Troubleshooting Mail Problems
Tracing Mail Delivery Difficulties
Trusted Solaris 8 4/01 software checks host and user labels before sending or forwarding mail.
-
The software checks that the mail is within the accreditation range of that host, as described in the following list and in Chapter 8, Specifying Routing and Security for Remote Computers.
-
The software checks that the mail is between the account's clearance and minimum label.
See "To Troubleshoot Mail Delivery Difficulties" for specific guidelines in debugging label difficulties.
Tracing sendmail's Activities
Multiple instances of sendmail are involved in local and remote mail delivery. To aid in debugging any problems with sendmail, Figure 6-1 shows how data flows through the sendmail processes.
Any mailer that is used to send mail (the default is dtmail) starts an instance of sendmail. This instance of sendmail attempts to deliver any mail that originates on the host, storing it in the local /var/spool/mqueue MLD until it is delivered [1 in Figure 6-1 shows this instance of sendmail]. Normally the message is delivered right away so its stay in the queue is only a matter of seconds. However, if the remote host is down, mail can stay in the queue indefinitely.
An instance of the sendmail program also starts when the system is booted. This instance of sendmail listens at port 25 and attempts to deliver any mail that it receives from a remote host, also storing each message in the mail queue MLD until it is delivered [3 and 5 in the example].
Yet another instance of sendmail periodically scans the mail queue and attempts to deliver any mail in the queue [2 and 4 in the example]. The following figure shows some of the sendmail processes on three hosts: cascade, trustworthy, and juggle. Host trustworthy is the mail relay host for juggle.
Figure 6-1 Sendmail Data Flow Example
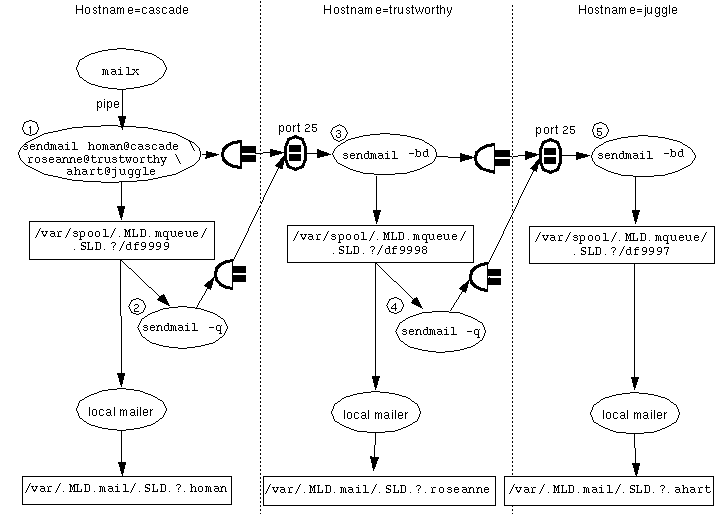
When mail is sent to username@hostname and hostname is a remote host, sendmail forwards the message to port 25 of hostname. In the example, when mail addressed to homan@cascade is sent from another account on host cascade, sendmail #1 puts the mail into an SLD within the /var/spool/.MLD.mqueue on cascade, where it is delivered by a local mailer. sendmail #2 on cascade periodically polls the queue and delivers mail that could not get delivered right away. sendmail #3 and #5 on hosts trustworthy and juggle listen on port 25 for incoming mail. The messages originating on cascade that are addressed to hosts trustworthy and juggle are both put into the local /var/spool/.MLD.mqueue and sent to port 25 of trusted, which is acting as a mail relay host in this example. The sendmail #3 on trusted also puts both messages into an SLD within the local /var/spool/mqueue, where the message to roseanne@trustworthy is delivered by the local mailer and the message to ahart@juggle is forwarded to sendmail #5, which is listening at port 25 of juggle.
Debugging sendmail
Debugging sendmail using the -d option is described in the sendmail Nutshell Handbook published by O'Reilly & Associates, Inc. To review briefly, you can get debugging information by specifying sendmail with the -d option followed by X. To limit the output of sendmail -d to a specific aspect of sendmail's behavior, you can specify a category optionally followed by a dot (.) followed by a level from 0-9, with 9 meaning the most information. Category 75, which is unique to the Trusted Solaris version of sendmail, selects Trusted Solaris debugging information.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
