Quality of Service (QOS) Features
Quality of Service features are configured from the CASA Editor, and include properties used to configure Retry (Redelivery) and Throttling.
This section contains the following topics:
Configuring the Quality of Service Properties
The QOS attributes are configured from the Config QoS Properties Editor, accessed from the Composite Application Service Assembly (CASA) Editor. For an example of how to access the Config QOS Properties Editor, see Configuring the HTTP Binding Component Endpoint for Throttling
Message Throttling: Configuring and Using
Throttling allows you to set the maximum number of concurrent messages that are processed by a particular endpoint. Increased message load and large message payloads can cause memory usage spikes that can decrease performance. Throttling limits resource consumption so that consistent performance is maintained.
The HTTP Binding Component, using functionality provided by the Grizzly HTTP Web Server, manages the flow of messages by evaluating endpoints to determine when it is necessary to suspend requests and when to resume processing as usual.
For more information in regard to HTTP BC and Throttling, see HTTP BC Throttling.
Configuring the HTTP Binding Component Endpoint for Throttling
For the HTTP Binding Component, throttling is a QOS feature configured from the CASA Editor.
 To configure Throttling for an HTTP/SOAP WSDL port
To configure Throttling for an HTTP/SOAP WSDL port
-
From the NetBeans IDE Projects window, right-click the Service Assembly node under your composite application, and select Edit from the popup menu.
The CASA Editor opens containing your composite application.
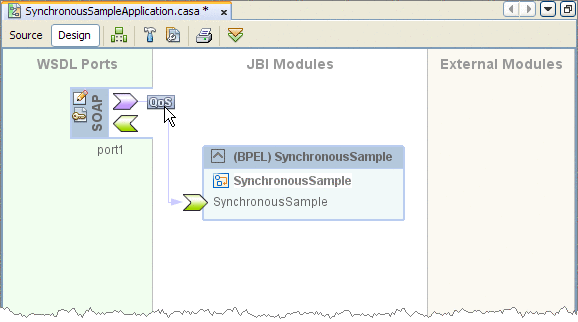
-
In the CASA Editor, click the QOS icon located on the link between your JBI Module and the WSDL port you want to configure.
The QOS Properties Editor appears.
-
In the QOS Properties Editor, click the property field for maximumConcurrencyLimit under ThrottlingExtension, and enter an integer for the maximum number of concurrent messages allowed for this endpoint.
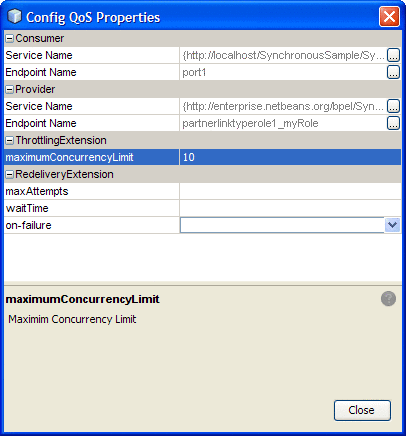
-
Click Close.
The appropriate throttling configuration for the connection is generated in the project's jbi.xml file, when the service assembly is built.
Redelivery: Configuring and Using
Redelivery is a Quality of Service mechanism that handles message delivery when first-time delivery fails. Redelivery allows you to define the number of attempts that the system makes to deliver a message, the time between attempts, and the final result for an undeliverable message or non-responsive endpoint.
Redelivery is configured for a specific connection from the Composite Application Service Assembly (CASA) Editor, by clicking the QoS icon for that connection. This opens the Config QoS Properties for that connection. From the RedeliveryExtension section of the editor, configure the Redelivery properties.
The Redelivery configuration parameters are:
-
maxAttempts: Specifies the number of times that the project attempts to re-deliver a message. An error status is returned to the JBI component for each failed attempt.
-
waitTime: Specifies the time, in milliseconds, that the project waits between redelivery attempts.
-
on-failure: Specifies the actions taken and the message destination when the specified redelivery attempts have been exhausted. This parameter has four options: delete, redirect, suspend, and error.
The on-failure parameter has four options: delete, redirect, suspend, and error.
-
delete: The delete option specifies that when the final attempt to re-deliver the message has failed, the QoS utility deletes the message and returns a Done status to the JBI component, at which time the component proceeds to its next process. The delete option only supports In-Only message exchanges.
-
redirect: The redirect option specifies that after the final attempt to re-deliver the message has failed, the QoS utility redirects the message to a user-defined endpoint, such as a “dead-message” folder. Upon successful delivery to the redirect endpoint, the QoS utility returns a Done status to the JBI component, at which time the component proceeds to its next process. The redirect option only supports In-Only message exchanges.
-
suspend: The suspend option specifies that when the final attempt to re-deliver the message has failed, the JBI component suspends the process instance . This option is only supported if monitoring is enabled in the JBI Component, since the user must use the monitoring tool to resume a suspended instance. This option is supported for both In-Only and In-Out message exchanges.
-
error: The error option specifies that when the final attempt to re-deliver the message is exhausted, the JBI component throws an exception. This option is only supported if monitoring is enabled in the JBI Component, since the user must use the monitoring tool to resume a suspended instance. This option is supported for both In-Only and In-Out message exchanges.
-
Note: The on-failure options: delete and redirect, cannot be applied to In-Out message exchanges because In-Out message exchanges require a specific response from the process instance to proceed further, and as such, the return value for these options does not suffice.
For more information regarding Redelivery, see Redelivery.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
