Special Networked Application Configurations
This section describes how to configure systems to run applications:
-
Elsewhere than on the system containing the action—on a remote execution host
-
Locally across file system mounts
Specifying a Remote Execution Host
In the typical application server configuration, the action definition is located on the same system as the application executable. However, actions can be written to execute commands on other systems. In this configuration, the system containing the application is called the execution host.
The action definition may be located on the session server or on a system that provides action and data type services to the session server—called a database server or database host.
Action definitions use the EXEC_HOST field to specify where their commands (EXEC_STRINGs) should be run. For example, the following action definition specifies
that an xload client be run on a system with host name SysDDD:
ACTION XloadSysDDD
{ TYPE COMMAND
EXEC_HOST SysDDD
EXEC_STRING /usr/bin/X11/xload -label SysDDD
}
If the EXEC_HOST field specifies
more than one host name, then the desktop tries to execute the EXEC_STRING on each host in order until it finds one that can run the action.
For example, the following EXEC_HOST
field specifies that the action should first attempt to run the EXEC_STRING on SysDDD, and, failing this, try SysEEE.
EXEC_HOST SysDDD,SYSEEE
If the EXEC_HOST field is
not set for an action, it defaults to the value %DatabaseHost%.
The value of %DatabaseHost% is obtained from the database
search path.
For example, suppose the database search path has been modified by adding the following line to /etc/dt/config/Xsession.d/0010.dtpaths:
DTSPSYSDATABASEHOSTS=SysAAA:,/net/SysBBB/etc/dt/appconfig/types/C
SysAAA is specified using the host-qualified syntax—SysAAA:. An action definition found using this element of the search path sets the database host to SysAAA. However, an action found using the /net/SysBBB… portion of the search path sets the database host to the local system because the syntax does not include the host qualifier.
To Configure the Remote Execution Host
-
Provide the operating system network configurations required by the desktop.
See Configuring Base Operating System Networking for the Desktop.
-
Provide the general desktop configuration required for servers.
-
Ensure that the applications are properly installed and configured for local execution.
To Configure the System Containing the Action Definition
-
Provide the operating system network configurations required by the desktop.
See Configuring Base Operating System Networking for the Desktop.
-
Provide the general desktop configuration required for servers.
-
Create and install the action definitions and application groups.
See Creating Actions that Run Applications on Remote Systems and Creating and Administering General Application Groups.
To Configure the Session Server
-
Provide the operating system network configurations required by the desktop.
See Configuring Base Operating System Networking for the Desktop.
-
Provide the general desktop configuration required for clients.
-
Modify the actions search path to include the database host.
-
Modify the application search path to include the execution host.
Running Applications Locally
The standard application server configuration runs applications on the application server. Sometimes it is desirable to have the application installed on a remote system but executed locally on the session server.
Figure 7–6 Execution across mount points
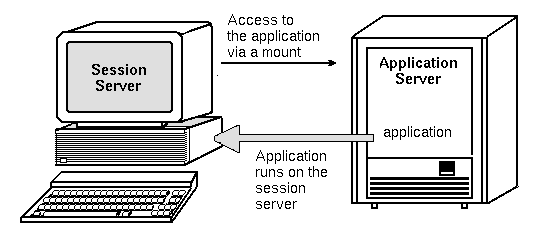
To Configure the Application Server
No special configuration is required.
To Configure the Session Server
Modify the application search path. Use the local absolute path to the application.
For example, you might use the following variable definition to find an application registered on sysAAA:
DTSPSYSAPPHOSTS=/net/SysAAA/etc/dt/appconfig/appmanager/C
The session server must be able to access the application's configuration files, such as app-defaults, message catalogs, and shared libraries.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
