Script Launcher Module
The Script Launcher module enables you to delegate management functions to agents. Management functions are management scripts written in a management scripting language. The Script Launcher module is a multi-instance module. All instances of the Script Launcher module access the same Script Repository module for language and script information.
The module includes the following two tables:
-
Launch Table – Describes scripts that are ready to be launched and indicates their parameters
-
Result Table – Enables you to view the results of running a selected script
The Script Launcher module enables you to manipulate scripts as follows:
-
Control who is allowed to read, write, and execute scripts from the Script Repository module
-
Specify arguments for management scripts
-
Initiate and terminate management scripts
-
Monitor and control running management scripts
-
View the results produced by running management scripts
-
Control who is allowed to read, write, and execute scripts
The security for Script Launcher module is implemented as follows:
-
root cannot be part of the LaunchOwner field of the Launch Table. To enable the root user of a machine to run scripts as a superuser, create a new user on the machine. Use that user name to run the scripts.
-
The launchOwner must be a part of new esscrusers group on the server. Only esscrusers can create rows or make changes in the Launch Table.
-
The Launch Owner, or launchOwner, must be a valid user on the agent machine. The user must be a local user or someone added through a service such as NIS on the agent. Scripts are run with the launch owner's permissions.
To Access the Script Launcher Module
-
Load the module.
See the Sun Management Center 3.5 User's Guide for more information. The Script Repository module is available under Local Applications in the Browser window.
-
Double-click Local Applications in the Browser window.
-
Double-click Script Launcher.
The Script Launcher displays the Launch Table and the Result Table.
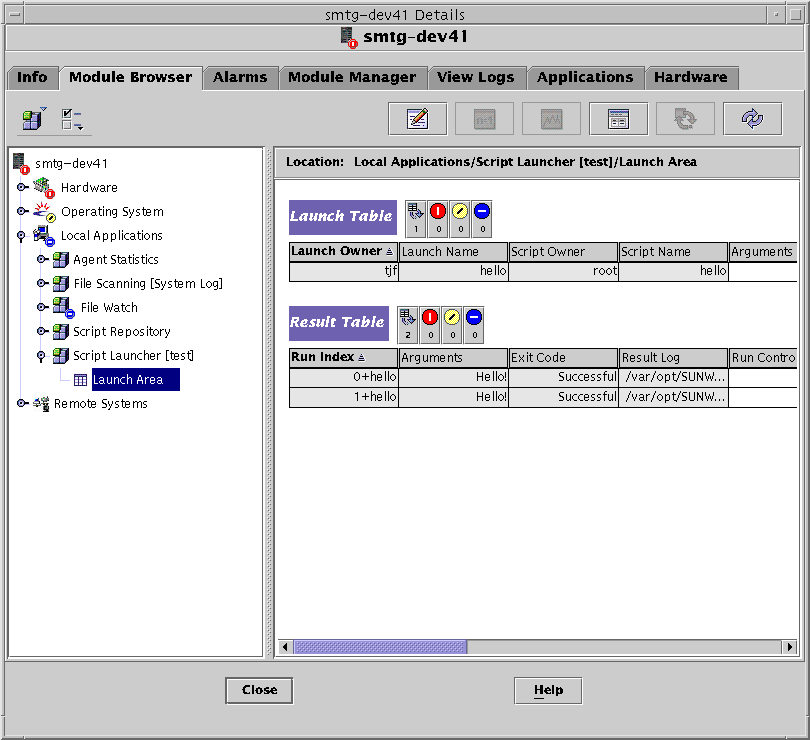
Launch Table
The Launch Table controls the execution of all scripts. This table describes scripts that are ready to be launched along with descriptions of their parameters.
An entry in the Launch Table attaches an argument to a script. The entry also defines the owner, who is used to associate permissions to execute the script.
Several instances of a script may be created through one single entry on this table. Also, several entries on this table may point to a same script on the Script Table. You can execute several identical scripts with different arguments and different permissions. Scripts can only be run with the launch owner's permissions.
The Launch Table has the attributes listed in the following table.
