Chapter 2 Sun N1 System Manager System and Network Preparation
This chapter provides the Sun N1 System Manager hardware and software requirements, reference architectures, and procedures for preparing your N1 System Manager components.
The tasks provided in this chapter can be performed in parallel with the management server preparation as described in Chapter 3 of this manual, “Installing and Configuring the Sun N1 System Manager Software” and inChapter 1, Installing and Configuring the Sun N1 System Manager Software, in Sun N1 System Manager 1.2 Installation and Configuration Guide.
Note –
Do not run discovery or use the N1 System Manager system until all provisionable servers have been configured as described in the following sections.
This chapter discusses the following topics:
Sun N1 System Manager Hardware and OS Requirements
The information in this section will help you determine what operating system, hardware, and storage resources must be allocated or acquired to implement the N1 System Manager system.
This section discusses the following topics:
Management Server Requirements
N1 System Manager management server hardware and operating software minimum requirements are listed in the following table. See Table 2–5 for specific management server sizing information based on the number of provisionable servers to be managed.
Dedicate the management server only to N1 System Manager software. Do not install other applications on the management server.
Table 2–1 SPARC-based Management Server Hardware and Operating System Requirements
|
Type |
Management Port Type |
Operating System |
Disk Space |
RAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
NetraTM 240, 440 |
ALOM |
Solaris 10 GA and later |
72 Gbytes minimum |
4 Gbytes minimum |
|
Sun FireTM V210, V240, V440 |
ALOM |
Solaris 10 GA and later |
||
|
Sun Fire T1000 and T2000 |
ALOM |
Solaris 10 HW2 and later |
Table 2–2 X86–Based Management Server Hardware and Operating System Requirements
|
Type |
Management Port Type |
Operating System |
Disk Space |
RAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Sun Fire X2100 with the 8081A IPMI 1.5 Remote Management Card: Part Number: 371-0743 |
SP |
Solaris x86 Version 10 HW1 and later Red Hat Enterprise Linux 3.0 AS Updates 2 through 5, 32–bit and 64–bit |
72 Gbytes minimum |
4 Gbytes minimum |
|
Sun Fire X4100 and X4200 |
ILOM |
Solaris x86 Version 10 HW1 and later Red Hat Enterprise Linux 3.0 AS Update 5, 32–bit and 64–bit |
||
|
Sun Fire V20z and V40z |
SP |
Solaris x86 Version 10 and later Red Hat Enterprise Linux 3.0 AS Updates 2 through 5, 32–bit and 64–bit |
A minimum of 3.0 Gbytes should be allocated for each OS distribution you plan to provision.
-
On a Solaris-based management server, OS distributions are stored as follows:
-
Linux OS distributions are stored in /var/opt/SUNWscs/share/allstart
-
Solaris OS distributions are stored in /var/js
-
-
On a Linux-based management server, OS distributions are stored as follows:
-
Linux OS distributions are stored in /var/opt/sun/scs/share/allstart/
-
Solaris OS distributions are stored in /var/opt/sun/scs/share/allstart/jumpstart/
-
Note –
If the server you have chosen for the management server has only two network interfaces, consider installing a third 10/100 NIC in the N1 System Manager. A third NIC enables you to assign the management, provisioning, and data networks to separate network interfaces, and simplifies administrative tasks. The example diagrams and configurations in this document assume that an additional NIC has been installed in the management server.
Provisionable Server Requirements
N1 System Manager provisionable server hardware and operating software requirements are listed in the following tables.
Table 2–3 SPARC-Based Provisionable Server Hardware and Operating System Requirements|
Type |
Management Port Type |
Provisionable OS |
Disk Space Requirements |
RAM Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Sun Netra 240 and 440 |
ALOM |
Solaris 10 GA and later Solaris 9 Update 7 and Update 8 |
12 Gbytes minimum for all provisionable servers |
512 Mbytes minimum, 1-Gbyte recommended for all provisionable servers |
|
Sun Fire V210, V240, and V440 |
ALOM |
Solaris 10 GA and later Solaris 9 Update 7 and Update 8 |
||
|
Sun Fire T1000 and T2000 |
ALOM |
Solaris 10 HW2 and later |
Table 2–4 X86–Based Provisionable Server Hardware and Operating System Requirements
|
Type |
Management Port Type |
Provisionable OS |
Disk Space Requirements |
RAM Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Sun Fire X2100 with the 8081A IPMI 1.5 Remote Management Card: Part Number: 371-0743 |
SP |
Solaris x86 Version 10 HW1 and later Red Hat Enterprise Linux 3.0 WS, ES, and AS Update 5, 32–bit and 64–bit Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4.0 WS, ES, and AS update 1, 32–bit and 64–bit SUSE Linux Professional 9.2, 64–bit only SUSE Linux Professional 9.3, 64–bit only |
12 Gbytes minimum for all |
512 Mbytes minimum, 1-Gbyte recommended |
|
Sun Fire X4100 and X4200 |
ILOM |
Solaris x86 Version 10 HW1 and later Red Hat Enterprise Linux 3.0 WS, ES, and AS Update 5, 32–bit and 64–bit Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4.0 WS, ES, and AS update 1, 64–bit only SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 9 SP1, 64–bit only |
||
|
Sun Fire V20z and V40z |
SP |
Solaris x86 Version 10 and later Solaris x86 Version 9 update 7 and update 8 Red Hat Enterprise Linux 3.0 WS, ES, and AS, Updates 1 through 5 for 32–bit only Red Hat Enterprise Linux 3.0 WS, ES, and AS, Updates 3 through 5, 64-bit only Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4.0 WS, ES, and AS, 64-bit only Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4.0 WS, ES, and AS update 1, 32–bit and 64-bit SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 9, 32–bit and 64–bit SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 9 SP1, 32–bit and 64–bit SUSE Linux Professional 9.2 , 32–bit and 64–bit SUSE Linux Professional 9.3, 32–bit and 64–bit |
Recommended Switch Configuration
You can use a single VLAN-programmable switch to provide the management, provisioning, and data network infrastructure. However, for ease of management, you should install one VLAN-programmable switch for the management network, and a second VLAN-programmable switch for the provisioning and data network. Each management, provisioning, and data network should be assigned to separate subnets and VLANs.
Note –
In order to support firmware updates for the Sun Fire V20z and V40z provisionable servers, the management network switch should be configured to auto-negotiate link speed.
The management switch and the provisioning and data network switch should support the following Ethernet connectivity.
-
-
10/100-megabit per second connectivity from the management server to the management switch to provide connectivity to each provisionable server's management port
-
10/100-megabit per second connectivity from each provisionable server's management port to the management switch
The management network should be on a private subnet, and must provide connectivity to a management port on each provisionable server
-
-
Provisioning and Data Network Switch
-
1 gigabit per second connectivity from the management server ETH1 port to the provisioning and data switch
-
1 gigabit per second connectivity from each provisionable server ETH0 port to the provisioning and data switch
-
1 gigabit per second connectivity from each provisionable server ETH1 port to the provisioning and data switch
-
1 gigabit per second connectivity from the provisioning and data switch to the corporate network
Considerations:
-
The provisioning network should be on a private subnet.
-
The data network should be on a public subnet accessible by the management server, provisionable servers, and the corporate network.
Due to the use of the DHCP protocol and the bandwidth requirements for OS provisioning, isolating the data network from the provisioning network might be required.
-
OS provisioning of Linux might fail if a delay occurs in the transmission of data between the management server and the provisionable server. A long delay can result if the spanning tree option is enabled for the switch port connected to the ETH0 port of the provisionable server. To address this issue, you can disable the spanning tree option for the switch or for the switch ports connected to the provisionable servers. Refer to your switch documentation for instructions about how to disable the spanning tree feature on your switch.
-
Sun N1 System Manager Connection Information
This section provides the connectivity requirements for the Sun N1 System Manager servers.
Management Server Connections
A SPARC or x86 based server can be used as the management server. Each server provides at least one 10/100/1000 (1-Gbit) network interface port, but adding additional Gbit network interface cards to the management server increases ease of management and physical separation of the corporate and provisioning networks. If you do not install additional NICs in your management server, you can configure your network to route the corporate and provisioning networks through a single 1-Gbit port as illustrated by the diagrams in Reference Configurations.
Each server also provides one or two system management ports depending on server architecture, labeled Net Mgmt (Network Management), ALOM (Advanced Lights Out Manager port), or ILOM (Integrated Lights Out Manager port) on single management port provisionable servers, and labeled SP0 and SP1 (Service Processor 1 and 2) on dual management port provisionable servers. The management server requires only a single management port to provide connectivity with the corporate network. In this document, the management port is always shown as MGMT.
