Private Virtual Network on a Single System
Figure 10–2 shows a single system with a private network behind packet filtering software that performs network address translation (NAT). This figure illustrates the scenario that is built in Example 11–7.
Figure 10–2 Private Virtual Network on a Single Host
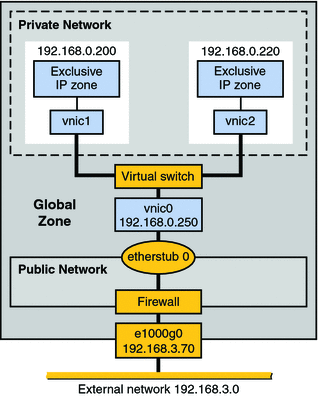
The topology features a single system with a public network, including a firewall, and a private network built on an etherstub pseudo-interface. The public network runs in the global zone and consists of the following elements:
-
GLDv3 network interface e1000g0 with the IP address 192.168.3.70.
-
A firewall implemented in the IP Filter software. For an introduction to IP Filter, refer to Introduction to Solaris IP Filter in System Administration Guide: IP Services.
-
etherstub0, a pseudo-interface upon which the virtual network topology is built. Etherstubs provide the ability to create a virtual network on a host. That network is totally isolated from the external network.
The private network consists of the following elements:
-
A virtual switch which provides packet forwarding among the VNICs of the private network.
-
vnic0, which is the VNIC for the global zone, and has the IP address 192.168.0.250.
-
vnic1 with the IP address 192.168.0.200 and vnic2 with the IP address 192.168.0.220. All three VNICs are configured over etherstub0.
-
zone1, which is configured over vnic1, and zone2, which is configured over vnic2.
Best Uses for a Private Virtual Network
Consider creating a private virtual network for a host that is used in a development environment. Using the etherstub framework, you can totally isolate software or features under development to the containers of the private network. Moreover, you can use firewalling software for network address translation of outgoing packets that originate in the containers of the private network. The private network is a smaller version of the eventual deployment environment.
For More Information
-
For tasks for implementing the private virtual network, go to Configuring a Private Virtual Network
-
For the example that shows how to configure the private virtual network shown in this section, go toExample 11–7.
-
For conceptual information about VNICs and virtual networks, go to Network Virtualization and Virtual Networks.
-
For conceptual information about zones, go to Chapter 16, Introduction to Solaris Zones, in System Administration Guide: Virtualization Using the Solaris Operating System.
-
For information about Solaris IP Filter, go to Introduction to Solaris IP Filter in System Administration Guide: IP Services.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
