Understanding the Database Binding Component
The topics in this document provide information about Understanding the Database Binding Component.
What You Need to Know
These topics provide information about Database Binding Component.
About Database Binding Component
The Database Binding Component (DB BC) provides a comprehensive solution for configuring and connecting to databases that support Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) from within a Java Business Integration (JBI) environment. Database BC is a JBI component that provides database operations as services. JBI components acting as consumers invoke these Web Services. The Database BC is an implementation in compliance with JBI Specification 1.0.
The Database BC supports the following database artifacts to be exposed as Services.
-
Table
-
Prepared Statements
-
Procedures
-
SQL File
Components of Database Binding Component
The Database BC helps users to handle databases with flexibility. It also provide Web Services in conjunction with other OpenESB components.
The following components are part of the Database BC.
-
The WSDL from Database wizard, which supports Table, Prepared Statements, Procedure, and SQL File (NetBeans plug-in).
-
Custom WSDL extensions for configuring the Web Service (NetBeans plug-in).
-
Database Binding Runtime component (JBI runtime component).
Supporting Features in Database Binding Component
The Database BC has all the features of the JDBC Binding Component and subset of SQL Service Engine. The Database BC supports the listed database artifacts that are exposed as Services.
-
Database Objects
-
Table
-
View
-
Prepared Statements
-
Procedures
-
SQL File
-
-
Database Operations (DDL)
-
Database Connectivity
Database connectivity through Java Naming and Directory Interface (JNDI) lookup
-
XSD Creation and Editing
-
WSDL Creation and Editing
Creating WSDL components through a wizard with relevant binding information, service, and port definitions
-
Table
-
Prepared Statements
-
Procedures
-
SQL File
-
-
Other Features
-
Transaction Control (including XA)
-
JDBC WSDL extension validations in the WSDL Editor
-
Fault Handling
-
-
Databases Supported
-
Tier 1 Databases Supported
-
MySQL
-
Oracle
Tier 2 Databases Supported
-
SQL Server
-
DB2
-
Sybase
-
-
Driver Types Supported
Drivers are uniquely different in what they do and the type of functions they support.
-
DataDirect 3.7 (Type 4)
-
Derby Network client driver for Derby 10.2
-
Oracle Database
-
Oracle Type 2 driver (thin) for Oracle 9i
-
Oracle Type 2 driver (thin) for Oracle 10G
-
Oracle Type 2 driver (thin) for Oracle 11G
ojdbc14.jar,ojdbc5.jar: This driver works with Table, Prepared Statements, and Procedures.
-
-
MySQL Native
mysql-connector-java-5.1.5-bin.jar: This driver works with Table, Prepared Statements, Procedures, and SQL File.
-
MySQL DataDirect Driver
This driver works with Table, Prepared Statements, Procedures, and SQL File.
-
Oracle Native
This driver works with Table, Prepared Statements (supports only during Runtime), Procedures, and SQL File (supports only during Runtime).
-
Oracle DataDirect Driver
This driver works with Table, Prepared Statements, and SQL File.
-
SQL SERVER 2005 Native
sqljdbc.jar: This driver works with Table, Prepared Statements, and SQL File.
-
SQL SERVER 2005 DataDirect Driver
sqljdbc.jar: This driver works with Table, Prepared Statements, and SQL File.
-
Sybase Native
jconn3.jar: This driver works with Table, Prepared Statements, and SQL File.
-
DB2 Native
db2jcc.jar: This driver works with Table, Prepared Statements, Procedures, and SQL File.
Note –With this, both the JAR Files and the NBM Files are installed together.
-
-
Supported Platforms
-
Windows
-
Solaris
-
Mac OS X
-
Linux
-
-
Support for OpenESB
NetBeans plug-in compliant with the NetBeans enterprise suite.
-
Systemic Qualities
-
Application Configuration and Variables
Provides support for application configuration at deployment time and runtime, that is, after an application has been packaged. Must allow for changing configuration without modifying the packaged application.
-
Logging
Develop a consistent logging strategy across all runtime components.
-
Monitoring and Management
Provides a shared model for instrumentation, aggregation, and presentation of monitoring data related to performance, activity, and status. Needs to allow for unified monitoring across Sierra. This includes the core platform as well as components.
-
Recovery
XA recovery is a big part of this picture, but it's not everything. All components need to be able to recover gracefully from failure, including failure of other components internally and externally; and dealing with faults or errors in a manner that does not compromise message reliability.
-
Dynamic Addressing
Extend the scope of an application dynamically through dynamic addressing or invocation.
-
Retry
Qualities that can be added to an interaction with an endpoints.
-
Throttling
Qualities that can be added to an interaction with an endpoints.
-
Serial Processing and Message Ordering
Needs explicit support by all components; might benefit from conventions with respect to the status (DONE or ERROR) is sent back (that convention is related to TX and reliable messaging as well).
-
Common Fault and Error Handling
Establishes a common fault or error framework for all components. This ensures consistency in fault behavior and content.
-
Transaction Propagation
Provides a transferable construct for transaction information within the context of a given invocation (parent -> child).
-
Configuration Usability
MBean and WSDL extensibility elements consistency or usability.
-
Open ESB Packages that Make Up the New Database Binding Component
This runtime component is available as a sun-database-binding.
The design-time components still leverage the org-netbeans-modules-wsdlextensions-jdbc.nbm. NetBeans Modules help create artifacts for the sun-database-binding. The artifacts that the new version of these components generate are deployed to the Database BC instead of the JDBC Binding Component or SQL Service Engine.
Database BC (DB BC) is a Java Business Integration (JBI) runtime component that provides a comprehensive solution for configuring and connecting to databases. Database BC provides data operations as Services. It supports the JDBC from within a JBI environment. Other JBI components invoke these Web Services acting as consumers. Database BC considers both Data Manipulation Language (DML) and Data Definition Language (DDL) operations as Web Services.
The services that the Database BC exposes are actually SQL operations on Table, Prepared Statements, and Procedures. The Database BC supports the following database artifacts to be exposed as Services.
-
Table
-
Prepared Statements
-
Procedures
-
SQL File
The Database BC can assume the role of either a JBI consumer (polling inbound requests) or a JBI provider (sending outbound messages).
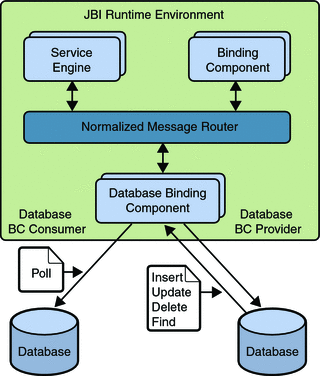
Once installed, the Database BC can be used to design, deploy, and run the Service Units. The most important part of a Service Unit is the WSDL that describes the Database services. Database BC provides a set of extension elements specific to Database BC for connecting to the Database.
Database Binding Component as Provider
Database BC acts as a provider in case of outbound message flow. Database BC acts as an external service provider when other engines and components 'invoke' it. In this role, when it receives a normalized message as part of the message exchange, it converts and extracts the SQL operation. The SQL operation is then executed on the specified database. In other words, when the Database BC acts as a JBI provider, it extracts the SQL query from a JBI message received from the JBI framework. It then executes the query on a specified database. It converts the reply from the database into a JBI message that other JBI components can service.
Database Binding Component as Consumer
Database BC also acts as a consumer incase of inbound functionality where Database BC polls for records from a particular table, converts them into normalized message, and sends to the Normalized Message Router (NMR). This process is analogous to the inbound connections implemented in CAPS 6. In other words, When the Database BC acts as a JBI consumer, it polls a specified database for updates to a table in the database. When a new record is stored in the table, the database polls for the record for the specified time interval and the Database BC picks up that record, constructs a JBI message, and sends the message to the JBI framework so it can be serviced by other JBI components.
Database Binding Component WSDL Extensibility Elements
The Database BC WSDL extensibility element is a template used to construct an instance of a Database BC WSDL. The Database BC WSDL extensibility elements contains information for constructing the Database BC message. These messages are constructed using the message parts, message formats, properties mapping, and other message related information necessary for the Database BC to properly map message exchanges to Database BC messages and vice versa. The Database BC WSDL extensibility elements also contain information about the database to which it connects.
Functional Architecture of Database Binding Component
The following figure shows the functional architecture of Database Binding Component.
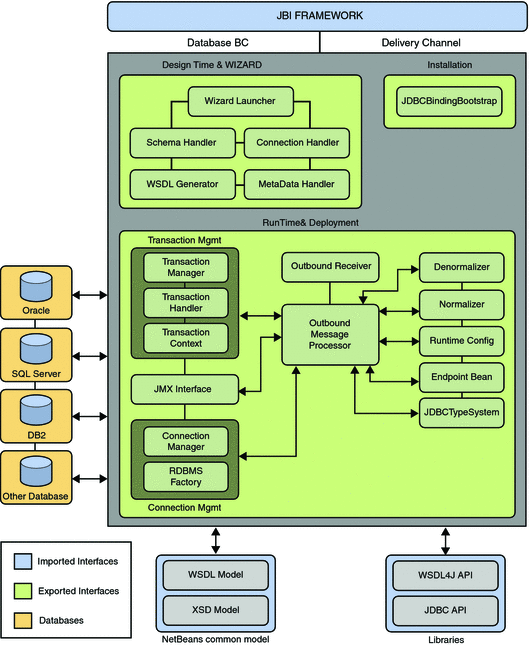
The following table briefly describes the functional operation of each module or wizard.
Table 1 Functional Description
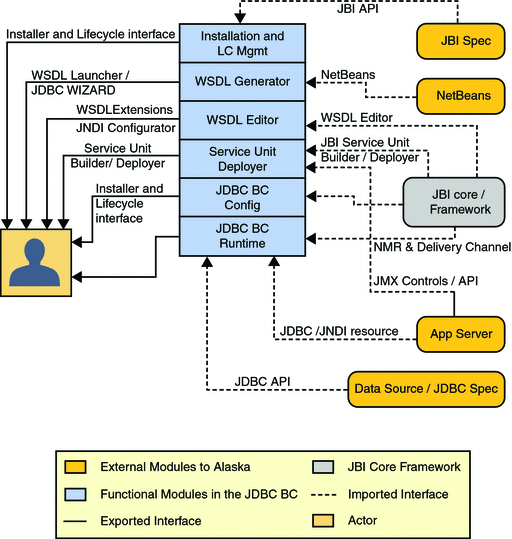
Functional Architecture of the JDBC Binding Component — Comparative Study
The following figure depicts the functional architecture of the Database BC including various logical components and external systems. The diagram is centered around the external and internal interfaces provided by the binding component. The term interface is used in a generic sense to mean any piece of information going back and forth between components.
The architecture includes the following:
-
Public Private (External to Alaska)
-
Project Private (Internal to Alaska but External to JDBC BC)
-
Imported Interfaces
-
Exported Interfaces
-
Core JDBC BC Functional Modules
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
