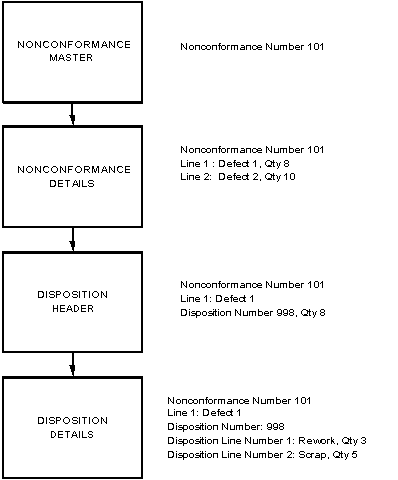
The following block diagram displays a simplified version of the nonconformance and disposition data structure. Following are the assumptions for this structure:
-
A nonconformance is reported in a specific functional area of the enterprise.
-
The Nonconformance Master is the central repository for all different nonconformance types.
-
When a nonconformance is logged, the nonconformance details have multiple lines with the quantity breakdown, different causes, and defect types. For example, as a result of inspection, a quantity of ten of item ABC is found to be nonconforming. In this case, a nonconformance is entered in the Nonconformance Master for a quantity of ten, and within the nonconformance details plan, the breakdown of the quantity might be provided. If three of ten were damaged, five of ten were broken, and the remaining two had visual defects, then three detail lines need to be entered in the nonconformance details. Review of each nonconformance line can be a separate discussion thread.
-
The nonconformance details will be the vehicle to carry Material Review Board (MRB) types of discussion, described later.
-
When a nonconformance has been reviewed and it requires disposition, then the disposition header information is required to be entered.
-
A single nonconformance line can have multiple dispositions. For example, we will assume a purchased item that has been received into inventory has defects. A nonconformance is logged and after the review process, it was determined that some of the nonconforming quantity will be returned to the vendor, some will be reworked internally, and the remaining quantity will be scrapped. In this case, the single nonconformance line can have multiple disposition header lines, or a single disposition header line.
-
The disposition details provide additional granularity on the specific dispositions that need to take place. For example, if the disposition was Rework, then the detail line will have additional information if the disposition status is to create a rework job, or create a rework operation for the existing job, etc. The disposition action chosen determines the execution of the automated disposition action.
Organization of Data in Nonconformance and Disposition
If your business organizes information in a simplified fashion, you can remove any level (collection plan) that is unnecessary. See: Setup Steps, Step 13.
How are Nonconformances and Disposition identified?
The current practice in your enterprise might require you to track Nonconformance and Disposition using standard operating procedures. In this solution, nonconformances and dispositions are identified using two collection elements: Nonconformance Number and Disposition Number. These are Sequence type collection elements and have specific attributes associated.
These attributes can be customized to match the naming convention used in your enterprise. See: Setup Steps, Step 3.
Who has privileges to access Nonconformances and Disposition information?
In any system that tracks nonconformances and dispositions, it is important to limit access to authorized individuals, due to information sensitivity. Once the information is accessed, the type of operations enabled for the user needs to be considered. You can utilize collection plan security to achieve this.
Different participants of the process can be given different privileges (create, update, view) to access different sets of information. In this manner, careful administration of user privileges is collection plan security. See: Setup Steps, Step 8.
How are user entered values validated?
New collection elements with a set of values have been provided as a starting point to record nonconformances and dispositions. The solution has included commonly used values for validation of some collection elements, listed below:
-
Nonconformance Source
-
Nonconform Severity
-
Nonconform Priority
-
Nonconformance Type
-
Nonconformance Code
-
Nonconformance Status
-
Nonconform Line Status
-
Action Executed
-
Disposition
-
Disposition Action
-
Disposition Status
-
Disposition Source
These values can be modified to your valid values, according to your business rules. See: Setup Steps, Step 4.
How are individuals informed about a nonconformance or disposition?
In this solution, e-mail alert and workflow notification capabilities have been provided. Depending on the prevalent practice in your organization, either one or both can be used to inform, update, and adding individuals to specific tasks during the nonconformance and disposition lifecycle. Optionally, the e-mail alerts can be sent to mailing lists, or people outside of your organization, such as suppliers, customers, etc. They can also be sent to mobile devices.
How do you implement the Material Review Board process?
Traditionally, when a material nonconformance is logged, depending on the business process in that industry or specific organization, the nonconformance is reviewed by a group of authorized individuals who determine how the nonconforming material needs to be dispositioned. This process can involve discussions between representatives from different functional areas, such as Quality Assurance, Inventory, and Purchasing.
If your organization has a formal MRB process, it can be modeled using the nonconformance solution; discussion threads on the cause and analysis of the nonconformance can be carried out. Initially, the nonconformance owner assigned to a distribution list can be used to send e-mail alerts on the nonconformance. It is possible to include additional reviewers or approvers in an ad hoc manner, based on the progress of the nonconformance lifecycle.
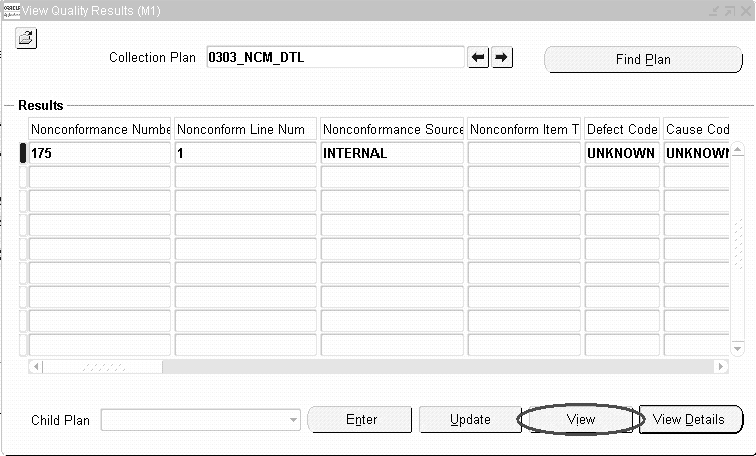
In the following example, the modeling of MRB activities via the solution templates is highlighted. When a nonconformance needs to be reviewed by a group of people (MRB, for example), the Action and Notes related elements of the Nonconformance Detail plan can be utilized.
For example, the nonconformance owner wants to ask the Quality Engineer to perform certain analysis, he or she could enter a record into Nonconformance Details with the following values:
| Action Executed By | Nonconformance Owner |
| Next Action Type | FOR ANALYSIS |
| Next Action Description | Please perform XYZ analysis... |
| Next Action Assigned To | Quality Engineer |
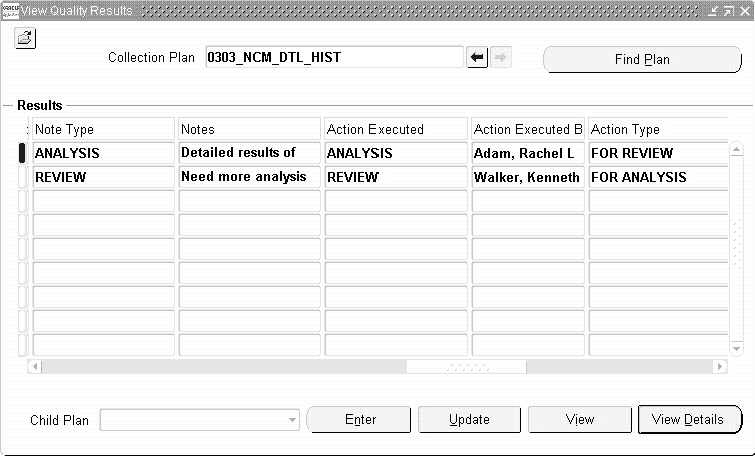
This Quality Engineer has performed the analysis and requests a review by his manager by updating the same Nonconformance Detail:
| Note Type | ANALYSIS |
| Notes | Detailed results of the analysis... |
| Action Executed | ANALYSIS |
| Action Executed By | Quality Engineer |
| Next Action Type | FOR REVIEW |
| Next Action Description | Please review this for analysis |
| Next Action Assigned To | Quality Manager |
The following screenshots illustrate how the Material Review process is handled using the Nonconformance and Disposition solution. All updates to these elements are captured in multiple history records of this parent record.
Nonconformance Detail Plan
Nonconformance Detail History, viewed from Nonconformance Detail
How is MRB Hold or segregation achieved?
When nonconforming material is found, if it is decided to put the material on hold and unavailable for use, the same can be achieved by segregation actions. The segregation actions supported are: Creation of a move order to move nonconforming material found during receiving inspection or in inventory to a MRB location and component return of a nonconforming component from WIP to a MRB subinventory. With these two segregation actions, the nonconforming material cannot be transacted until a decision on its disposition is made. The designated MRB subinventory should be defined with the appropriate parameters to make it non-nettable and not reservation enabled.
There are two segregation plans that are child plans to the Nonconformance Master. The can be used to execute these segregation actions.
How is an Audit Trail of Nonconformance and Disposition maintained?
All collection plans provided in the solution contain a History plan as one of the children. When these collection plans are used out-of-the-box after copying them to real collection plans, the history plan captures all updates made to any collection element in the parent plan. Therefore, from an auditing perspective, if it is required to display the details on all changes made to a nonconformance line, the same can be demonstrated.
If there are only some collection elements that need to be captured for audit trail purposes, then the parent-child copy relationship between the parent and child plans for the non-essential collection elements needs to be removed. If for compliance purposes, the audit trail needs to be reported, custom reports can be built to generate the same.
How do you link the Corrective Action system to the Nonconformance and Disposition system?
When logging a Corrective Action Request as part of your Nonconformance or Disposition process flow, the Corrective Action system can be linked to the collection plan corresponding to the step in your process. See: Setup Steps, Step 11.
How do you use attachments for nonconformance and dispositions?
The current functionality of adding attachments within the Enter Quality Results and Update Quality Results windows is applicable to nonconformance and disposition. When logging a nonconformance, it might be required to attach pictures of the nonconforming material. In the case of dispositions, such as rework, additional instructions can be provided by drawing attachments.
In addition, for the disposition actions of creating a rework job or adding a rework operation, when attachments (for work instructions) are added at the line level of the respective disposition action, the attachments will be copied to the newly created rework job and operations. This facilitates the personnel to review the work instructions when performing a re-work.
How do you maintain a link between multiple nonconformances?
To illustrate how to link multiple nonconformances, two scenarios are used. In the first case, a nonconformance is logged for an assembly and it is later found that the actual nonconformance is because of a component in the assembly. This can be modeled in the following manner:
The collection plans, Nonconformance Master and Nonconformance Details have a collection element, Nonconform Item Type. The initial values available for this element are Assembly and Component. When the nonconformance is logged in the Nonconformance Master, the Nonconform Item Type can be entered as Assembly with the item number in the item collection element. When it is later determined that the cause of the nonconformance is the component, the Nonconform Item Type can be updated to the component with the relevant item number. Because history for the nonconformance is captured, it is possible to trace back and infer that the initial nonconformance was for the assembly and then it later became a component nonconformance.
In the second case, a nonconformance is logged for a finished product. Initial analysis reveals that it is an assembly problem. The Nonconform Item Type can be used to specify that the assembly caused the nonconformance. Additional investigation by disassembling the finished product reveals that there are multiple components in the assembly nonconforming. A nonconformance can be logged for each nonconforming component.
To maintain an association with the original nonconformance, you can create a new collection element, Parent Nonconformance, of character data type, and add the element to the Nonconformance Master and/or Details plan. When a new nonconformance is logged for each nonconforming component, a unique nonconformance number is generated. The Parent Nonconformance element can be used to maintain a link with the original nonconformance. Later, if all nonconformances for a specific parent nonconformance is required to be reported, the parent nonconformance number can be used as the query criterion to find all nonconformances. See: Reporting Overview.
How do you capture nonconformance and disposition costs?
The following steps can be performed:
-
Create new elements, such as Nonconformance Cost and Disposition Cost
-
Add these new elements to the appropriate plans at any level in the nonconformance and disposition, parent-child collection plan structure
-
If you want the costs to roll up to a parent level plan, set up appropriate parent-child element relationships. For example, if you add Nonconformance Cost to the Nonconformance Master and Nonconformance Detail plan, then you can set up the parent-child element relationship in the following manner:
-
Parent Plan: Nonconformance Master
-
Child Plan: Nonconformance Details
-
Parent Element: Nonconformance Cost is the sum of Child element, Nonconformance Cost
-
-
Where appropriate, when entering the Nonconformances Details, enter the nonconformance cost for each line; the costs will be summed up from the nonconformance line level to the Nonconformance Master
-
You can build reports using Oracle Quality Results Report Writer with the new cost collection element
Implementation Roadmap
The following process flow illustrates a generic nonconformance and disposition lifecycle:
Simplified Flow for Nonconformance Management
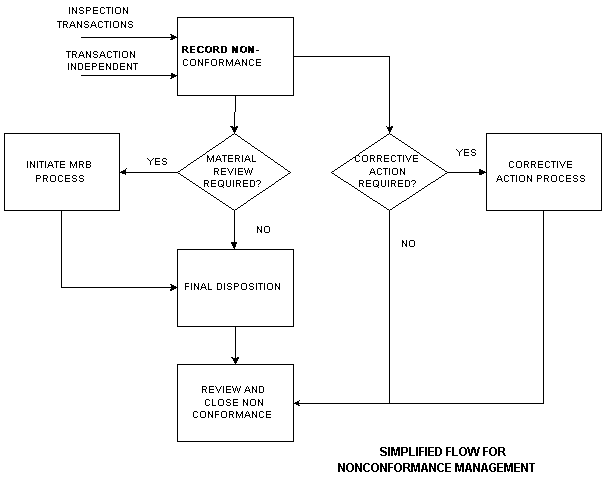
Nonconformance and Disposition Lifecycle
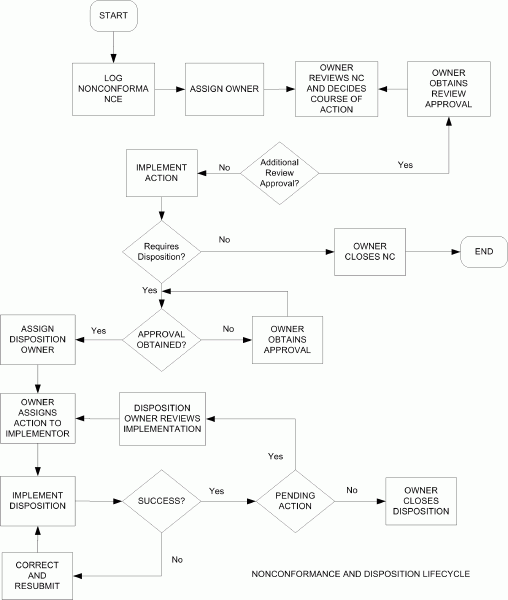
Each rectangle represents an action step in the business flow and corresponds to step(s) to be executed in the Oracle Quality Nonconformance Solution. The following table illustrates the business flow step and the equivalent step in the nonconformance and disposition solution. Additional details, based on the function area of the nonconformance, are provided in the remaining chapters.
| Business Flow Steps | Oracle Quality Nonconformance and Disposition Solution Steps |
|---|---|
| Log Nonconformance | Enter a new record into the Nonconformance Master Collection Plan within Oracle Quality |
| Assign Owner | Update Owner collection element in the Nonconformance Master |
| Segregate Nonconforming Material | Enter information in the inventory or WIP segregation plan to segregate the material and move to a MRB or other quarantine subinventory |
| Review Nonconformance | Update elements such as Priority and Severity in the Nonconformance Master Enter a new record into the Nonconformance Detail (child collection plan of Nonconformance Master) to capture additional details and notes Update elements such as Notes and Action in the Nonconformance Detail |
| Approve Nonconformance | Update Action Executed to Approval in the Nonconformance Detail (Customized workflows can also be used to achieve approvals, based on approval hierarchy) |
| Record Disposition | Enter a new record in Disposition Header to describe the Disposition Enter one or more records in the Disposition Detail (child plan of Disposition Header) to indicate the Disposition Action(s) |
| Disposition Implementation | Enter one or more records in the Disposition Implementation collection plan for the corresponding functional area (In-Process, Inventory) |
| Close Disposition | Update Status element to Closed in Disposition Implementation, Disposition Detail, and Disposition Header plans |
| Close Nonconformance | Update Status element to Closed in Nonconformance Detail and Nonconformance Master plans |
Implementation Checklist
The implementation might span multiple functional areas. The following list provides information on the process flow and steps to implement within these functional areas:
-
Setup
As seen in the above mapping table, the system is based on a set of Oracle Quality collection plans (Nonconformance Master, Nonconformance Details, Disposition Header, Disposition Details), and the most important setup step is to create these plans. See: Overview of Setting Up.
-
Implementation by functional area
Chapters 4 and 5 discuss the generic business process flow and the steps of implementation for each business function that would generate or report a nonconformance. The functional areas are limited to Supplier, Receiving, Work-in-Process, Inventory, and Customer Nonconformances.
Refer to Process Steps for information on how nonconformance and disposition can be implemented in a mobile application environment (Oracle Warehouse Management or Mobile Supply Chain Applications).
The appendices list all seeded collection plans, as well as their collection elements, parent-child relationships, and actions.
Note: It has been attempted to depict the business flow in a general manner. It is possible that the actual business flow in your enterprise to report, review, and disposition nonconformances are different from the process flow diagrams above. Please use the process flow diagram as a guidance tool.
-
Reporting and other Solution Configurations
Chapter 7 describes how to generate reports on Nonconformance and Disposition.
Chapter 8 describes the other configurations that can be built on top of the Nonconformance and Disposition Solution. Some of them are Workflow configuration, SQL *Plus Report, and Modification of E-mail Notifications to suit your business needs.