| C H A P T E R 1 |
|
Introduction |
This chapter provides an overview of the Sun StorageTek PCI Express SAS 8-Channel Internal HBA (SG-XPCIE8SAS-I-Z).
PCI Express SAS 8-Channel Internal HBA (SG-XPCIE8SAS-I-Z).
The SG-XPCIE8SAS-I-Z is a host bus adapter (HBA) in the form of a PCI Express card that can be delivered with a spectrum of Sun servers and workstations. As a disk controller, it is chosen because of its ability to create hardware RAID (Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks) configurations that are faster than RAID configurations created with software.
This chapter contains the following sections:
The Sun StorageTek PCI Express SAS 8-Channel HBA (SG-XPCIE8SAS-I-Z) is a low-profile adapter that provides connectivity to a server’s internal disks. The SG-XPCIE8SAS-I-Z provides eight-channel SAS connectivity for the Solaris , Linux, and Windows OS.
, Linux, and Windows OS.
A simplified view of the board is shown in FIGURE 1-1.
FIGURE 1-1 Sun StorageTek PCI Express SAS 8-Channel HBA
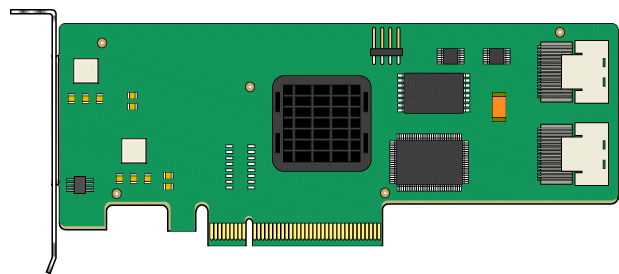
The SG-XPCIE8SAS-I-Z includes the following features:
The PCI Express interface is compliant with the PCI Express Specification, revision 1.0a. All PCI software is backward compliant with previous versions of the PCI Express specifications. The PCIe to SAS HBA interface is compatible with the ANSI Serial Attached SCSI Specification, revision 1.0 and the Serial ATA Specification, revision 1.0a.
The SG-XPCIE8SAS-I-Z HBA is based on LSI’s 1068E chip.
The HBA can create hardware RAID volumes of types RAID 0, 1, or 1E. There are various ways you can create these volumes:
The SG-XPCIE8SAS-I-Z HBA can create two and only two volumes. The two volumes can contain up to 12 disks total plus zero, one, or two hot spares (no more than 14 disks).
RAID 0 can have two to 10 striped disks.
RAID 1 can have two mirrored disks plus zero, one, or two hot spares. Only two disks are permitted in a RAID 1 mirror.
RAID 1E can have up to 12 mirrored disks plus zero, one, or two hot spares, if all disks are in one volume and there is no other volume. RAID 1E requires a minimum of three disks.
You can simultaneously have one volume of RAID 0 and another of either RAID 1 or 1E.
| Note - The Sun LSI 106x RAID User’s Guide (document number 820-4933) describes the different types of RAID volumes in detail. This guide can be found in the collection of documents for your server at http://docs.sun.com. |
The SG-XPCIE8SAS-I-Z can simultaneously address RAID volumes and individual disks that are not in RAID volumes.
If you want to mirror your boot disk, you should create the RAID volume before you install your OS. There is an LSI RAID configuration utility you can use to do this. It is entered from the server’s BIOS and can be used for any Linux, Solaris, or Windows operating system.
| Note - If you want to migrate your boot disk to a RAID volume you create after installing the OS, you must save space at the end of the boot disk for this purpose. |
|
1. Power off your server and then power it back on. The BIOS screen appears. Watch for the LSI Logic Corp. screen.
FIGURE 1-2 Opening Screen of a Typical Server BIOS

2. When the BIOS screen shows the LSI Logic Corp. message, press Ctrl-C to start the LSI Logic Configuration Utility (see FIGURE 1-3).
FIGURE 1-3 BIOS Screen Showing LSI Logic Corp. Message

3. Follow the on-screen instructions to create a mirrored RAID.
You can choose between RAID 1 (two mirrored disks with zero, one, or two hot spares) or RAID 1E (three or more mirrored disks with zero, one, or two hot spares).
4. Exit the LSI RAID configuration utility.
5. Install your OS on this RAID volume.
The LSI BIOS RAID configuration utility is described in detail in the Sun LSI 106x RAID User’s Guide (820-4933), which is in the collection of documents for your server at http://docs.sun.com.
This guide also covers the use of the MegaRAID Storage Manager (MSM) for Linux and Windows operating systems, and the Solaris utility raidctl.
Copyright © 2009 Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved.