Part V Deploying Communications Express
This part contains the following chapters:
-
Chapter 26, Developing a Communications Express Architecture
-
Chapter 27, Understanding Communications Express Pre-Installation Considerations
Chapter 25 Introduction to Communications Express Software
Communications Express provides an integrated web-based communications and collaboration client. Communications Express is a common part of Messaging Server and Calendar Server, providing end users with a web interface to their calendar information and mail, as well as an address book.
Communications Express consists of three client modules: Calendar, Address Book, and Mail.
This chapter contains the following sections:
Communications Express Overview
Communications Express depends upon the following Sun Java System component products:
-
Directory Server
-
Access Manager (if you are using Sun Java System LDAP Schema Version 2)
-
Calendar Server
-
Messaging Server
You install Communications Express as a front-end server (in a multi-tier environment). You must install the complete set of Messaging Server packages on the same host that Communications Express is running on. Also, both Communications Express and Messenger Express must run on the same IP address. The Messaging Server packages can then be configured to run as Messenger Express or as MEM, which connects to a back-end store running Messenger Express.
In addition, you can configure Communications Express to have the Address Book on the front-end machine store its data either in the LDAP directory infrastructure or on an LDAP server other than the Communications Express machine. See the Sun Java System Communications Express 6 2005Q4 Administration Guide for more information.
Communications Express communicates with Calendar Server through the Calendar Server HTTP service, the mshttpd daemons for Messaging Server, and the LDAP service for address book. The cshttpd daemon can be local or remote, the mshttpd daemon can be either the local Webmail server or MEM, and the LDAP service can be either local or remote.
When using a load balancer or port director type device, make sure to utilize “sticky” (persistent) connections such that users are continually routed to the same front-end server for the duration of their session.
Communications Express Features
-
Communications Express has an integrated user interface for calendar, mail, and address book and enables the access of one client module from another without re-authenticating user credentials.
-
Communication between mail and calendar is established using Access Manager or Messaging Server single sign-on mechanism.
-
Both calendar and mail applications share the same address book.
-
All modules share the common user preferences specified in the Options tab of Communications Express.
-
The Address Book Store provides horizontal scalability. See the Sun Java System Communications Express 6 2005Q4 Administration Guide for more information.
-
Communications Express supports virtual domains.
Communications Express High-Level Architecture
The Calendar and Address Book client modules are deployed as a single web application in a web container, which can be either Sun Java Systems Web Server or Sun Java Systems Application Server. The mail module is rendered by Messenger Express. Messenger Express is the standalone web-based mail application that uses the HTTP service of the Messaging Server.
Messenger Express or MEM should be deployed on the same system where Communications Express is deployed.
Figure 25–1 shows the Communications Express software architecture.
Figure 25–1 High Level Communications Express Software Architecture
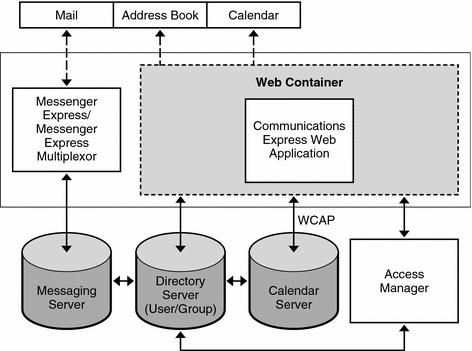
Communications Express consists of the following modules:
-
Mail. The Mail component uses the JavaScript language that is read and interpreted by the client. The JavaScript files are located on the server and downloaded to the client. The client extracts data from the JavaScript code to customize Communications Express functions. All modifications and customizations are done on the server.
-
Calendar. The presentation layer of the Calendar module is based on JavaServer PagesTM. These JavaServer Pages pages can be customized to suit the requirements of the client. The data layer accesses a Java API for Calendar (JCAPI) to enable exchange of data with Calendar Server over HTTP-based protocol.
-
Address Book. The Address Book component uses XML/XSL files that contain XSL tags, static HTML and .js scripts. The XSL and JavaScript code are used to display dynamic data. These XSL files can be edited for customizing the Address Book component.
Chapter 26 Developing a Communications Express Architecture
This chapter contains Communications Express basic deployment architectures. Depending on the features you want to implement in your deployment, you will need to install different sets of hosts and other networking infrastructure.
This chapter contains the following sections:
Basic Communications Express Architecture
This basic Communications Express architecture provides Calendar, Address Book, and Mail modules in a web container on a single host. Messenger Express is the standalone web interface mail application that uses the HTTP service of the Messaging Server. Messenger Express is deployed on the same system as the Calendar and Address Book modules.
To provide this basic functionality, you need to install the following components:
-
Directory Server
-
Access Manager (If you are using Sun Java System LDAP Schema Version 2)
-
Calendar Server
-
Messaging Server
-
Web Server or Application Server (for the web container)
In this example:
-
You install the complete set of Messaging Server packages on the host that Communications Express is running on.
-
The AddressBook server of Communications Express is configured to store its data in the LDAP directory infrastructure.
-
SSL has not been configured.
Figure 26–1 shows the basic Communications Express architecture.
Figure 26–1 Basic Communications Express Architecture
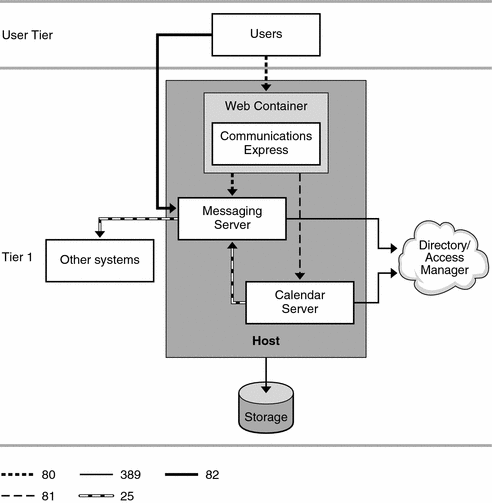
The following table explains the protocols and port numbers used by this architecture.
Table 26–1 Protocols And Ports Used by Basic Communications Express Deployment Architecture|
Protocol |
Port |
Used By |
|---|---|---|
|
SMTP |
25 |
Messaging Server MTA component to communicate with other systems, and Calendar Server (csenpd) components for email notifications |
|
HTTP |
80 |
Internet users to communicate with Communications Express front-end, and Communications Express to communicate with Messaging Server |
|
HTTP |
81 |
Calendar Express on Communications Express to communicate with Calendar Server |
|
MSHTTP |
82 |
Internet users to communicate with Messenger Express |
|
LDAP |
389 |
Messaging Server and Calendar Server to communicate with LDAP directory |
Communications Express on Remote Host Architecture
Figure 26–2 shows a Communications Express architecture for both intranet and Internet users. The intranet users log on to the Communications Express back-end host. The Internet users log on to the Communications Express front-end host in the DMZ, which then communicates with the back-end host. Single sign-on is enabled on the back-end host.
You install the front-end host with the following components:
You install the back-end with the following components:
-
Communications Express
-
Web container
-
Messaging Server (Messenger Express)
-
Calendar Server
-
Directory Server
-
Access Manager
Figure 26–2 shows the Communications Express on remote host architecture.
Figure 26–2 Communications Express on Remote Host Architecture
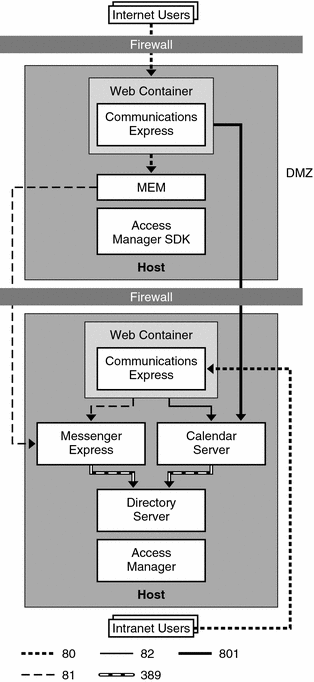
The following table explains the protocols and port numbers used by this architecture.
Table 26–2 Protocols And Ports Used by Communications Express Remote Host Deployment Example|
Protocol |
Port |
Used By |
|---|---|---|
|
HTTP |
80 |
Internet users to communicate with the Communications Express front-end host in the DMZ |
|
HTTP |
81 |
Messaging Express Multiplexor (MEM) on the Communications Express front-end host in the DMZ to communicate with Messenger Express on the back-end host behind the DMZ |
|
HTTP |
82 |
Communications Express on the back-end host to communicate with Calendar Server, also on the back-end host |
|
LDAP |
389 |
Messaging Server and Calendar Server to communicate with LDAP directory |
|
HTTP |
8081 |
Communications Express on the front-end host to communicate with Calendar Server on the back-end host |
Chapter 27 Understanding Communications Express Pre-Installation Considerations
This chapter describes considerations you need to think about before installing Communications Express.
This chapter contains the following sections:
Communications Express Installation Considerations
Before installing Communications Express, consider the following planning aspects:
-
Delegated Administrator requires that you install Access Manager and the web container (either Web Server or Application Server) on the same host.
-
You can deploy Communications Express and Access Manager in both SSL and non-SSL modes, either on the same or a different web container.
-
Due to a JavaScript security dependency, you must install Communications Express and Messenger Express on the same host, or Communications Express and Messaging Express Multiplexor on same host (in a multi-tiered environment).
-
You can plan for a distributed deployment in which Directory Server, Messaging Server, Calendar Server, and Access Manager are installed on separate hosts.
-
If you are using Calendar Server hosted domains, you enable Communications Express support for hosted domains during the configuration phase.
-
You can configure Communications Express for SSL or non-SSL. If you configure SSL, you can choose between having Communications Express clients use SSL only for authentication, or to use SSL for the entire session.
Requirements for Using S/MIME with Communications Express Mail
Communications Express Mail now includes the security advantages of the Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extension (S/MIME). Communications Express Mail users who are set up to use S/MIME can exchange signed or encrypted messages with other Communications Express Mail users, and with users of the Microsoft Outlook mail system or other mail clients that support S/MIME.
General Requirements for S/MIME
The signature and encryption features of S/MIME are available to a Communications Express Mail user only after:
-
A private and public key pair are issued with a certificate in standard X.509 format. The certificate assures other mail users that the keys really belong to the person who uses them. Keys and their certificate are issued from within your organization or purchased from a third-party vendor. Regardless of how the keys and certificate are issued, the issuing organization is referred to as a certificate authority (CA).
-
The private-public key pair, with its certificate, are properly stored electronically in a local key store or distributed to end users on common access cards (CACs), referred to as smart cards.
-
All public keys and certificates are stored to an LDAP directory, accessible by Directory Server. This is referred to as publishing the public keys to make them available to other mail users who are creating S/MIME messages.
-
Card reading devices are properly installed on the client machines when private-public key pairs and their certificates are stored on smart cards.
-
All the necessary platform software is installed on the client machines where Communications Express Mail is accessed.
-
All the necessary Sun Microsystems software is installed and configured for S/MIME.
-
The Communications Express Mail user is set up to use the Sun Microsystems mail system. This includes giving the user permission to use the S/MIME features.
Concepts You Should Know Before Deploying S/MIME
Before you deploy your mail system for S/MIME, be sure you are familiar with these concepts:
-
Basic administrative procedures of your platform
-
Structure and use of an LDAP directory
-
Addition or modification of entries in an LDAP directory
-
Configuration process for Sun Java System Directory Server
-
Concepts and purpose of the following:
-
Secure Socket Layer (SSL) for a secured communications line
-
Digitally signed email messages
-
Encrypted email messages
-
Local key store of a browser
-
Smart cards and the software and hardware to use them
-
Private-public key pairs and their certificates
-
Certificate authorities (CA)
-
Verifying keys and their certificates
-
Certificate revocation list (CRL)
-
Where to Go for More Communications Express Information
To install and configure Communications Express, see the instructions in the Sun Java System Communications Express 6 2005Q4 Administration Guide.
To administer S/MIME, see Chapter 20, Administering S/MIME for Communications Express Mail, in Sun Java System Messaging Server 6 2005Q4 Administration Guide.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
