| C H A P T E R 2 |
|
ILOM Network Configurations |
|
Learn about ILOM network communication settings and network port assignments |
|
|
Learn about configuring ILOM in a dual-stack IPv4/IPv6 network environment |
|
|
Oracle Integrated Lights Out Manager (ILOM) 3.0 Getting Started Guide (820-5523-10) |
||
|
Oracle Integrated Lights Out Manager (ILOM) 3.0 CLI Procedures Guide (820-6412) |
||
|
Oracle Integrated Lights Out Manager (ILOM) 3.0 Web Interface Procedures Guide (820-6411) |
||
|
Oracle Integrated Lights Out Manager (ILOM) 3.0 Management Protocols Reference Guide (820-6413) |
||
|
The ILOM 3.0 Documentation Collection is available at: http://docs.sun.com/app/docs/prod/int.lights.mgr30#hic |
||
You can establish communication with ILOM through a console connection to the serial management port on the server or chassis monitoring module (CMM), or through an Ethernet connection to the network management port on the server or CMM.
A dedicated network management port will help you manage your server platform optimally with ILOM. Using the network management port, traffic destined for ILOM is kept separate from any data transfers made by the host operating system.
Refer to your platform documentation to determine how to connect to your network management port.
You can use Dynamic DNS to automatically assign a host name and IP address on new ILOM installations based on the system’s serial number. See Appendix A for an overview of Dynamic DNS and configuration instructions.
The way in which you connect to ILOM depends on your server platform. Refer to your platform documentation for details.
The following table lists the different methods you can use to connect to ILOM.
|
Connect to the Ethernet network management port. You must know ILOM’s host name or IP address. |
||||
|
Verify support for this feature in your platform ILOM Supplement Guide or Administration Guide. |
Enables you to connect to ILOM directly from the host operating system without the need of a physical network connection to the server SP. This feature is not supported on all Sun servers. For more information, see Local Interconnect Interface: Local Connection to ILOM From Host OS. |
|||
The worksheet in TABLE 2-2 describes the information that you need to establish initial communication with ILOM
|
Mandatory - if network environment does not support IPv4 DHCP or IPv6 stateless |
ILOM, by default, learns the IPv4 network address using DHCP and the IPv6 network address using IPv6 stateless. If your network environment does not support IPv4 DHCP or IPv6 stateless, you must establish a local serial console connection to ILOM via the serial management port on the server or Chassis Monitoring Module (CMM). If your network environment supports IPv4 DHCP or IPv6 stateless, see the setup information for Management Connection - Ethernet (below). For more information about how to attach a serial console to a server or CMM, refer to your platform documentation. |
|
|
You can access ILOM remotely when using the IP address, host name, or local link address assigned to the server SP. This method requires a connection from your local area network to the Ethernet network management port (NET MGT) on the server or CMM. To establish a physical network connection to your server, refer to the installation documentation provided for your server or CMM. |
||
|
You can assign a meaningful host name to a server SP. For more information, see the Oracle Integrated Lights Out Manager (ILOM) 3.0 CLI Procedures Guide or the Oracle Integrated Lights Out Manager (ILOM) 3.0 Web Interface Procedures Guide. |
||
|
You can assign a system identifier (meaningful name) to a Sun server. For more information, see the Oracle Integrated Lights Out Manager (ILOM) 3.0 CLI Procedures Guide or the Oracle Integrated Lights Out Manager (ILOM) 3.0 Web Interface Procedures Guide. |
||
|
You can configure Dynamic DNS to support the use of host names to access server SPs. For example information about setting up Dynamic DNS, see Appendix A. For Dynamic DNS configuration procedures, see Oracle Integrated Lights Out Manager (ILOM) 3.0 CLI Procedures Guide. |
TABLE 2-3 identifies the default network ports used by ILOM. Most of these network ports are configurable.
| Note - TABLE 2-3 identifies default network ports as of ILOM 3.0.6. Some network ports might not be available if you are not using ILOM 3.0.6 or a later version of ILOM. |
ILOM supports the ability on some Sun servers to switch the serial port output from the server between the SP console (SER MGT) and the host console (COM1). This is referred to as serial port sharing. By default, the SP console is connected to the system serial port. This feature is beneficial for Windows kernel debugging, as it enables you to view non-ASCII character traffic from the host console.
For more information and procedures for switching the serial port output, see the Oracle Integrated Lights Out Manager (ILOM) 3.0 CLI Procedures Guide
You can use the ILOM CLI interface, web interface, or SNMP to manage ILOM’s communication settings, including network, serial port, web, and Secure Shell (SSH) configurations. ILOM lets you view and configure system host names, IP addresses, DNS settings, and serial port settings. You also can enable or disable HTTP or HTTPS web access, and enable or disable SSH.
For more information and procedures for managing ILOM communication settings, see one of the following guides:
Since the SP network management port is not designed to behave like a switch port, the SP network management port does not support switch port features like spanning-tree portfast.
When configuring spanning tree parameters, consider these recommendations:
|
Enable this interface to immediately move to a forwarding state. |
|
ILOM, by default, uses IPv4 DHCP to learn the IPv4 address for the server SP. If DHCP is not supported in your network environment or if you prefer to set up a static IPv4 address, you can configure the IPv4 network settings in ILOM from the CLI or web interface. An example of the ILOM web interface settings is shown in FIGURE 2-1.
FIGURE 2-1 ILOM Network Settings for IPv4
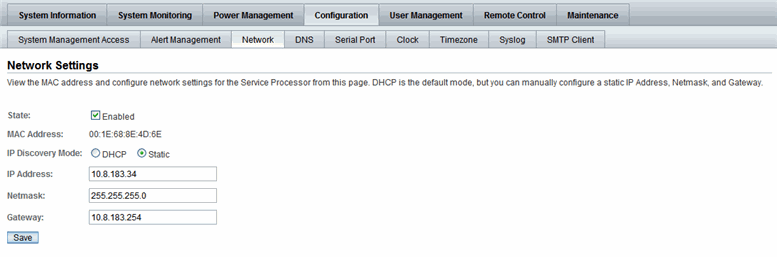
For instructions on how to configure the network settings in ILOM for IPv4, refer to one of the following ILOM procedure guides:
ILOM, by default, uses IPv6 stateless to learn the IPv6 address for the server SP. If IPv6 statesless is not supported in your network environment or if you prefer to use another IPv6 network setting to communicate with ILOM, you can modify the IPv6 network settings using the ILOM CLI or web interface.
| Note - As of ILOM 3.0.12, dual-stack IPv4 and IPv6 network settings are supported on some servers. Verify support of the IPv6 settings in your platform ILOM Supplement Guide or Administration Guide. |
ILOM enhancements for IPv6 include:
The settings for configuring ILOM in a dual-stack IPv4 and IPv6 network environment are accessible for the server SP (web and CLI) or CMM (CLI only). See FIGURE 2-2 for an example of the dual-stack IPv4 and IPv6 web interface properties available for a server SP.
FIGURE 2-2 ILOM Server SP Web Interface - Network Settings for Dual-stack IPv4 and IPv6

For a brief description of the IPv6 configuration options shown in FIGURE 2-2, see TABLE 2-4 IPv6 Address Auto-Configuration Options in ILOM.
For instructions on how to configure the dual-stack network settings in ILOM for IPv4 and IPv6, refer to one of the following ILOM procedure guides:
As of ILOM 3.0.12, a communication channel known as the Local Interconnect Interface was added to ILOM to enable you to locally communicate with ILOM from the host operating system (OS) without the use of a network management (NET MGT) connection to the server. The local interconnect feature to ILOM is particularly useful when you want to locally perform these ILOM tasks from the host operating system:
Oracle servers supporting the Local Interconnect Interface between ILOM and the host operating system are shipped from the factory with an internal USB Ethernet device installed.

The internal USB Ethernet device provides two network connection points that are known as the ILOM SP connection point and the host OS connection point. In order to establish a local connection to ILOM from the host operating system, each connection point (ILOM SP and host OS) must be either automatically or manually assigned a unique non-routable IPv4 address on the same subnet.
| Note - Non-routable IPv4 addresses are considered secured private addresses that prevent external Internet users from navigating to your system. |
To verify whether your server supports the Local Interconnect Interface feature in ILOM, refer to the ILOM Supplement guide or Administration guide that is provided with your server.
In ILOM you can choose to either have the Local Interconnect Interface automatically configured for you or manually configured. Details about both of these configuration options are provided below.
Oracle automates the configuration of the Local Interconnect Interface feature when you install the Oracle Hardware Management Pack 2.1.0 or later software. No configuration is necessary from ILOM in this case.
For more details about using the Oracle Hardware Management Pack 2.1.0 software to auto-configure the Local Interconnect Interface between the ILOM SP and the local host OS, see the Oracle Server Hardware Management Pack User’s Guide (821-1609).
If you are an advanced network administrator and prefer not to auto-configure the Local Interconnect Interface by installing the Oracle Hardware Management Pack 2.1.0 or later software, you can manually configure the connection points on the ILOM SP and host operating system.
In order to manually configure the Local Interconnect Interface connection points, you must:
a. On the host operating side, ensure that an Ethernet driver for your host OS was provided by the OS distribution and installed on the server. After you have confirmed that the appropriate Ethernet driver was installed on your server and your operating system recognizes the internal USB Ethernet device, you must manually configure an IPv4 address for the host OS connection point.
For more details, see Manual Host OS Configuration Guidelines for Local Interconnect Interface.
b. On the ILOM SP side, you must manually configure the Local Host Interconnect settings in ILOM. For more details about these settings, see Local Host Interconnect Configuration Settings in ILOM. For procedural information describing how to configure the Local Interconnect Interface, see Chapter 3 of the Integrated Lights Out Manager (ILOM) 3.0 CLI Procedures Guide or the Integrated Lights Out Manager (ILOM) Web Interface Procedures Guide.
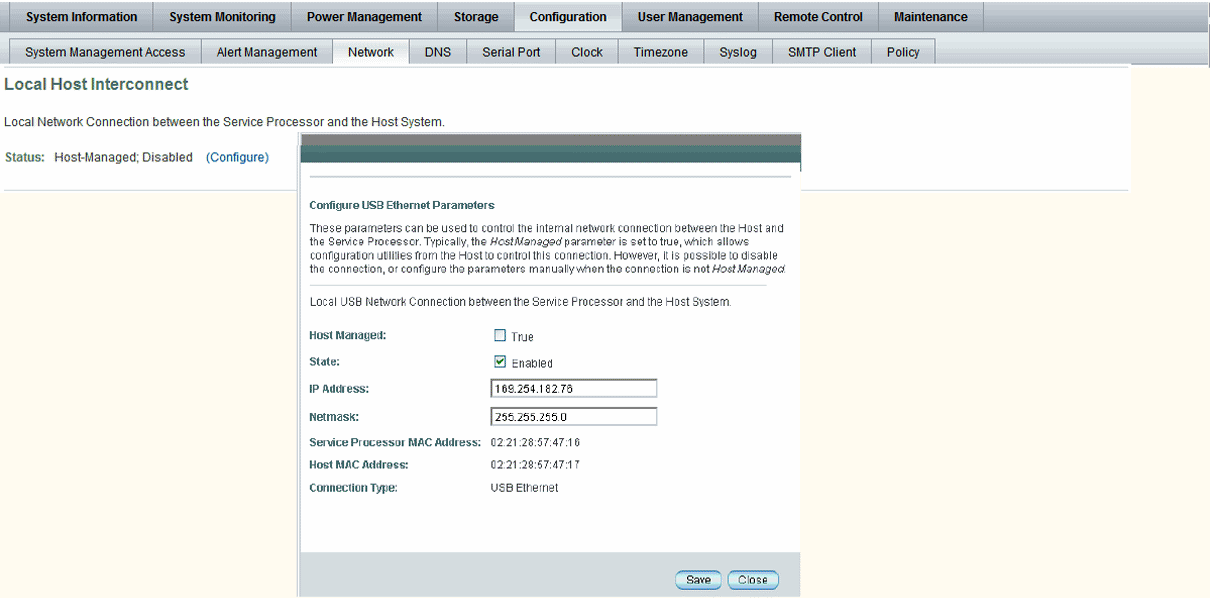
The Local Host Interconnect configuration settings in the ILOM web interface (or CLI) enable users with Administrator role privileges to control the Local Interconnect Interface between the host OS and the ILOM SP. See TABLE 2-5 for a brief description about the settings provided in ILOM for the Local Host Interconnect. For an example of the ILOM web interface settings for Local Host Interconnect, see FIGURE 2-3.
FIGURE 2-3 Local Host Interconnect Settings
|
The Host Managed setting, by default, is set to True. When the Host Managed setting is set to True (enabled), ILOM permits the Oracle Hardware Management Pack configuration utility (known as ilomconfig) to auto-configure the connection points for the ILOM SP and the host OS on the Local Interconnect Interface. To prevent the Oracle Hardware Management Pack software from auto-configuring the connection points on the Local Interconnect Interface, the setting for Host Managed must be set to False (disabled). |
|
|
The State setting, by default, is disabled. When the setting for State is disabled, the Local Interconnect Interface feature between the ILOM SP and the host OS is disabled. When the setting for State is enabled, the Local Interconnect Interface feature between the ILOM SP and host OS is enabled. |
|
|
ILOM, by default, provides a static non-routable IPv4 address (169.254.182.76) for the ILOM SP connection point on the Local Interconnect Interface. The IP address property is, by default, a read-only setting when the Host Managed setting is set to True. When the Host Managed setting is disabled (or property value is set to False), ILOM will allow you to modify the property value for the IPv4 address. Note - The default non-routable IPv4 address (169.254.182.76) should not be changed unless a conflict exists in your network environment with the default IPv4 address. When this address is left unchanged, this is the IP address you would use to locally connect to ILOM from the host operating system. |
|
|
ILOM, by default, provides a static Netmask address (255.255.255.0) for the ILOM SP connection point on the Local Interconnect Interface. The Netmask property is, by default, a read-only setting when the Host Managed setting is set to True. When the Host Managed setting is disabled (or property value is set to False), ILOM will allow you to modify the property value for the Netmask address. The default Netmask address (255.255.255.0) should not be changed unless a conflict exists in your network environment with the default Netmask address. |
|
|
The Service Processor MAC Address is a read-only setting. This setting displays the MAC address assigned to the ILOM SP. |
|
|
The Host MAC Address is a read-only setting. This setting displays the MAC address assigned to the server and it represents how the host server sees the internal USB Ethernet device. Note - The internal USB Ethernet device is presented in the system as a traditional “Ethernet” interface. If you decide to manually configure the Local Interconnect Interface between the ILOM SP and the host OS, it might be necessary to use the host MAC address to determine which interface you will need to configure from the host OS side (like Solaris). For additional information about manually configuring the Local Interconnect Interface on the host OS connection point, see Manual Host OS Configuration Guidelines for Local Interconnect Interface. |
|
|
The Connection Type is a read-only setting. This setting indicates a USB Ethernet connection. |
If you chose to manually configure a non-routable IPv4 address for the ILOM SP connection point on the Local Interconnect Interface, you will also need to manually configure a non-routable IPv4 address for the host OS connection point on the Local Interconnect Interface. General guidelines, per operating system, for configuring a static non-routable IPv4 address for the host OS connection point are provided below. For additional information about configuring IP addresses on the host operating system, consult the vendor operating system documentation.
