Prerequisites
Provisioning an operating system using the OS provisioning plug-in requires that you have a basic understanding of system administration and networking. In addition, to provision the operating system requires that basic IP connectivity exists between the machines.
Basic OS Provisioning Environment
The basic OS provisioning environment has the following requirements:
-
N1 Grid SPS Master Server — A system upon which the N1 Grid Service Provisioning System software is installed and that is configured to run as a Master Server.
-
OS provisioning server — A Solaris 9 9/04 (or later) system upon which the OS provisioning server is installed through the plug-in. The OS provisioning server runs DHCP services to respond to target host requests.
-
Solaris boot and install server — To provision Solaris systems, you need a Solaris boot and install server on which Solaris 9 9/04 or later is installed.
-
Linux boot and install server — To provision Linux systems, you need a Linux boot and install server on which Linux is installed.
-
Windows boot and install server — To provision Windows systems, you need a Windows boot and install server on which Windows 2003 is installed.
-
The OS provisioning server, boot and install servers, and provisioning targets must be accessible in a network through a native LAN, a VLAN or through routers. Refer to the appropriate networking and operating system documentation for more information about configuring your network.
-
DHCP packets from the provisioning targets must be able to reach the OS provisioning server.
Note –
The N1 Grid SPS Master Server, OS provisioning server, and Solaris boot and install server can be one physical system. However, running all three servers on one system increases the load on the server and increases the network traffic that the server has to handle. Keeping them separate enables you to scale better in the future.
Target Hosts
You need to set up provisionable target systems for OS provisioning. The OS provisioning server needs to know information about these targets, such as MAC address, GUID, remote management connections, and access information. For information about defining targets, see Chapter 8, Target Hosts for OS Provisioning.
Network
The OS provisioning plug-in is designed to work with a wide range of network configurations and topologies. As such, the plug-in does not dictate any network topology nor does it manipulate network elements like switches or routers for its needs. However, the plug-in relies on the existence of some network communication:
-
Layer 2 connectivity between the provisioning interface of the OS provisioning server and the provisioning interface of the target host
-
IP connectivity between the provisioning interface of the boot and install server and the provisioning interface of the target host
-
IP connectivity between the OS provisioning server, the network management port of the target host, and the control network interface of the boot and install server
These requirements on the networking infrastructure are imposed by the needs of the two network types central to the function of the OS provisioning server. Those network types are the control network and the provisioning network.
Note –
An access network is the network used to access the OS provisioning and boot and install servers. An example of an access network is the corporate intranet. This network is not needed for OS provisioning functionality. From a security standpoint, you should keep the access network separate from the control and provisioning networks.
The following diagram illustrates the network environment.
Figure 3–1 Network Environment Diagram for OS Provisioning
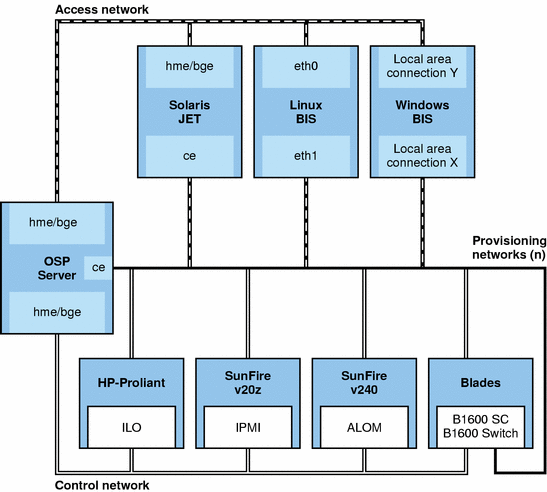
Provisioning Network
A provisioning network is comprised of the provisioning interface of the OS provisioning server, the provisioning interfaces of the target platforms, and the provisioning interfaces of one or more boot and install servers. The provisioning network can be comprised of one or more subnets. An OS provisioning plug-in installation supports the use of multiple provisioning networks for OS provisioning. The protocols and technologies that are required for network-based provisioning dictate the requirements of these provisioning networks. These requirements are:
-
The provisioning interface of the OS provisioning server and the provisioning interfaces of the target platform should be in a common Layer 2 broadcast domain,
-
The boot and install servers provisioning interface serving the host should have IP connectivity to the subnet of the target platforms' provisioning interface. This can be achieved by one of two ways:
-
The boot and install server has a network interface in the provisioning subnet,
-
The boot and install server has a provisioning interface that is reachable from the provisioning subnet by means of routing.
-
Control Network
The control network is the network used by the OS provisioning server for two primary functions:
-
Managing the network management port of the target host to control power state, boot order, and console of the target platform
-
Configuring the boot and install servers for provisioning activity
The control network can be a pure IP network or may have serial/terminal server elements. The OS provisioning server communicates with the boot and install servers over an IP network. At the same time, communication with the network management port of the target host may occur over an IP network or a serial network. The control network can span many subnets. The only requirement on the control network is that all boot and install servers and target network management ports can be routed from the OS provisioning server.
Switched Networks
The above requirements take on special meaning in a switched environment. In a switched network, the switched connections can be in either trunk or access (non-trunk) modes. For the control network, switched connections can be in access mode because IP routing from the OS provisioning server is all that is required. The provisioning network can have switched ports in either trunk or access modes depending on the provisioning network design.
Security
The OS provisioning plug-in software leverages the N1 Grid SPS security model. Most communication between the different servers occurs through the N1 Grid SPS Remote Agents (RAs). Configure the RAs for secure communication. See documents for more information on how to enable secure communication between the Master Server and the RAs.
For remote management of the targets, the encrypted passwords are stored on the OS provisioning server. For information about encrypting the passwords, see Password Encryption.
For communication with the Windows boot and install server, you need to activate either RSH or SSH services. Use SSH services to secure communications between the OS provisioning server and Windows boot and install server. For information, see How to Install Windows SSH Server on the Windows RIS Server.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