Note –
Depending on the system architecture and the operating system installed, the operating system refers to the Ethernet ports by different names. For example, the first Ethernet port on a machine is referred to as ETH0, HME0, or BGE0 depending on the operating system. This document refers to the lowest order Ethernet port on a machine as ETH0, the next port as ETH1 and so on regardless of architecture and operating system.
The following illustration provides the logical diagram for a management server with three 1-Gbyte NICs, and is used in subsequent sections to illustrate the reference architecture diagrams.
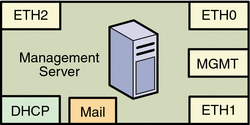
|
Provisionable Server Connections
A SPARC or x86–based server can be used as a provisionable server as described in Management Server Requirements. Each server provides one or two 10/100/1000 network interface ports. Each server also provides one or two system management ports depending on server architecture, labeled ALOM or ILOM on single management port provisionable servers, and labeled SP0 and SP1 on dual management port provisionable servers. In this document, the management port is always shown as MGMT.
The following illustration provides the logical diagram for a provisionable server with two 1-Gbyte NICs, and is used in subsequent sections to illustrate the reference architecture diagrams.
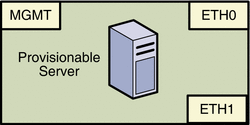
|
Reference Configurations
This section provides reference configuration diagrams and connectivity information for each reference configuration that will assist you in designing and connecting your N1 System Manager equipment.
Other configurations are possible, such as using separate switches for each network. You can implement your network using any combination of VLANs and switches. Each network, whether management, provisioning or data, should be assigned to separate VLANs.
Note –
In each of the following reference configurations, corporate access is shown as a connection to the management server. Alternatively, corporate access to the N1 System Manager can be provided through a switch instead of the management server.
Separate Management, Provisioning, and Data Networks
Figure 2–1 Separate Management, Provisioning, and Data Networks
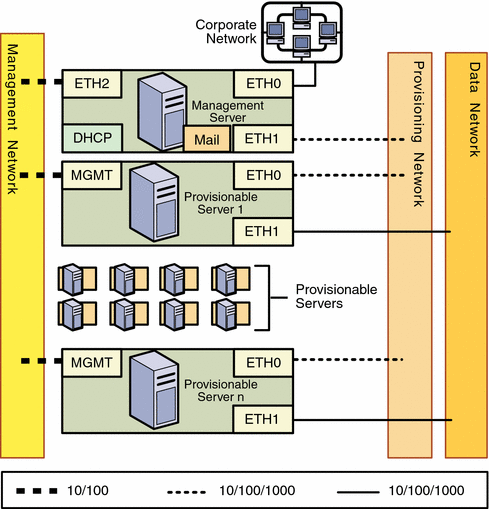
When designing a network, keep the following information in mind:
-
Configuring separate management, provisioning, and data networks is the best practice
-
Separate networks provide the highest security and the lowest number of points of failure
-
The data center DHCP service can be used to assign IP addresses to provisioned servers
Note –The management server DHCP service does not provide DHCP services for the data network. If you plan to dynamically configure IP services on the data network, you must provide an external DHCP server for the data network. You must not have another DHCP server on the same provisioning network.
-
You might need to install additional NICs in the management server and some provisionable servers to support this configuration
The following list summarizes the connectivity requirements for the separate management, provisioning, and data networks configuration.
-
Management Server
The management server should provide connectivity to the management network, provisioning network, and corporate network as follows:
-
ETH0 connects the management server to the corporate network to provide external access to the management server. The management server ETH0 IP address, netmask, and gateway should be configured to meet your corporate environment connectivity requirements. DNS configuration is performed during the N1 System Manager configuration process. ETH0 should be a 1-Gbit NIC interface.
-
ETH1 connects the management server to the provisioning network and should be on the same switch and network as the ETH0 connections of the provisionable servers. The management server ETH1 IP address, netmask, and gateway can be configured to support hundreds of provisionable servers. No devices other than the management server and the provisionable servers should reside on the provisioning network. ETH1 should be a 1-Gbit NIC interface.
