Assigning a Reserved IP Address to a DHCP Client
The Solaris DHCP service attempts to provide the same IP address to a client that has previously obtained an address through DHCP. However, sometimes an address has already been reassigned to another client.
Routers, NIS or NIS+ servers, DNS servers, and other hosts that are critical to the network should not be DHCP clients. Hosts that provide services to the network should not rely on the network to obtain their IP addresses. Clients such as print servers or file servers should have consistent IP addresses as well. These clients can receive their network configurations and also be assigned a consistent IP address from the DHCP server.
You can set up the DHCP server to supply the same IP address to a client each time the client requests its configuration. You reserve the IP address for the client by manually assigning the client's ID to the address that you want the client to use. You can set up the reserved address to use either a dynamic lease or a permanent lease. If the client's address uses a dynamic lease, you can easily track the use of the address. A diskless client is an example of a client that should use a reserved address with a dynamic lease. If the client's address uses a permanent lease, you cannot track address use. Once a client obtains a permanent lease, the client does not contact the server again. The client can obtain updated configuration information only by releasing the IP address and restarting the DHCP lease negotiation.
You can use the pntadm -M command or DHCP Manager's Address Properties dialog box to set up lease properties.
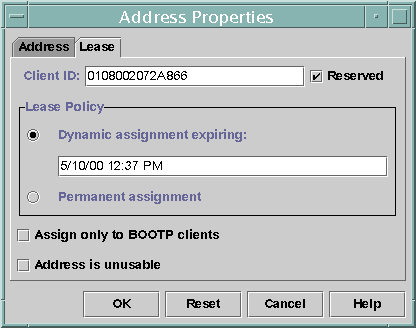
The following figure shows the Lease tab of the Address Properties dialog box, which is used to modify the lease.
Figure 14–13 Address Properties Lease Tab in DHCP Manager
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
