Administering Users
You can administer users through either the SMC User Tool applications or from the command line. This section is divided into these parts:
Note -
To administer users, you need the User Manager rights profile (for general user attributes) and the User Security rights profile (for security-related attributes).
Default User Attributes
The task of entering new users is greatly simplified by setting up default user attributes so that only those attributes unique to a specific user need be added. There are three mechanisms for setting up defaults:
-
policy.conf(4) database--lets you specify authorizations, rights profiles, password generation, account locking, label display, and unattended workstation controls.
-
label_encodings(4) database--lets you specify default values for user clearances and minimum SLs and public alternative names for ADMIN_HIGH and ADMIN_LOW.
-
user templates--let you specify all user properties not covered by the policy.conf(4) and the label_encodings(4) databases except properties specific to a user such as user name and ID.
The tools for creating new users are the Add User With Wizard... and Add User From Template... menu options. The wizard approach offers simplicity but with these tradeoffs:
-
The login shell defaults to Bourne.
-
It does not set a skeleton path for initialization files.
-
Secondary groups are not set.
The user template approach offers a larger set of user properties, but requires you to set up one or more templates of default user attributes ahead of time. Both methods should be used in conjunction with the policy.conf(4) and the label_encodings(4) databases. The User Properties dialog box lets you make modifications after the initial user information has been entered.
User Attribute Databases
The user information is held in the following databases:
-
user_attr(4)--The /etc/user_attr file contains extended user attributes, using a keyword=value format.
-
auth_attr(4)--The /etc/security/auth_attr file contains the definitions of authorizations, which can be included in rights profiles.
-
prof_attr(4)--The /etc/security/prof_attr file contains the name, description, authorizations, subordinate rights profiles, and help files for rights profiles.
These databases can be edited manually, although this practice is not generally recommended.
The following figure shows how the databases work together to provide user attributes.
Figure 2-5 User Database Relationships
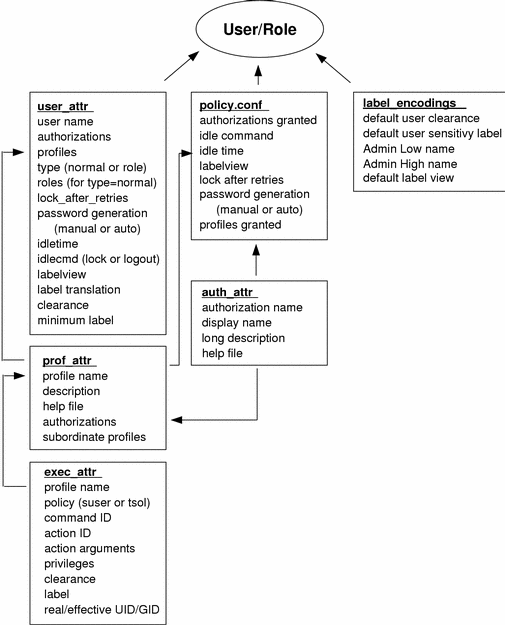
The user_attr database contains the attributes shown, including a comma-separated list of profile names. The contents of the profiles are split between the prof_attr file, which contains profile identification information, authorizations assigned to the profile, and subordinate profiles, and the exec_attr file, which contains commands and actions with their associated security attributes. The auth_attr file supplies available authorizations to the prof_attr file and the policy.conf file. (Note that although you can assign authorizations directly to users through user_attr, this practice is discouraged.) The policy.conf file supplies default attributes to be applied to all users. The label_encodings file supplies label defaults if they are not otherwise specified.
Managing Users from the Command Line
The user files can also be managed from the command line. The smuser(1M) command adds, modifies, deletes, and lists user information. You can use smmultiuser(1M) to enter a batch of users.
Managing Users through the SMC
This section describes the SMC User Tool collection and selected dialog boxes as follows:
For complete descriptions of elements in the User Tool collection, refer to the online help.
User Tool Collection Summary
The SMC User Tool collection is shown in the following figure.
Figure 2-6 SMC User Tool Collection
The six dialog boxes in the User Tool collection are:
-
Administrative Roles dialog box--Lets you create or edit a role account and assign users to roles. Note that the roles data is the same as the user data except that (1) there is no Roles tab since roles cannot be assigned to other roles, (2) there is no Password Options tab because these are not appropriate for roles, and (3) the Roles dialog box has a Users tab for assigning users to the role.
-
Groups dialog box--Lets you create or edit user groups and change the members in the group.
-
Mailing Lists dialog box--Lets you create or edit mail aliases, including changing the recipients in the list.
-
Rights dialog box--Lets you create or edit a rights profile. See "Right Properties Dialog Box" for an example of the Rights Properties dialog box and a description of the rights profile data.
-
User Accounts dialog box--Lets you add new users singly or in a batch, with or without a template, and lets you edit the properties of existing users. See "User Properties Dialog Box" for an example of the User Properties dialog box and a description of the user data.
-
User Templates dialog box--Lets you create a named set of user properties that can be applied to new users to facilitate data entry.
User Properties Dialog Box
The User Properties dialog box is shown below with the General tab selected.
Figure 2-7 User Properties Dialog Box
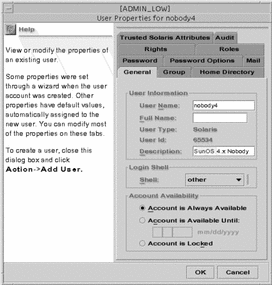
The following table describes the purpose of each tab in the User Properties dialog box.
Table 2-2 User Properties Summary|
Tab |
Description |
|---|---|
|
General |
Specifies the user, the default login shell, and the account availability. |
|
Group |
Sets the user's primary and secondary groups for the purpose of accessing and creating files and directories. |
|
Home Directory |
Specifies the user's home directory, home directory server, automounting, and directory access. |
|
Password |
Specifies whether the user or the adminstrator will select the first password and whether the selection and changes will be manual or from the password generator. |
|
Password Options |
Sets the time limits and requirements for password changes. |
|
|
Specifies the server that provides email and the mailbox in which it is received. |
|
Rights |
Allows rights profiles to be assigned to the user. The precedence of the assigned rights profiles can be changed. |
|
Roles |
Allows available roles to be assigned to the user. |
|
Trusted Solaris Attributes |
Specifies the clearance and minimum label at which the user can operate and how labels are displayed to the user. Also specifies a time limit for which a workstation may remain idle and the action taken when the limit is reached. |
|
Audit |
Specifies the audit classes for which the user is to be audited. |
Right Properties Dialog Box
The Rights Properties dialog box is shown below with the General tab selected.
Figure 2-8 Rights Properties Dialog Box
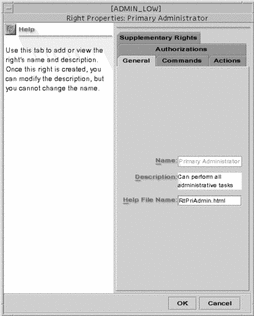
The following table describes the purpose of each tab in the Right Properties dialog box
Table 2-3 Rights Manager Dialog Box Summary|
Tab |
Description |
|---|---|
|
General |
Identifies and describes the rights profile and provides the name of the help file used to explain it. |
|
Commands |
Assigns commands to the rights profile and adds security attributes (effective and real UIDs and GIDs; minimum label and clearance; and inheritable privileges) to specific commands in the profile. |
|
Actions |
Assigns CDE actions to the rights profile and adds security attributes (effective and real UIDs and GIDs; minimum label and clearance; and inheritable privileges) to specific actions in the profile. |
|
Authorizations |
Assigns authorizations to the profile. |
|
Supplementary Rights |
Specifies other rights profiles to be contained within the current rights profile. |
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
