How Access Control Works
When the server gets a request for a page, the server uses the rules in the ACL file to determine if it should grant access or not. The rules can reference the hostname or IP address of the computer sending the request. The rules can also reference users and groups stored in the LDAP directory.
Note –
If there are more than one ACLs that match, the server uses the last ACL statement that has a match. The default ACL is bypassed since the uri ACL is the last statement that matches.
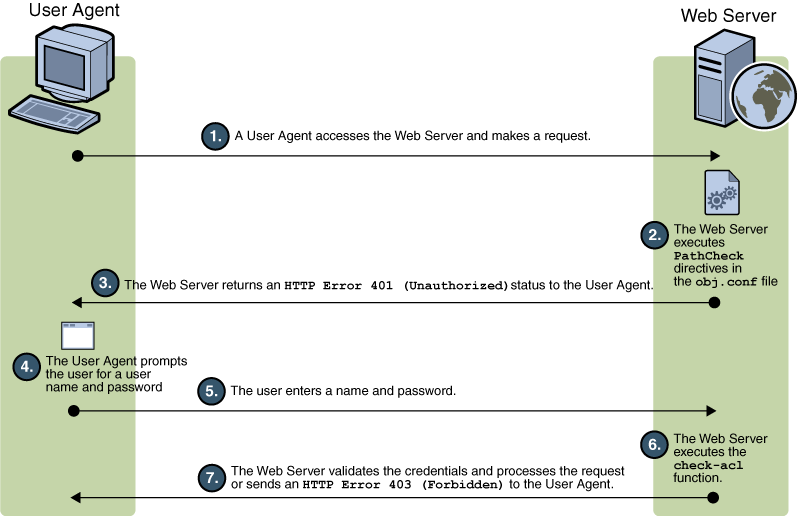
The above figure depicts how access control works in Web Server . The user agent (client) accesses the Web Server. The Web Server executes PathCheck directives in obj.conf file. The Web Server returns an HTTP 401 (unauthorized) to the client. The client prompts the user for authentication. In case if the client is a browser, it pops up a login dialog box. The user enter the login information. The Web Server executes an internal check-acl function. The Web Server validates the user credentials and processes the request.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
