| C H A P T E R 3 |
|
System Power On and Setup |
This chapter provides information to enable you to power on your system for the first time and perform software setup procedures using the system controller command-line interface. For instructions on how to subsequently power on your system, see To Power On the System.
|
Note - When you are setting up your system for the first time, it is strongly suggested that you bring up the one domain set up for you, domain A, by installing the Solaris operating environment in that domain and then booting it before creating additional domains.
|
This chapter contains the following topics:
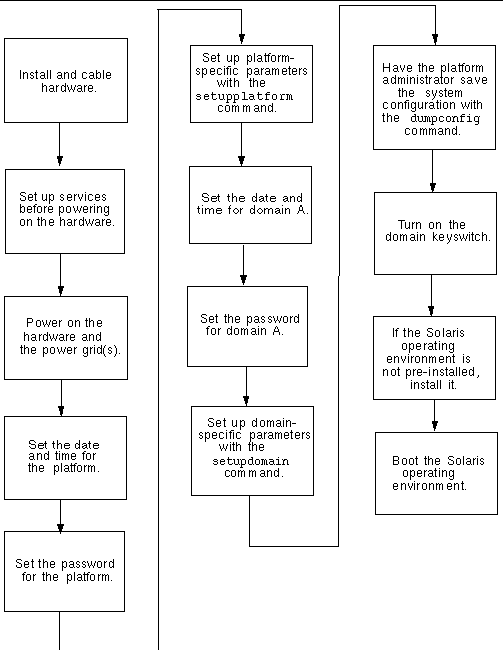
FIGURE 3-1 is a flowchart summarizing the major steps you must perform to power on and set up the system. These steps are explained in the procedures presented in this chapter.
This section contains the following procedures:
1. Refer to the installation guide for your system and connect a terminal to your system using the serial port.
2. When you set up the terminal, set the ASCII terminal to the same baud rate as the serial port.
The default serial port settings for the System Controller board are:
Because this is the platform console connection, log messages are displayed.
 Before you power on the system for the first time, set up the services described in TABLE 3-1.
Before you power on the system for the first time, set up the services described in TABLE 3-1.
 Complete the hardware power-on steps detailed and illustrated in the installation guide for your system.
Complete the hardware power-on steps detailed and illustrated in the installation guide for your system.
1. Access the system controller and connect to the system controller main menu.
See Establishing Connections to the SC.
2. Connect to the platform shell.
3. Power on the power grid or grids.
The poweron gridx command powers on power supplies in grid x.
The poweron grid0 system controller command powers on power supplies in power grid 0.
After powering on the power grids, set up your system using the commands described in this chapter.
|
Note - To ensure that you choose the optimum security settings (such as the selection of a remote connection protocol: SSH or Telnet) when you set up the platform, review Chapter 6 before proceeding. |
This section contains the following procedures:
Although you can set a different date and time for the platform and for each domain, it is strongly suggested that you use the same date and time for the platform and domains. Using the same date and time for the platform shell and each domain shell may help during interpretation of error messages and logs. The date and time set on the domains are also used by the Solaris operating environment.
If you have a redundant SC configuration, the platform date and time settings on both the main and spare system controller must always be synchronized for SC failover purposes. Sun strongly suggests that you configure both the main and spare system controller to synchronize their date and time settings against a Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) server.
SNTP, described in RFC 2030, is an adaptation of the Network Time Protocol (NTP), described in RFC 1305. SNTP does not change the NTP specification, but it clarifies certain design features of NTP to allow operation in a simple, stateless remote-procedure call (RPC) mode. SNTP clients such as the Sun Fire midrange SC can interoperate with existing NTP or SNTP clients and servers. SNTP is intended to be used only at the extremities of the time synchronization subnet.
NTP concepts are more fully described in the following Sun BluePrints OnLine articles:
These articles are available at:
For details on the setupplatform command, refer to the Sun Fire Midrange System Controller Command Reference Manual.
By configuring SNTP on the SCs, the SCs will periodically check the SNTP server to ensure that their date and time are accurate and synchronized. If the main and spare SC do not have the same date and time and an SC failover occurs, a time jump may occur in running domains.
The system controller password that you set for the main SC also serves as the same password for the spare SC.
1. From the platform shell, type the system controller password command.
2. At the Enter new password: prompt, type in your password.
3. At the Enter new password again: prompt, type in your password again.
For examples, refer to the password command in the Sun Fire Midrange System Controller Command Reference Manual.
|
Note - One of the platform configuration parameters that can be set through the setupplatform command is the partition parameter. Determine if you want to set up your system with one partition or two partitions. Read Domains and Segments before completing the following steps. |
1. From the platform shell, type setupplatform.
For a description of the setupplatform parameter values and an example of this command, refer to the setupplatform command in the Sun Fire Midrange System Controller Command Reference Manual.
|
Note - If you press the Return key after each parameter, the current value will not be changed. If you type a dash (), this clears the entry (if the entry can be blank). |
2. If you have a second System Controller board installed, run the setupplatform command on the second system controller.
All the parameters, except for the network settings (such as the IP address and host name of the system controller) and the POST diag level, are copied from the main system controller to the spare, only when SC failover is enabled.
This section contains the following procedures on setting up domain A.
For more information, see System Controller Navigation.
 Type the setdate command in the domain A shell to set the date and time for the domain.
Type the setdate command in the domain A shell to set the date and time for the domain.
|
Note - Because you can have up to four domains on an E6900 or 6800 system, you must eventually set the date and time for each domain. To start, just set the date and time for domain A. |
For command syntax and examples, refer to the setdate command description in the Sun Fire Midrange System Controller Command Reference Manual and the To Set the Date, Time, and Time Zone for the Platform.
1. From the domain A shell, type the password command (CODE EXAMPLE 3-1).
2. At the Enter new password: prompt, type your password.
3. At the Enter new password again: prompt, type your password again (CODE EXAMPLE 3-1).
schostname:A> password Enter new password: Enter new password again: schostname:A> |
1. From the domain A shell, type the setupdomain command.
For a listing of parameter values and sample output, refer to the setupdomain command description in the Sun Fire Midrange System Controller Command Reference Manual.
To facilitate the ability to restore domain A, set the following setupdomain parameter value as indicated:
All system board components are tested with all tests and test patterns, except for memory and Ecache modules. For memory and Ecache modules, all locations are tested with multiple patterns. More extensive, time-consuming algorithms are not run at this level.
When a hardware error occurs, the system controller pauses the domain. This setting controls the automatic restoration of domains after the auto-diagnosis (AD) engine identifies and, if possible, deconfigures components associated with a domain hardware error. See Automatic Diagnosis and Recovery Overview for details.
The system controller automatically resets a hung domain when the domain does not respond to interrupts or the domain heartbeat stops.
2. Perform steps listed in TABLE 3-2.
|
This section describes how to use the dumpconfig command, which must be run by the platform administrator, to save the current system controller (SC) configuration to a server. Use dumpconfig to save the SC configuration for recovery purposes.
Use the dumpconfig command when you perform any of the following tasks:
|
|
Use dumpconfig to save the platform and domain configurations to a server so that you can restore the platform and domain configurations to a replacement system controller (if the current system controller fails).
|
Note - Do not save the configuration to any domain on the platform, because the domain will not be available if the platform fails. |
 Type the system controller dumpconfig command from the platform shell to save the present system controller configuration to a server.
Type the system controller dumpconfig command from the platform shell to save the present system controller configuration to a server.
For details, refer to the dumpconfig command description in the Sun Fire Midrange System Controller Command Reference Manual.
See To Navigate Between The Platform Shell And a Domain.
2. Turn the domain A keyswitch to the on position. Type setkeyswitch on.
The setkeyswitch on command powers on the domain. If the OpenBoot PROM auto-boot? parameter is set to true, you might obtain an error message similar to CODE EXAMPLE 3-2.
{0} ok boot ERROR: Illegal Instruction debugger entered. {0} ok |
The OpenBoot PROM (OBP) displays this error message because the Solaris operating environment might not yet be installed, or perhaps you are booting off the wrong disk. For more information on OBP parameters, refer to the setupdomain command description in the Sun Fire Midrange System Controller Command Reference Manual and also the OpenBoot Command Reference Manual included with your Solaris operating environment release.
3. Insert the CD for the Solaris operating environment into the CD-ROM drive.
4. Install the Solaris operating environment on your system.
Refer to the Solaris Installation Guide included with your operating environment release.
5. Boot the Solaris operating system by typing the OpenBoot PROM boot cdrom command at the ok prompt.
Copyright © 2004, Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved.