Enterprise Server Concepts
The Enterprise Server consists of one or more domains. A domain is an administrative boundary or context. Each domain has an administration server (also called Domain Administration Server or DAS) associated with it and consists of zero or more standalone instances and/or clusters. Each cluster has one or more homogeneous server instances. A server instance is a single Java Virtual Machine (JVM) that runs the Application Server on a single physical machine. Server instances (whether standalone or clustered) in a domain can run on different physical hosts.
This section contains the following topics:
Domain
A domain is a group of instances that are administered together. However, an application server instance can belong to just one domain. In addition to the administration boundary, a domain provides the basic security structure whereby different administrators can administer specific groups (domains) of application server instances. By grouping the server instances into separate domains, different organizations and administrators can share a single Enterprise Server installation. Each domain has its own configuration, log files, and application deployment areas that are independent of other domains. If the configuration is changed for one domain, the configurations of other domains are not affected.
The Sun GlassFish Enterprise Server installer creates the default administrative domain (named domain1). It also creates an associated domain administration server (named server). You must provide the administration server port number. The default administration server port is 4848. The installer also queries for the administration username and master password. After installation, additional administration domains can be created.
Domain Administration Server (DAS)
Each domain has its own Domain Administration Server (DAS) with a unique port number. The Admin Console communicates with a specific DAS to administer the associated domain. Each Admin Console session allows you to configure and manage the specific domain.
The Domain Administration Server (DAS), is a specially-designated application server instance that hosts the administrative applications. The DAS authenticates the administrator, accepts requests from administration tools, and communicates with server instances in the domain to carry out the requests. The DAS is sometimes referred to as the admin server or default server. It is referred to as the default server because it is the only server instance that gets created on Sun GlassFish Enterprise Server installation and can be used for deployments. The DAS is simply a server instance with additional administration capabilities.
Each Admin Console session allows you to configure and manage a single domain. If you created multiple domains, you must start an additional Admin Console session to manage the other domains. When specifying the URL for the Admin Console, be sure to use the port number of the DAS associated with the domain to be administered.
Usage Profiles
Every administrative domain is associated with a usage profile, which identifies the capabilities of that domain. Enterprise Server provides the following profiles:
-
Developer: Use this profile if you are running your domain in a development environment and if your applications do not need the NSS keystore or clustering features, such as load balancing, and session persistence.
-
Cluster: Use this profile if you need to create clusters but do not require the high-availability database (HADB) or the NSS keystore.
Note –In the cluster and developer profile, the DAS is set to be in non-secure mode, by default. While running asadmin commands, use --secure=false, wherever required. Do not use this flag if you have made changes to set DAS to secure mode.
-
Enterprise:: Use this profile if you need HADB and NSS. This profile is usable only if you install HADB and NSS separately or if you install Enterprise Server as part of enterprise offerings, such as Java Enterprise System (JES). For information on how you can use the enterprise profile with Enterprise Server, see Using the Enterprise Profile
The domain provides a preconfigured runtime for the user applications. Usage profiles facilitates the distinction between the Application Server binaries and the runtime configuration. Profiles enable you to use the same installation of Enterprise Server to create different domains with profiles that suit specific needs. For example, a developer may want to use the Enterprise Server to get to know the latest Java EE specifications. This developer does not need stringent security settings. Another user who wants to deploy applications in a production environment needs an inherently secure environment.
Table 1–1 lists the features available with each profile:
Table 1–1 Features Available for Each Profile|
Feature |
Developer Profile |
Cluster Profile |
Enterprise Profile (not available with Sun GlassFish Communications Server) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Security store |
JKS |
JKS |
NSS |
|
Clustering/Standalone instances |
Not available |
Available |
Available |
|
Security Manager |
Disabled |
Enabled |
Enabled |
|
HADB |
Not available |
Not available |
Available |
|
Load balancing |
Not available |
Available |
Available |
|
Node agents |
Not available |
Available |
Available |
Cluster
A cluster is a named collection of server instances sharing the same set of applications, resources, and configuration information. A server instance can belong to exactly one cluster. A cluster facilitates server instance load-balancing through distribution of a load across multiple machines. A cluster facilitates high availability through instance-level failover. From an administrative perspective, a cluster represents a virtualized entity in which operations on a cluster (e.g. deployment of an application) act on all instances that make up the cluster.
Horizontal scaling is achieved by adding Enterprise Server instances to a cluster, thereby increasing the capacity of the system. It is possible to add Enterprise Server instances to a cluster without disrupting service. The HTTP, RMI/IIOP, and JMS load balancing systems distribute requests to healthy Enterprise Server instances in the cluster.