-
ETH2 connects the management server to the management network and should be on the same switch and network as the management port connections of the provisionable servers. The management server connection is not required to be on the same switch as the management port connections of the provisionable servers as long as connectivity to the provisionable servers management port is provided. The management server ETH2 IP address, netmask, and gateway should be configured to enable connectivity to the provisionable server's management port IP addresses. ETH2 should be a 100-megabit NIC interface.
-
The management server DHCP service allocates IP addresses to the provisionable servers for loading operating systems.
-
The management server mail service enables ALOM architecture provisionable servers to send hardware monitoring information to the N1 System Manager over the management network.
-
-
Provisionable Server
Each provisionable server should provide connectivity to the management network, provisioning network, and data network as follows:
-
The management port connects the provisionable server to the management network and should be on the same switch and network as the ETH2 connection of the management server. The provisionable server management port connection is not required to be on the same switch as the ETH2 connection of the management server as long as connectivity to the management server ETH2 port is provided.
The management port should be a 100-megabit connection.
-
ETH0 connects the provisionable server to the provisioning network and must be on the same switch and network as the ETH1 connection of the management server.
ETH0 should be a 1-Gbyte connection.
-
ETH1 connects the provisionable server to the data network through the switch to provide external corporate network access to the provisionable server.
ETH1 should be a 1-Gbyte connection.
-
Combined Management and Provisioning Network, and a Separate Data Network
Figure 2–2 Combined Management and Provisioning Networks, and a Separate Data Network
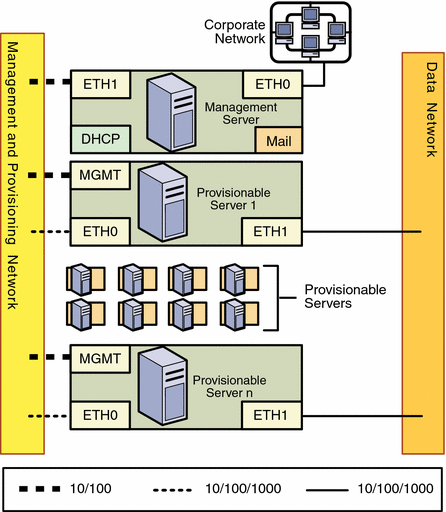
For this configuration:
-
An additional NIC does not need to be installed on the management server
-
The combined management and provisioning network reduces system and network security
-
The data center DHCP service can be used to assign IP addresses to provisioned servers
Note –The management server DHCP service does not provide DHCP services for the data network. If you plan to dynamically configure IP services on the data network, you must provide an external DHCP server for the data network. You must not have another DHCP server on the management and provisioning network.
The statically-assigned management IP addresses and the dynamically assigned IP addresses used during OS provisioning are part of the same network. The N1 System Manager does not manage IP addresses. You must ensure that the IP addresses used during provisioning do not conflict with the management network IP addresses.
The following list summarizes the connectivity requirements for the combined management and provisioning network and the separate data network configuration.
-
Management Server
The management server should provide connectivity to the management and provisioning network as follows:
-
ETH0 connects the management server to the corporate network to provide external access to the management server. The management server ETH0 IP address, netmask, and gateway should be configured to meet your corporate environment connectivity requirements. DNS configuration is performed during the N1 System Manager configuration process.
ETH0 should be a 1-Gbit NIC interface.
-
ETH1 connects the management server to the management and provisioning network and should be on the same switch and network as the MGMT and ETH0 connections of the provisionable servers. The management server ETH1 IP address, netmask, and gateway can be configured to support hundreds of provisionable servers. No devices other than the management server and the provisionable servers should reside on the management and provisioning network.
The management server ETH1 connection is not required to be on the same switch as the management port connections of the provisionable servers as long as connectivity to the provisionable server's management port is provided. The management server ETH1 IP address, netmask, and gateway should be configured to enable connectivity to the provisionable server's management port IP addresses.
ETH1 should be a 1-Gbit NIC interface.
-
The management server DHCP service allocates IP addresses to the provisionable servers for loading operating systems.
-
The management server mail service enables ALOM architecture provisionable servers to send hardware monitoring information to the N1 System Manager over the management network.
-
-
Provisionable Server
Each provisionable server should provide connectivity to the management and provisioning network and the separate data network as follows:
-
The management port connects the provisionable server to the management and provisioning network and should be on the same network as the ETH1 connection of the management server. The provisionable server management port connection is not required to be on the same switch as the ETH1 connection of the management server as long as connectivity to the management server ETH1 port is provided.
The management port should be a 100-megabit connection.
-
ETH0 connects the provisionable server to the management and provisioning network and must be on the same switch and network as the ETH1 connection of the management server.
ETH0 should be a 1-Gbyte connection.
-
ETH1 connects the provisionable server to the data network through the switch to provide external corporate network access to the provisionable server.
ETH1 should be a 1-Gbyte connection.
-
Combined Provisioning and Data Network, and a Separate Management Network
Figure 2–3 Combined Provisioning and Data Network, and a Separate Management Network
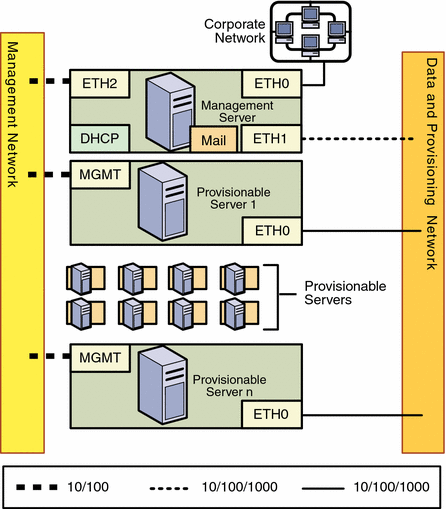
For this configuration:
-
The combined provisioning and data network reduces system and network security
-
The data network must use the N1 System Manager DHCP service
The N1 System Manager DHCP service must be the only DHCP service on the data network.
The following list summarizes the connectivity requirements for the combined data and provisioning network and the separate management network configuration.
-
Management Server
The management server should provide connectivity to the provisioning and data network and to the separate management network as follows:
-
ETH0 connects the management server to the corporate network to provide external access to the management server. The management server ETH0 IP address, netmask, and gateway should be configured to meet your corporate environment connectivity requirements. DNS configuration is performed during the N1 System Manager configuration process.
ETH0 should be a 1-Gbit NIC interface.
-
ETH1 connects the management server to the provisioning and data network and should be on the same switch and network as the ETH0 connections of the provisionable servers. The management server ETH1 IP address, netmask, and gateway can be configured to support hundreds of provisionable servers. No devices other than the management server and the provisionable servers should reside on the data and provisioning network.
ETH1 should be a 1–Gbit NIC interface.
-
ETH2 connects the management server to the management network and should be on the same switch and network as the management port connections of the provisionable servers. The management server connection is not required to be on the same switch as the management port connections of the provisionable servers as long as connectivity to the provisionable server's management port is provided. The management server ETH2 IP address, netmask, and gateway should be configured to enable connectivity to the provisionable server's management port IP addresses. ETH2 should be a 100-megabit NIC interface.
-
The management server mail service enables ALOM architecture provisionable servers to send hardware monitoring information to the N1 System Manager over the management network.
-
The management server DHCP service allocates IP addresses to the provisionable servers for loading operating systems.
-
-
Provisionable Server
Each provisionable server should provide connectivity to the management network and to the combined data and provisioning network as follows:
-
The management port connects the provisionable server to the management network and should be on the same network as the ETH2 connection of the management server. The provisionable server management port connection is not required to be on the same switch as the ETH2 connection of the management server as long as connectivity to the management server ETH2 port is provided.
The management port should be a 100-megabit connection.
-
ETH0 connects the provisionable server to the data and provisioning network to enable deployment of an operating system to the provisionable server, and to provide external corporate network access to the provisionable server. The provisionable server ETH0 connection must be on the same network as the ETH1 connection of the management server.
ETH0 should be a 1-Gbyte connection.
-
Combined Provisioning, Data, and Management Network
Figure 2–4 Combined Provisioning and Data Network, and a Separate Management Network
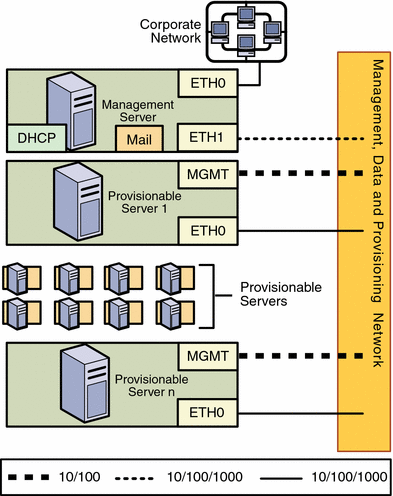
For this configuration:
-
An additional NIC does not need to be installed on the management server
-
The combined management, provisioning, and data networks greatly reduces system and network security
-
The data network must use the N1 System Manager DHCP service
The N1 System Manager DHCP service must be the only DHCP service on the data network.