| Note - ILOM will present the internal USB Ethernet device installed on your server as an USB Ethernet interface to the host operating system. |
|
After Windows discovers the internal USB Ethernet device, you will most likely be prompted to identify a device driver for this device. Since no driver is actually required, identifying the .inf file should satisfy the communication stack for the internal USB Ethernet device. The .inf file is available from the Oracle Hardware Management Pack 2.1.0 software distribution. You can download this management pack software from the Oracle software product download page (www.oracle.com) as well as extract the .inf file from the Management Pack software. For additional information about extracting the .inf file from the Management Pack software, see the Oracle Server Hardware Management Pack User’s Guide (821-1609). After applying the .inf file from the Oracle Hardware Management Pack 2.1.0 software distribution, you can then proceed to configure a static IP address for the host OS connection point of the Local Interconnect Interface by using the Microsoft Windows Network configuration option located in the Control Panel (Start --> Control Panel). For more information about configuring an IPv4 address in Windows 2008, see the Microsoft Windows Operating System documentation or the Microsoft Tech Net site (http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc754203%28WS.10%29.aspx). |
|
|
Most supported Linux operating system installations on an Oracle Sun platform server include the installation of the device driver for an internal Ethernet device. Typically, the internal USB Ethernet device is automatically discovered by the Linux operating system. The internal Ethernet device typically appears as usb0. However, the name for the internal Ethernet device might be different based on the distribution of the Linux operating system. The instructions below demonstrate how to configure a static IP address corresponding to usb0, which typically represents an internal USB Ethernet device found on the server: \> ifconfig usb0 169.254.182.77 \> ifconfig usb0 netmask 255.255.255.0 \> ifconfig usb0 broadcast 169.254.182.255 Note - Rather than performing the typical ifconfig steps, it is possible to script the configuration of the interface. However, the exact network scripts vary among the Linux distributions. Typically, the operating version of Linux will have examples to model the network scripts. For more information about how to configure an IP address for device using a Linux operation system, see the Linux operating system documentation. |
|
|
Most Solaris Operating System installations on a Oracle Sun platform server include the installation of the device driver for an internal USB Ethernet device. If this driver was not supported, you can extract this driver from the Oracle Hardware Management Pack 2.1.0 or later software. For information about how to extract the Solaris-specific OS driver for the Ethernet interface, see the Oracle Server Hardware Management Pack User’s Guide (821-1609). Typically, the internal USB Ethernet device is automatically discovered by the Solaris operating system. The internal Ethernet device typically appears as usbecm0. However, the name for the internal Ethernet device might be different based on the distribution of the Solaris operating system. After the Solaris Operating System recognizes the local USB Ethernet device, the IP interface for the USB Ethernet device needs to be configured. The following instructions demonstrate how to configure a static IP address corresponding to usbecm0, which typically represents an internal USB Ethernet device found on the server. ifconfig usbecm0 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 169.254.182.255 169.254.182.77 ping <IPv4 address of Solaris Host> ping <IPv4 address of SP-Ethernet USB> Note - Rather than performing the typical ifconfig steps, it is possible to script the configuration of the interface. However, the exact network scripts can vary among the Solaris distributions. Typically, the operating version will have examples to model the network scripts. For more information about how to configure a static IP address for a device using the Solaris Operating System, see the Solaris Operating System documentation. |
Copyright © 2010, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.