Communications Suite Single-tiered Logical Deployment Example for One Host
As its name implies, this example installs and configures components onto a single server. Consult with your Sun Client Services representative to determine the server type and configuration that best suits your needs.
In general, the single-tiered one host architecture is best suited for enterprises that are:
-
Composed of less than 1,000 users
-
Not geographically distributed
-
Served by few administrators
-
Seeking an entry-level configuration
The trade-offs associated with a single-host configuration include:
-
No high availability to the infrastructure to ensure service reliability (unless the server itself provides automatic system reconfiguration)
-
No ability to counteract denial of service attacks
Figure 28–1 shows a single-host deployment example. The following Communications Suite components are installed on the same host:
-
Messaging Server (MTA, Message Store, and Webmail Server)
-
Calendar Server (Administration service, HTTP service, and Backup service)
-
Communications Express
-
Web Server
In this example, the directory service resides on a different host than Communications Suite. Directory Server and Access Manager are a complex deployment on their own. This figure represents those components by a “cloud.”
Figure 28–1 Communications Suite Single-tiered Deployment Example for One Host
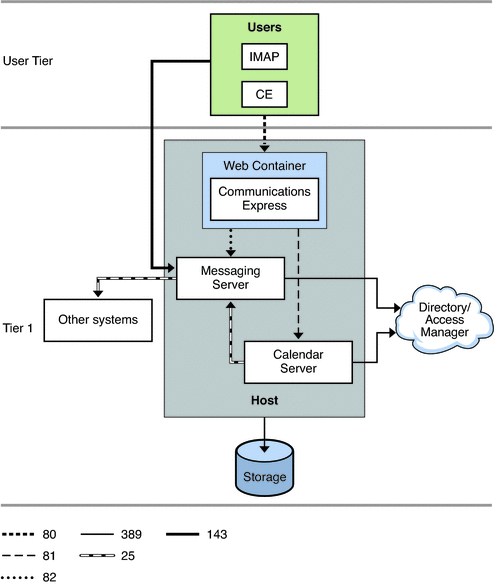
The following table explains the protocols and port numbers used by this deployment.
Table 28–1 Protocols And Ports Used by Single-tiered Deployment Example
To position this deployment for future growth, you would use logical service names to install. Logical service names position deployments for easier expansion. See Using Logical Service Names for more information. You would consider expanding to a two-tiered architecture when issues arise with capacity, performance, multiple geographic sites, and availability.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
