About Applications
A Java EE application is a logical collection of one or more Java EE modules tied together by application annotations or deployment descriptors. Components can be assembled at either the module or the application level. Components can also be deployed at either the module or the application level.
The following diagram illustrates how components are assembled into modules and then assembled into an Application Server application and deployed. EJB components are assembled in a JAR file with annotations or ejb-jar.xml and sun-ejb-jar.xml deployment descriptors. Web components are assembled in a WAR file with annotations or web.xml and sun-web.xml deployment descriptors. An application client is assembled in a JAR file with application-client.xml and sun-application-client.xml deployment descriptors. A resource adapter is assembled in a RAR file with a ra.xml deployment descriptor. All modules are assembled in an EAR file and deployed to the Application Server.
Figure 1–2 Application Assembly and Deployment
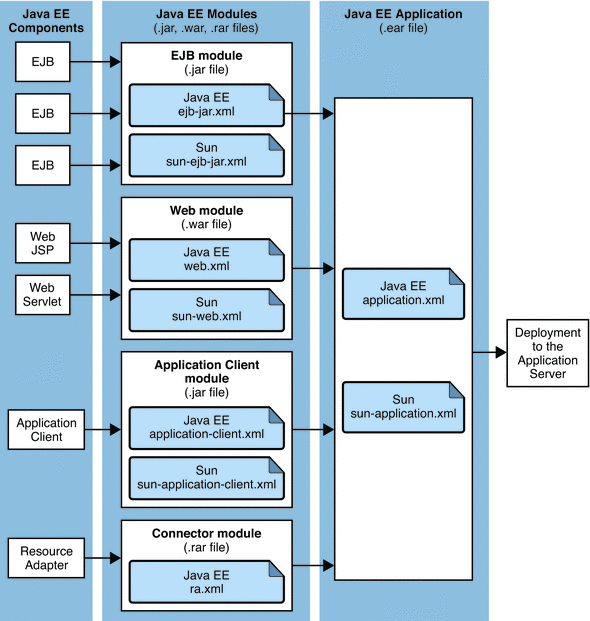
Each module has an optional Application Server deployment descriptor and annotations or a Java EE deployment descriptor. The Application Server uses the annotations or deployment descriptors to deploy the application components and to register the resources with the Application Server.
An application consists of one or more modules, an optional Application Server deployment descriptor, and annotations or a Java EE application deployment descriptor. All items are assembled, using the Java ARchive (.jar) file format, into one file with an extension of .ear.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