Table 5–2 Launch Table Attributes
To Add a New Entry to the Launch Table
-
Access the Launch Table as described in To Access the Script Launcher Module.
-
Press mouse button 3 on the Launch Table header.
A pop-up menu is displayed.
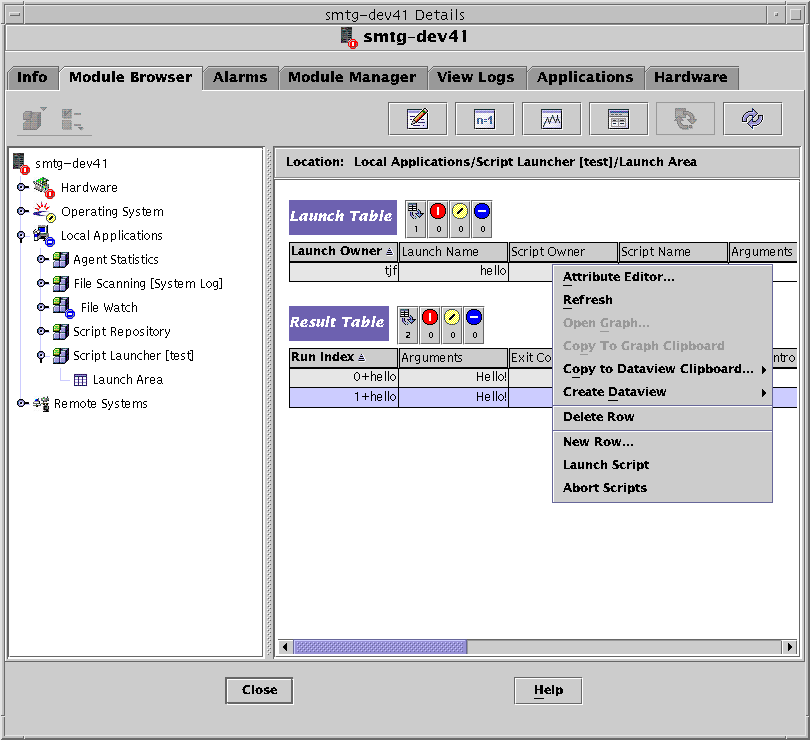
-
Choose New Row and provide all the required parameters.
The Script Owner and Script Name values point to the script that is started from this launch button.
To Launch an Instance of a Script
-
Access the Launch Table as described in To Access the Script Launcher Module.
-
Press mouse button 3 on the row displaying the desired script name.
-
Select Launch Script.
The script is launched.
To Stop Scripts
-
Access the Launch Table as described in To Access the Script Launcher Module.
-
Press mouse button 3 on the row displaying the script you want to stop.
A pop-up menu appears.
-
Choose Abort Scripts.
The script stops running.
Result Table
The Result Table lists all scripts that are currently running or have recently terminated. This table contains the following information:
-
The time the script started and finished execution
-
The reason the script finished executing
-
The result of the script
-
The remaining time the script is allowed to run
Every row in the Result Table contains the arguments passed during script invocation, the results produced by the script, and the script exit code. The Result Table also provides information about the current run state, and start and end timestamps.
The Result Table shows the attributes listed in the following table.
Table 5–3 Result Table Attributes
To View the Results From the Result Table
-
Access the Result Table as described in To Access the Script Repository Module.
-
In the Result Table, press mouse button 3 on a running script entry.
A pop-up menu is displayed.
-
Choose View the Result Log to view the result log file corresponding to the selected running script.
The Probe Viewer appears, and displays the result of the log.
Note –You can also access log files at the command line. The log files are saved in the /var/opt/SUNWsymon/SysMgmtPack/script-launcher/scripts/UserName/logs directory. The log file name includes the running instance so that the current log file is identifiable when a user runs the same script several times.
To Delete a Row From the Result Table
-
Access the Result Table as described in To Access the Script Repository Module.
-
In the Result table, press mouse button 3 on a row.
A pop-up menu is displayed.
-
Choose Delete Row.
A dialog box appears to confirm or cancel the deletion.
-
Click Yes to confirm.
Once the row has been deleted, the Run Table is automatically refreshed.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
