SSL and 3DES Keys Protection Summary
SSL and 3DES Keys Protection Summary summarizes how Identity Synchronization for Windows protects sensitive information that is sent over the network.
Table 10–1 Protecting Sensitive Information Using Network Security
SSL and 3DES Keys Protection Summary contains an overview of the security features discussed in this section.
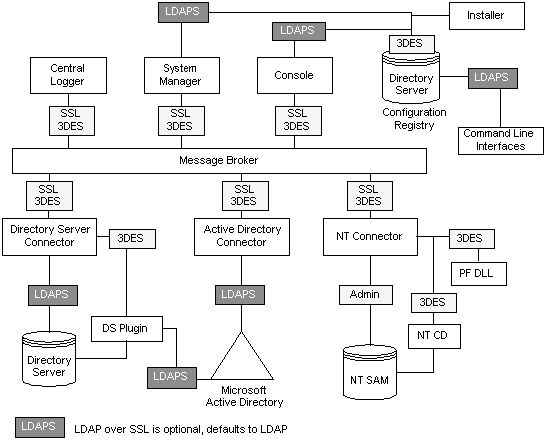
Figure 10–1 Security Overview for Identity Synchronization for Windows
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
