Server Layer
The server layer accepts requests through the console and passes these requests to the appropriate agent. The server then relays the response from the agent back to the console.
For example, if you request information on the number of users that are accessing a host, the server layer receives this request from the console. The server layer then sends the request to the agent on that host. The agent finds the answer and sends the answer back to the server, which forwards the information to the console.
Similarly, if an error condition is created on one of the hosts, the agent on that host notifies the server. The server forwards the information to the console as an alarm.
In addition, the server layer provides the console with a secure entry point to interface with the agents.
The server layer includes the following components, as illustrated in Figure 1–2:
-
Sun Management Center server
-
Sun Management Center web server
-
Topology manager
-
Trap handler
-
Configuration manager
-
Event manager
Figure 1–2 Sun Management Center Server Layer
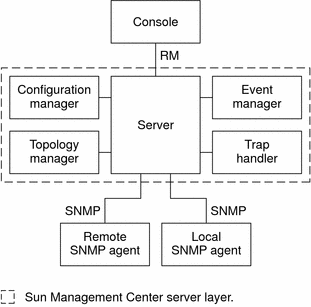
The server component is the core of the server layer. The server component consists of two servers: a Java server and a web server. Both the Java server and the web server are multi-threaded. These servers can handle multiple data requests from various Sun Management Center users.
The topology manager provides services that include managing user administrative domains and arranging managed object topology.
The trap handler is a centralized SNMP trap receptor that logs and forwards traps to interested components. This server layer component is responsible for receiving all alarm notifications.
The configuration manager provides security services to the server and the agents.
The event manager receives event information from the agents. These events can trigger alarms, which are forwarded to the console.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