High Availability - Availability allows for failover protection of Enterprise Server instances in a cluster. If one application server instance goes down, another Enterprise Server instance takes over the sessions that were assigned to the unavailable server. Session information is stored using the session replication feature or by using the high-availability database (HADB). HADB supports the persistence of HTTP sessions and stateful session beans.
Node Agent
A lightweight agent (e.g. hosting a JMX runtime only) is required on each node in the domain to facilitate remote lifecycle management of instances. Its primary purpose is to start, stop, and create server instances as instructed by the DAS. The Node Agent also acts as a watchdog and restarts failed processes. Like the DAS, the Node Agent should only be required for certain administrative operations and should not be expected to be highly available. However, the Node Agent is an “always on” component, and must be configured to be started by the native O/S node bootstrap (e.g. Solaris/Linux inetd, or as a Windows service). A Node Agent is not required for the DAS.
Server Instance
The server instance is a single Java EE compatible Java Virtual Machine hosting an Enterprise Server on a single node. Each server instance has a unique name in the domain. A clustered server instance is a member of a cluster and receives all of its applications, resources, and configuration from its parent cluster; ensuring that all instances in the cluster are homogeneous. An unclustered server instance does not belong to a cluster and as such has an independent set of applications, resources, and configuration. The following figure shows an application server instance in detail. The application server instance is a building block in the clustering, load balancing, and session persistence features of the Enterprise Server.
Figure 1–1 Enterprise Server Instance
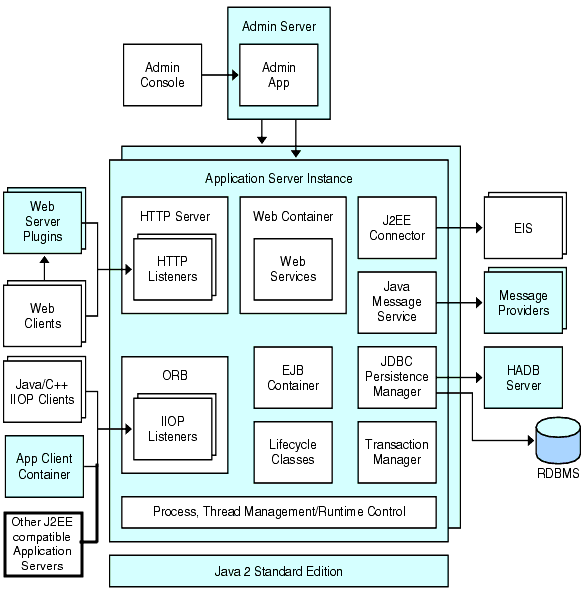
The Sun GlassFish Enterprise Server creates one application server instance, called server, at the time of installation. For many users, one application server instance meets their needs. However, depending upon your environment, you might want to create one or more additional application server instances. For example, in a development environment you can use different application server instances to test different Enterprise Server configurations, or to compare and test different application deployments. Because you can easily add or delete an application server instance, you can use them to create temporary sandbox area for experimentation purposes.
In addition, for each application server instance, you can also create virtual servers. Within a single installed application server instance you can offer companies or individuals domain names, IP Addresses, and some administration capabilities. For the users, it is almost as if they have their own web server, without the hardware and basic server maintenance. These virtual servers do not span application server instances. For more information about virtual servers, see Chapter 13, Configuring the HTTP Service.
In operational deployments, for many purposes you can use virtual servers instead of multiple application server instances. However, if virtual servers do not meet your needs, you can also use multiple application server instances. On stopping, application server instance stops accepting new connections, then waits for all outstanding connections to complete. If your machine crashes or is taken offline, the server quits and any requests it was servicing may be lost.
Ports in the Enterprise Server
The following table describes the port listeners of the Enterprise Server.
Table 1–2 Enterprise Server Listeners that Use Ports|
Listener |
Default Port Number |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Administrative server |
4848
|
A domain’s administrative server is accessed by the Admin Console and the asadmin utility. For the Admin Console, specify the port number in the URL of the browser. When executing an asadmin command remotely, specify the port number with the --port option. |
|
HTTP |
8080 |
The server listens for HTTP requests on a port. To access deployed Web applications and services, clients connect to this port. |
|
HTTPS |
8181 |
Web applications configured for secure communications listen on a separate port. |
|
IIOP |
3700 |
Remote clients of enterprise beans (EJB components) access the beans through the IIOP listener. |
|
IIOP, SSL |
3820 |
Another port is used by the IIOP listener configured for secure communications. |
|
IIOP, SSL and mutual authentication |
3920 |
Another port is used by the IIOP listener configured for mutual (client and server) authentication. |
|
SIP |
5060 |
The server listens for SIP requests on a port. |
|
SIPS |
5061 |
SIP/converged applications configured for secure communications listen on a separate port. |
|
JMX_ADMIN |
8686 | |
|
JMS |
7676 |
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