The following list summarizes the connectivity requirements for the separate management, provisioning, and data networks configuration.
-
Management Server
The management server should provide connectivity to the combined management, provisioning, and data network and to the corporate network as follows.
-
ETH0 connects the management server to the corporate network to provide external access to the management server. The management server ETH0 IP address, netmask, and gateway should be configured to meet your corporate environment connectivity requirements. DNS configuration is performed during the N1 System Manager configuration process. ETH0 should be a 1-Gbit NIC interface.
-
ETH1 connects the management server to the comnbined management, provisioning, and data network and should be on the same network as the MGMT and ETH0 connections of the provisionable servers. The management server ETH1 IP address, netmask, and gateway should be configured to enable connectivity to the provisionable servers management port IP addresses, and can be configured to support hundreds of provisionable servers. The management server connection is not required to be on the same switch as the management port connections of the provisionable servers as long as connectivity to the provisionable server's management port is provided. No devices other than the management server and the provisionable servers should reside on the provisioning network. ETH1 should be a 1-Gbit NIC interface.
-
The management server mail service enables ALOM architectureprovisionable servers to send hardware monitoring information to the N1 System Manager over the management network.
-
The management server DHCP service allocates IP addresses to the provisionable servers for loading operating systems.
-
-
Provisionable Server
Each provisionable server should provide connectivity to the management network, provisioning network and data network as follows:
-
The management port connects the provisionable server to the management, provisioning, and data network and should be on the same switch and network as the ETH1 connection of the management server. The provisionable server management port connection is not required to be on the same switch as the ETH1 connection of the management server as long as connectivity to the management server ETH1 port is provided.
The management port should be a 100-megabit connection.
-
ETH0 connects the provisionable server to the management, provisioning, and data network, and must be on the same network as the ETH1 connection of the management server. ETH0 also connects the provisionable server to the data network through the switch to provide external corporate network access to the provisionable server.
ETH0 should be a 1-Gbyte connection.
-
Site Planning
This section provides guidelines for determining your management server and switch needs. The following topics are discussed:
Management Server Considerations
Hard drive capacity and the number of provisionable servers to be managed are the primary considerations for your management server.
-
Hard drive capacity is affected by two factors: the number of OS distributions that are to be provisioned, and the log files generated by each N1 System Manager job. OS distributions are stored in the/var file hierarchy on the management server. Allocate 3 Gbytes for each OS distribution and its associated profiles and scripts.
Sufficient disk space should also be allocated for the N1 System Manager event logs. Log file size depends on how you set up event monitoring and the amount of detail chosen for each log. The n1smconfig utility is used to configure logging during initial N1 System Manager configuration, and can subsequently be used after the system is in production to reconfigure logging. For further information, see Chapter 5, Monitoring Your Servers, in Sun N1 System Manager 1.2 Administration Guide.
-
System processing is affected by three major factors: The number of provisionable servers being managed, the types of monitoring being performed on the provisionable servers, and the number of jobs running on the management server.
The following table provides sizing guidelines for the management server.
Table 2–5 Management Server Hardware Sizing Guidelines|
Small scale deployment: 1 to 128 provisionable servers |
||
|
Total number of processors |
1 or more single-core AMD Opteron processors 1 or more 1x1 Ghz Ultra SPARC IIIi minimum |
|
|
Total memory |
4 Gbytes minimum |
|
|
Total file system space |
73 Gbytes minimum |
|
|
Media |
1 DVD ROM drive |
|
|
Qualified Models |
Sun Fire V20z, V40z, X2100, X4100, X4200, V210, V240, V440, and T1000 |
|
|
Sample Configuration |
Sun Fire V20z Single Processor (single-core) Opteron processor, 4 GB RAM, 1x73 GB HDD, DVD ROM Drive |
|
|
Medium scale deployment: 129 to 256 provisionable servers |
||
|
Total number of processors |
2 or more single-core AMD Opteron processors, or 1 or more dual-core AMD Opteron processors 2 or more 1x1 Ghz Ultra SPARC IIIi minimum |
|
|
Total memory |
8 Gbytes minimum |
|
|
Total file system space |
146 Gbytes minimum |
|
|
Media |
1 DVD ROM drive |
|
|
Qualified Models |
Sun Fire V20z, V40z, X4100, X4200, V210, V240, V280, V440, and T2000 |
|
|
Sample Configuration |
Sun Fire V40z Dual Processor (dual-core), 8 GB RAM, 1x146 GB HDD, DVD ROM Drive |
|
|
Large scale deployment: 257 to 512 provisionable servers |
||
|
Total number of processors |
4 single-core AMD Opteron processors, or 2 or more dual-core AMD Opteron processors 4 1x1 Ghz Ultra SPARC IIIi minimum |
|
|
Total memory |
16 Gbytes minimum |
|
|
Total file system space |
300 Gbytes minimum |
|
|
Media |
1 DVD ROM drive |
|
|
Qualified Models |
Sun Fire V20z, V40z, X4100, X4200, V440, and T2000 |
|
|
Sample Configuration |
Sun Fire V40z Dual Processor (dual-core), 16 GB RAM, 1x300 GB HDD, DVD ROM Drive |
|
Switch Considerations
Switch requirements are determined by the following factors:
-
Whether you have added a third 1–Gbit NIC to the management server
-
The number of management ports on each provisionable server
-
The number of provisionable servers to be connected to the switch
The Sun Fire V20z and V40z servers have two management ports, and subsequently can be daisy-chained. For further information, see Appendix A, Alternate Sun Fire V20z and V40z Reference Configuration.
-
The network topology you have chosen
The following worksheet can assist you in determining the total number of switch ports by type that you will need on your switch or switches.
Table 2–6 Switch Port Requirements Worksheet
Use the above totals to determine your switch requirements, and then connect the servers and switches according to your site plan.
Setting Up Provisionable Servers
Before you can use the N1 System Manager to discover provisionable servers, each provisionable server must be set up as follows:
-
An IP address must be assigned to each provisionable server's management port.
Refer to your provisionable server documentation for management port IP address assignment. You can also locate the server documentation online at http://sunsolve.sun.com/handbook_pub/Systems/.
-
The telnet account credentials must be configured for the management processor of SPARC architecture provisionable servers.
Refer to your provisionable server documentation for configuring the telnet management processor credentials on SPARC architecture servers.
Automatic configuration of credentials is supported for Sun Fire V20z and V40z servers if they are in the factory default state. If you do specify the login accounts and passwords for discovery of a Sun Fire V20z or V40z, the discovery process configures the Sun Fire V20z or V40z using the credentials you provide.
Discovery of a provisionable server will fail if the server's management port has not been assigned an IP address.
Discovery of a SPARC architecture provisionable server will fail if the management processor telnet credentials have not been configured.
If provisionable server credentials are not specified when running discovery, the discovery process uses the default credentials shown in the following tables.
Table 2–7 SPARC Architecture Provisionable Server Default Credentials|
Type |
Telnet Login |
Telnet Password |
|---|---|---|
|
Netra 240 and 440 |
admin |
admin |
|
Sun Fire V210, V240, and V440 |
admin |
admin |
|
Sun Fire T1000 and T2000 |
admin |
admin |
Table 2–8 x86 Architecture Provisionable Server Default Credentials
|
Type |
SSH Login |
SSH Password |
IPMI Login |
IPMI Password |
SNMP Read Community String |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Sun Fire V20z and V40z |
admin |
admin |
- |
admin |
public |
|
Sun Fire X2100 |
- |
- |
Admin |
admin |
- |
|
Sun Fire X4100 and X4200 |
root |
changeme |
root |
changeme |
public |
If only one credential is specified for x86 architecture provisionable servers, the missing credential is configured with one of the defaults specified above.
ALOM-based provisionable servers do not support SNMP, and therefore use the mail service on the management server to send hardware notifications to the N1 System Manager.
Although the Sun Fire X2100 does not support SNMP, the X2100 does support IPMI platform event trap (PET), which generates SNMP V1 traps for IPMI events. The N1 System Manager listens for the X2100 IPMI events.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
