Packaging Applications
A Java EE application is delivered in an Enterprise Archive (EAR) file, a standard Java Archive (JAR) file with an .ear extension. Using EAR files and modules makes it possible to assemble a number of different Java EE applications using some of the same components. No extra coding is needed; it is only a matter of assembling (or packaging) various Java EE modules into Java EE EAR files.
An EAR file (see Figure 1–6) contains Java EE modules and deployment descriptors. A deployment descriptor is an XML document with an .xml extension that describes the deployment settings of an application, a module, or a component. Because deployment descriptor information is declarative, it can be changed without the need to modify the source code. At runtime, the Java EE server reads the deployment descriptor and acts upon the application, module, or component accordingly.
Figure 1–6 EAR File Structure
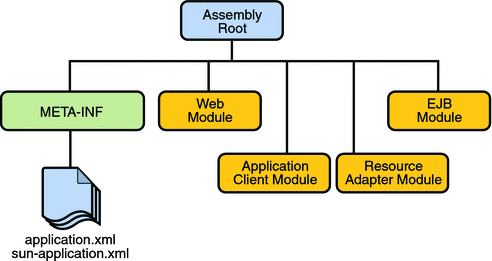
There are two types of deployment descriptors: Java EE and runtime. A Java EE deployment descriptor is defined by a Java EE specification and can be used to configure deployment settings on any Java EE-compliant implementation. A runtime deployment descriptor is used to configure Java EE implementation-specific parameters. For example, the Sun Java System Application Server Platform Edition 9 runtime deployment descriptor contains information such as the context root of a web application, the mapping of portable names of an application’s resources to the server’s resources, and Application Server implementation-specific parameters, such as caching directives. The Application Server runtime deployment descriptors are named sun-moduleType.xml and are located in the same META-INF directory as the Java EE deployment descriptor.
A Java EE module consists of one or more Java EE components for the same container type and one component deployment descriptor of that type. An enterprise bean module deployment descriptor, for example, declares transaction attributes and security authorizations for an enterprise bean. A Java EE module without an application deployment descriptor can be deployed as a stand-alone module.
The four types of Java EE modules are as follows:
-
EJB modules, which contain class files for enterprise beans and an EJB deployment descriptor. EJB modules are packaged as JAR files with a .jar extension.
-
Web modules, which contain servlet class files, JSP files, supporting class files, GIF and HTML files, and a web application deployment descriptor. Web modules are packaged as JAR files with a .war (Web ARchive) extension.
-
Application client modules, which contain class files and an application client deployment descriptor. Application client modules are packaged as JAR files with a .jar extension.
-
Resource adapter modules, which contain all Java interfaces, classes, native libraries, and other documentation, along with the resource adapter deployment descriptor. Together, these implement the Connector architecture (see J2EE Connector Architecture) for a particular EIS. Resource adapter modules are packaged as JAR files with an .rar (resource adapter archive) extension.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
