Installing and Configuring Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB
This chapter explains how to install and configure Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB. From version 7.5, SAP DB is distributed under the name MaxDB for MySQL (MaxDB). In this book, all versions of this database are referred to as MaxDB.
Note –
If you are using the Solaris 10 OS, you can install and configure this data service to run in the non-global zone. Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB is supported in non-global zones.
This chapter contains the following sections.
-
Overview of the Installation and Configuration Process for Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB
-
Planning the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB Installation and Configuration
-
Configuring the HAStoragePlus Resource Type to Work With Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB
-
Verifying the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB Installation and Configuration
Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB Overview
To eliminate single points of failure in an MaxDB system, Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB provides the following features:
-
Fault monitoring and automatic failover for the MaxDB application. You must configure Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB as a failover data service.
-
Fault monitoring and automatic restart for SAP xserver. You must configure SAP xserver as a scalable data service.
For conceptual information about failover data services and scalable data services, see the Sun Cluster Concepts Guide for Solaris OS.
Each component of MaxDB has data service that protects the component when the component is configured in Sun Cluster. See the following table.
Note –
The files that are associated with the SUNW.sap_xserver resource type are supplied with the Sun Cluster HA for SAP liveCache data service. The Sun Cluster HA for SAP liveCache data service is installed when you install Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB data service.
Table 1 Protection of MaxDB Components by Sun Cluster Data Services
|
MaxDB Component |
Data Service |
|---|---|
|
MaxDB |
Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB The resource type is SUNW.sapdb. |
|
SAP xserver |
Sun Cluster HA for SAP liveCache The resource type is SUNW.sap_xserver. |
|
NFS file system |
Sun Cluster HA for NFS The resource type is SUNW.nfs. For more information about this data service, see Sun Cluster Data Service for NFS Guide for Solaris OS. |
Overview of the Installation and Configuration Process for Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB
The following table summarizes the tasks for installing and configuring Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB and provides cross-references to detailed instructions for performing these tasks. Perform the tasks in the order that they are listed in the table.
Table 2 Tasks for Installing and Configuring Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB|
Task |
Cross-Reference |
|---|---|
|
Plan the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB installation and configuration |
Your SAP documentation. Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS Planning the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB Installation and Configuration |
|
Install and configure MaxDB | |
|
Verify the MaxDB installation and configuration | |
|
Install the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB packages | |
|
Configure the HAStoragePlus resource to work with Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB |
Configuring the HAStoragePlus Resource Type to Work With Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB |
|
Register and configure the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB data service | |
|
(Optional) Tune the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB fault monitors | |
|
Verify the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB installation and configuration |
Verifying the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB Installation and Configuration |
|
(Optional) Upgrade the SUNW.sap_xserver resource type |
Planning the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB Installation and Configuration
This section contains the information that you need to plan your Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB installation and configuration.
Note –
Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB can be configured to run in a whole root or a sparse root non-global zone, if required.
Note –
Before you begin, consult your MaxDB documentation for configuration restrictions and requirements that are not imposed by Sun Cluster software. For information about restrictions that the Sun Cluster software imposes, see the Sun Cluster documentation.
Configuration Requirements
The configuration requirements in this section apply only to Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB.
If your data service configuration does not conform to these requirements, the data service configuration might not be supported.
For requirements that apply to all data services, see Configuration Guidelines for Sun Cluster Data Services in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS.
MaxDB Software Version Requirements
Use MaxDB version 7.4 or compatible versions.
Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB Configuration Requirements
Configure Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB as a failover data service. You cannot configure Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB as a scalable data service. For more information, see the following sections:
SAP xserver Configuration Requirements
To enable client applications to access Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB, you must use SAP xserver. Configure SAP xserver as a scalable data service. Do not configure SAP xserver as a failover data service.
Configure SAP xserver so that SAP xserver starts on all nodes to which the MaxDB resource can fail over. To implement this configuration, ensure that the node list of the SAP xserver resource group contains all nodes that are in the node list of the MaxDB resource group. For more information, see How to Register and Configure an SAP xserver Resource.
Supported Configurations of This Data Service
The Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB data service supports configurations that conform to the requirements in Configuration Requirements.
If you plan to use MaxDB with other highly available SAP applications, you must also configure the Sun Cluster data services for those applications. For more information, see the following table.
|
SAP Application |
Sun Cluster Data Service |
Associated Document |
|---|---|---|
|
SAP R/3 |
Sun Cluster HA for SAP | |
|
SAP liveCache |
Sun Cluster HA for SAP liveCache |
Sun Cluster Data Service for SAP liveCache Guide for Solaris OS |
|
SAP Web Application Server |
Sun Cluster HA for SAP Web Application Server |
Sun Cluster Data Service for SAP Web Application Server Guide for Solaris OS |
The examples that follow show these supported configurations of Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB:
-
Two-node cluster configuration
-
Four-node cluster configuration with SAP R/3
-
Four-node cluster configuration with SAP R/3 and SAP liveCache
Note –
Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB might support additional configurations. However, you must contact your Sun service provider for information about additional configurations.
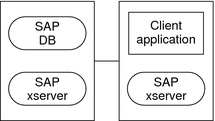
Example 1 Two-Node Configuration
This example shows a two-node configuration in which a client application accesses the MaxDB resource through the SAP xserver resource. The characteristics of this configuration are as follows:
-
The MaxDB resource is configured as a failover data service.
-
The SAP xserver resource is configured as a scalable data service.
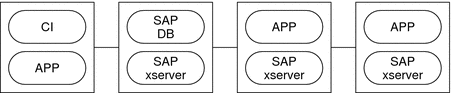
Example 2 Four-Node Configuration With SAP R/3
This example shows a four-node configuration in which MaxDB is used with SAP R/3. This configuration uses multiple Advanced Planner & Optimizer (APO) application servers. The characteristics of this configuration are as follows:
-
The SAP APO Central Instance (CI) resource is configured as a failover data service.
-
The MaxDB resource is configured as a failover data service.
-
The SAP xserver resource is configured as a scalable data service.
-
APO application server (APP) resources are configured as scalable data services.
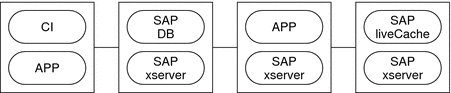
Example 3 Four-Node Configuration With SAP R/3 and SAP liveCache
This example shows a four-node configuration in which MaxDB is used with SAP R/3 and SAP liveCache. This configuration uses multiple APO application servers. The characteristics of this configuration are as follows:
-
The SAP APO CI resource is configured as a failover data service.
-
The MaxDB resource is configured as a failover data service.
-
The SAP xserver resource is configured as a scalable data service.
-
APP resources are configured as scalable data services.
-
The SAP liveCache resource is configured as a failover data service.
Configuration Considerations
The configuration considerations in the subsections that follow affect the installation and configuration of Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB.
Device Group for the MaxDB Application
Ensure that you create a device group for the MaxDB application as follows:
-
Install MaxDB on its own global device group. For more information, see Installing and Configuring MaxDB. This separate global device group for MaxDB ensures that the MaxDB resource can depend on the HAStoragePlus resource only for MaxDB.
-
Create an HAStoragePlus resource for the global device group on which MaxDB is installed. For more information, see Configuring the HAStoragePlus Resource Type to Work With Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB.
-
Ensure that the resource for MaxDB depends on the HAStoragePlus resource for the global device group on which MaxDB is installed. For more information, see Registering and Configuring Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB.
Dependencies of the MaxDB Application on SAP xserver
Configure MaxDB so that MaxDB starts only on a node where SAP xserver is running. To implement this configuration, configure resources and resource groups as follows:
-
Ensure that the resource for MaxDB depends on the resource for SAP xserver.
-
Create on the MaxDB resource group a strong positive affinity for the SAP xserver resource group.
For more information, see Registering and Configuring Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB.
Administration of SAP xserver by a User Other Than Root
You might be required to administer SAP xserver as a user other than root. In this situation, you must create and define that user as follows:
-
You must create that user on all cluster nodes or zones that master SAP xserver.
-
You must define that user when you register and configure Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB. For more information, see Registering and Configuring Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB.
Configuration Planning Questions
Answer the questions in this section to plan the installation and configuration of Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB. Write the answers to these questions in the space that is provided on the data service worksheets in Appendix D, Data Service Configuration Worksheets and Examples, in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS.
-
Which resource group will you use for the MaxDB application resource and for the logical host name for the MaxDB resource?
Use the answer to this question when you perform the procedure How to Enable MaxDB to Run in a Cluster.
-
What is the logical host name for the MaxDB resource? Clients access the data service through this logical host name.
Use the answer to this question when you perform the following procedures:
-
Where will the system configuration files reside?
See Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS for the advantages and disadvantages of using the local file system instead of the cluster file system.
Installing and Configuring MaxDB
To enable Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB to make MaxDB highly available, additional installation and configuration operations are required. These operations supplement the standard installation and standard configuration of MaxDB.
During a standard installation, MaxDB is installed with a physical host name. To enable MaxDB to run in a cluster, you must modify MaxDB to use a logical host name.
For information about the standard installation and standard configuration of MaxDB, see the following documentation:
-
If you are using MaxDB with SAP R/3, see the SAP R/3 documentation for information about how to install and configure SAP R/3 with MaxDB.
-
If you are using MaxDB independently of SAP R/3, see the MaxDB documentation.
 How to Install and Configure MaxDB
How to Install and Configure MaxDB
-
On one node of the cluster, install the MaxDB software.
Ensure that you install MaxDB on its own global device group.
-
Perform a standard configuration of MaxDB.
-
Create the .XUSER.62 file in the home directory of the operating system (OS) user who administers the MaxDB instance.
Note –If you are using MaxDB 7.5 or MaxDB 7.6, the UNIX user identity of the OS user who administers the MaxDB database is sdb. You must specify this user in DB_User extension property when you create the MaxDB resource in a later step. Otherwise, the MaxDB fault monitor cannot probe the MaxDB database.
-
Create a plain text file that contains information about the database user who administers the MaxDB database instance.
For information about the content of this file, see the MaxDB documentation. For the name of the server on which the database is running, specify the logical host name for the MaxDB resource that you specified in Configuration Planning Questions.
For an example of the content of this file, see Example 4.
-
As MaxDB admin user, generate the .XUSER.62 file from the plain text file that you created in Step a.
Use the MaxDB command xuser for this purpose.
# xuser -b user-info-file
- -b user-info-file
-
Specifies the plain text file from which you are generating the .XUSER.62 file
-
-
Copy the /usr/spool/sql directory and its contents from the node on which you installed MaxDB to all nodes where resources for MaxDB and SAP xserver will run.
To ensure that the same owner owns the directory and its contents on all nodes, use the tar(1) command and the rsh(1)
# tar cfB - /usr/spool/sql | rsh destination tar xfB -
- destination
-
Specifies the node to which you are copying the /usr/spool/sql directory and its contents
The following example shows a plain text file that contains information about a database user who administers an MaxDB instance.
-
If you are installing MaxDB 7.5 or MaxDB 7.6, perform this step. If you are installing a previous version, proceed to the next step.
Copy the /etc/opt/sdb directory and its contents from the node on which you installed MaxDB to all nodes where resources for MaxDB and SAP xserver will run.
To ensure that the same owner owns the directory and its contents on all nodes, use the tar(1) command and the rsh(1)
# tar cfB - /etc/opt/sdb | rsh destination tar xfB -
- destination
-
Specifies the node to which you are copying the /etc/opt/sdb directory and its contents
-
If you are using MaxDB version earlier than 7.6.03.09, comment out /net in /etc/auto_master file and remove nis from the automount entry in /etc/nsswitch.conf file.
Example 4 Information About a Database User Who Administers a MaxDB Instance
DEFAULT dbm dbm TST srvr-1 blank line blank line -1 -1 blank line
This example specifies the following information about a database user who administers an MaxDB instance:
-
The user key that is used to address this combination of XUSER data is named DEFAULT.
-
The user name and password of the database user are dbm.
-
The name of the MaxDB instance is TST.
-
The logical host name for the MaxDB resource is srvr-1.
-
No structured query language (SQL) mode is specified.
-
The default time-out value of the MaxDB instance is used.
-
The default isolation level of the MaxDB instance is used.
For more information, see the MaxDB documentation.
 How to Enable MaxDB to
Run in a Cluster
How to Enable MaxDB to
Run in a Cluster
-
Create a failover resource group to contain the MaxDB application resources and the logical host name for the MaxDB resource.
Use the resource group that you identified when you answered the questions in Configuration Planning Questions.
# clresourcegroup create -n node-zone-list sapdb-rg
- sapdb-rg
-
Specifies that the resource group that you are creating is named sapdb-rg.
- -n node-zone-list
-
Specifies a comma-separated, ordered list of zones that can master this resource group. The format of each entry in the list is node. In this format, node specifies the node name and zone specifies the name of a non-global Solaris zone. To specify the global zone, or to specify a node without non-global zones, specify only node.
This list is optional. If you omit this list, the global zone of each cluster node can master the resource group.
-
Ensure that all network resources that you intend to you use are added to your name service database.
-
Add a logical host name resource to the failover resource group that you created in Step 1.
# clreslogicalhostname create -g sapdb-rg \ -h sapdb-logical-hostname sapdb-logical-hostname
- -g sapdb-rg
-
Specifies that the logical host name's database resource is to be added to the failover resource group that you created in Step 1.
- -h
-
Specifies the host name list. You must use this option either when more than one logical host needs to be associated with the new MaxDB resource or when the logical host does not have the same name as the MaxDB resource itself. MaxDB is the resource for the sapdb-logical-hostname that you specified in Configuration Planning Questions.
- sapdb-logical-hostname
-
Specifies the logical host name of the server on which the database is running. This host name must be the logical host name for the MaxDB resource that you specified in Configuration Planning Questions.
Note –If you require a fully qualified hostname, you must specify the fully qualified name with the -h option and you cannot use the fully qualified form in the resource name.
-
Enable the resource group that you created in Step 1.
# clresourcegroup online -emM sapdb-rg
- -emM
-
Enables the resource group sapdb-rg created in Step 1 and moves it to the MANAGED state.
Example 5 Enabling MaxDB to Run in a Cluster
This example shows the sequence of commands that are required to enable MaxDB to run in a cluster. The commands are run on only one cluster node.
-
The following command creates a failover resource group to contain the MaxDB application resources and the logical host name for the MaxDB resource. The resource group is named sapdbrg. The sapdbrg resource group can be brought online on all cluster nodes or zones.
# clresourcegroup create sapdbrg
-
The following command adds a logical host name resource to the sapdbrg resource group. The logical host name of the server on which the database is running is srvr-1. When the sapdbrg resource group is brought online, an attempt is made for each node to discover a network interface on the subnet that the host name list identifies.
# clreslogicalhostname create -g sapdbrg -h sdrvr-1 -d sapdblr
Note –If you require a fully qualified hostname, you must specify the fully qualified name with the -h option and you cannot use the fully qualified form in the resource name.
-
The following command moves the sapdbrg resource group to the MANAGED state, brings the resource group online, and monitors the resources in the resource group.
# clresourcegroup online -emM sapdbrg
Verifying the MaxDB Installation and Configuration
Before you install the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB packages, verify that the MaxDB software is correctly installed and configured to run in a cluster. This verification does not verify that the MaxDB application is highly available because the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB data service is not yet installed.
 How to Verify MaxDB Installation
and Configuration on Each Node
How to Verify MaxDB Installation
and Configuration on Each Node
Perform this procedure on each node or zone that can master the MaxDB resource group.
-
Log in as superuser to a node or zone that can master the MaxDB resource group.
-
Switch the MaxDB resource group to the node that you logged in to in Step 1.
# clresourcegroup switch -n node sapdb-rg
- -n node
-
Specifies the node to which the MaxDB resource group is to be switched
- sapdb-rg
-
Specifies that the MaxDB resource group sapdb-rg is to be switched to another node
-
Confirm that the MaxDB database can be started and be stopped.
-
Become the OS user who administers the MaxDB database.
# su - os-sapdb-adm-user
- os-sapdb-adm-user
-
Specifies the UNIX user identity of the OS user who administers the MaxDB database. This user's home directory contains the .XUSER.62 file that was created during the installation and configuration of MaxDB. For more information, see Installing and Configuring MaxDB. You specify this user when you set the DB_User extension property as explained in How to Register and Configure a MaxDB Resource.
If you are using MaxDB 7.5 or MaxDB 7.6, the UNIX user identity of the OS user who administers the MaxDB database is sdb.
-
$ x_server start
-
Manually start the MaxDB database instance on the node that you logged in to in Step 1.
$ dbmcli -U sapdb-adm-key db_online
- -U sapdb-adm-key
-
Specifies that the dbmcli command is run with the user key of the database user who administers the MaxDB instance. This user key is created during the installation and configuration of MaxDB. For more information, see Installing and Configuring MaxDB. You specify this user key when you set the User_Key extension property as explained in How to Register and Configure a MaxDB Resource.
-
Confirm that the MaxDB database instance is started.
-
Manually stop the MaxDB database instance.
$ dbmcli -U sapdb-adm-key db_offline
- -U sapdb-adm-key
-
Specifies that the dbmcli command is run with the user key that you used for starting the database in Step c
-
Confirm that the MaxDB database instance is stopped.
-
Installing the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB Packages
If you did not install the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB packages during your initial Sun Cluster installation, perform this procedure to install the packages. To install the packages, use the Sun JavaTM Enterprise System Installation Wizard.
Note –
You need to install the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB packages in the global cluster and not in the zone cluster.
 How to Install the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB Packages
How to Install the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB Packages
Perform this procedure on each cluster node where you are installing the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB packages.
You can run the Sun Java Enterprise System Installation Wizard with a command-line interface (CLI) or with a graphical user interface (GUI). The content and sequence of instructions in the CLI and the GUI are similar.
Note –
Even if you plan to configure this data service to run in non-global zones, install the packages for this data service in the global zone. The packages are propagated to any existing non-global zones and to any non-global zones that are created after you install the packages.
Before You Begin
Ensure that you have the Sun Java Availability Suite DVD-ROM.
If you intend to run the Sun Java Enterprise System Installation Wizard with a GUI, ensure that your DISPLAY environment variable is set.
-
On the cluster node where you are installing the data service packages, become superuser.
-
Load the Sun Java Availability Suite DVD-ROM into the DVD-ROM drive.
If the Volume Management daemon vold(1M) is running and configured to manage DVD-ROM devices, the daemon automatically mounts the DVD-ROM on the /cdrom directory.
-
Change to the Sun Java Enterprise System Installation Wizard directory of the DVD-ROM.
-
Start the Sun Java Enterprise System Installation Wizard.
# ./installer
-
When you are prompted, accept the license agreement.
If any Sun Java Enterprise System components are installed, you are prompted to select whether to upgrade the components or install new software.
-
From the list of Sun Cluster agents under Availability Services, select the data service for MaxDB.
-
If you require support for languages other than English, select the option to install multilingual packages.
English language support is always installed.
-
When prompted whether to configure the data service now or later, choose Configure Later.
Choose Configure Later to perform the configuration after the installation.
-
Follow the instructions on the screen to install the data service packages on the node.
The Sun Java Enterprise System Installation Wizard displays the status of the installation. When the installation is complete, the wizard displays an installation summary and the installation logs.
-
(GUI only) If you do not want to register the product and receive product updates, deselect the Product Registration option.
The Product Registration option is not available with the CLI. If you are running the Sun Java Enterprise System Installation Wizard with the CLI, omit this step.
-
Exit the Sun Java Enterprise System Installation Wizard.
-
Unload the Sun Java Availability Suite DVD-ROM from the DVD-ROM drive.
Next Steps
Go to Configuring the HAStoragePlus Resource Type to Work With Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB.
Configuring the HAStoragePlus Resource Type to Work With Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB
For maximum availability of the MaxDB database, resources that Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB requires must be available before the MaxDB database instance is started. An example of such a resource is the file system where programs and libraries for the MaxDB runtime environment reside. To ensure that these resources are available, configure the HAStoragePlus resource type to work with Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB.
For information about the relationship between resource groups and disk device groups, see Relationship Between Resource Groups and Device Groups in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS.
Configuring the HAStoragePlus resource type to work with Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB involves the following operation:
-
Registering and configuring an HAStoragePlus resource
 How to Register and Configure an HAStoragePlus Resource
How to Register and Configure an HAStoragePlus Resource
Perform this procedure on any one cluster node.
-
Register the SUNW.HAStoragePlus resource type.
# clresourcetype register SUNW.HAStoragePlus
-
Create an HAStoragePlus resource for the global device group on which MaxDB is installed.
Create this resource in the MaxDB resource group. This resource must perform an affinity switchover for all global devices that are defined for this resource.
# clresource create -d -g sapdb-rg \ -t SUNW.HAStoragePlus -p filesystemmountpoints=mountpoint-list \ -p globaldevicepaths=sapdb-device-group \ -p affinityon=TRUE hsp-resource
- -d
-
Specifies that a new resource is to be created in a disabled state.
- -g sapdb-rg
-
Specifies that the resource is to be added to the MaxDB resource group.
- -t SUNW.HAStoragePlus
-
Specifies that the resource is an instance of the SUNW.HAStoragePlus resource type.
- -p filesystemmountpoints=mountpoint-list
-
Specifies a list of valid mount points for the file system.
- -p globaldevicepaths=sapdb-device-group
-
Specifies the name of the global device group on which the MaxDB software is installed.
- -p affinityon=TRUE
-
Specifies that this resource performs an affinity switchover for all global devices that are defined for this resource.
- hsp-resource
-
Specifies that the resource that you are creating is named hsp-resource.
The resource is created in the enabled state.
Example 6 Creating an HAStoragePlus Resource
# clresource create -g sapdbrg \ -t SUNW.HAStoragePlus -p filesystemmountpoints=/global/sapdbdata \ -p globaldevicepaths=sapdbdg -p affinityon=TRUE hsprs |
This example shows the creation of a SUNW.HAStoragePlus resource that has the following characteristics:
-
The resource is named hsprs.
-
The resource is a member of a resource group that is named sapdbrg. The creation of this resource group is shown in Example 5.
-
The resource is an instance of the SUNW.HAStoragePlus resource type. The registration of this resource type is not shown in this example.
-
The mount point for the file system is /global/sapdbdata.
-
The MaxDB software is installed on a global device group that is named sapdbdg.
-
The hsprs resource performs an affinity switchover for all global devices that are defined for this resource.
Next Steps
Go to Registering and Configuring Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB.
Registering and Configuring Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB
To enable Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB to make MaxDB highly available, configure Sun Cluster data services as follows:
-
Configure SAP xserver as a scalable data service.
-
Configure Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB as a failover data service.
Before you perform this procedure, ensure that the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB data service packages are installed.
One SAP xserver serves multiple MaxDB instances and, if SAP liveCache is used, multiple SAP liveCache instances in the cluster. Therefore, do not configure more than one SAP xserver resource on the same cluster. If more than one SAP xserver resource runs on the same cluster, conflicts between the SAP xserver resources occur. These conflicts cause all SAP xserver resources to become unavailable. If you attempt to start the SAP xserver a second time, the attempt fails. The error message Address already in use is also displayed.
Setting Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB Extension Properties
The sections that follow contain instructions for registering and configuring resources. These instructions explain how to set only extension properties that Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB requires you to set. For information about all Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB extension properties, see Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB Extension Properties. You can update some extension properties dynamically. You can update other properties, however, only when you create or disable a resource. The Tunable entry indicates when you can update a property.
To set an extension property of a resource, include the following option to modify the resource:
-p property=value |
- -p property
-
Identifies the extension property that you are setting
- value
-
Specifies the value to which you are setting the extension property
You can also use the procedures in Chapter 2, Administering Data Service Resources, in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS to configure resources after the resources are created.
Administering SAP xserver as a User Other Than Root
You might be required to administer SAP xserver as a user other than root. In this situation, you must create and define that user as follows:
-
You must create that user on all cluster nodes or zones that master SAP xserver.
-
You must define that user when you register and configure an SAP xserver resource. To define the user who administers SAP xserver, set the Xserver_User extension property when you create an SAP xserver resource. For more information about the Xserver_User extension property, see SUNW.sap_xserver Extension Properties.
 How to Register and Configure an SAP xserver Resource
How to Register and Configure an SAP xserver Resource
-
Become superuser on a cluster node.
-
Register the SUNW.sap_xserver resource type.
# clresourcetype register SUNW.sap_xserver
-
Create a scalable resource group for the SAP xserver resource.
Configure SAP xserver so that SAP xserver starts on all nodes to which the MaxDB resource can fail over. To implement this configuration, ensure that the node list of the SAP xserver resource group contains all nodes that are in the node list of the MaxDB resource group. This resource group is created when the procedure How to Enable MaxDB to Run in a Cluster is performed.
# clresourcegroup create -n node-zone-list \ -p Maximum_primaries=nodes-in-sapdb-rg \ -p Desired_primaries=nodes-in-sapdb-rg xserver-rg
- -n node-zone-list
-
Specifies a comma-separated, ordered list of zones that can master this resource group. The format of each entry in the list is node. In this format, node specifies the node name and zone specifies the name of a non-global Solaris zone. To specify the global zone, or to specify a node without non-global zones, specify only node.
This list is optional. If you omit this list, the global zone of each cluster node can master the resource group.
- -p Maximum_primaries=nodes-in-sapdb-rg
-
Specifies the maximum number of nodes on which the SAP xserver resource can start. This number is equal to the number of nodes that are in the node list of the MaxDB resource group. You must specify the same number as the value of the Desired_primaries property.
- -p Desired_primaries=nodes-in-sapdb-rg
-
Specifies the desired number of nodes on which the SAP xserver resource can start. This number is equal to the number of nodes that are in the node list of the MaxDB resource group. You must specify the same number as the value of the Maximum_primaries property.
- xserver-rg
-
Specifies that the resource group that you are creating is named xserver-rg.
-
Add the HAStoragePlus resource to the SAP xserver resource group.
# clresource create -g xserver-rg \ -t SUNW.HAStoragePlus \ -p filesystemmountpoints=mountpoints \ -p affinityon=false xserver-storage-resource
- -g xserver-rg
-
Specifies that the resource that you are creating is added to the resource group xserver-rg.
- -t SUNW.HAStoragePlus
-
Specifies that the resource type of the resource you are creating is SUNW.HAStoragePlus.
- -p filesystemmountpoints=mountpoint, ...
-
Specifies the mount points for the resource group you are creating.
- -p affinityon=false
-
Indicates that the SAP xserver resource does not have to be colocated with the device group.
- xserver-storage-resource
-
Specifies that the resource that you are creating is named xserver-storage-resource.
The resource is created in the enabled state.
For more details on how to set up an HAStoragePlus resource, see Enabling Highly Available Local File Systems in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS.
-
Create an SAP xserver resource in the resource group that you created in Step 3.
# clresource create -d -g xserver-rg \ -t SUNW.sap_xserver \ -p resource_dependencies=xserver-storage-resource xserver-resource
- -g xserver-rg
-
Specifies that the resource is to be added to the resource group that you created in Step 3
- -t SUNW.sap_xserver
-
Specifies that the resource is an instance of the SUNW.sap_xserver resource type
- -p resource_dependencies=xserver-storage-resource
-
Sets a resource dependency between xserver-storage-resource and the HAStoragePlus resource we created in Step 4.
- xserver-resource
-
Specifies that the resource that you are creating is named xserver-resource.
The resource is created in the enabled state.
-
Enable the resource group that you created in Step 3.
# clresourcegroup online -emM xserver-rg
- -emM
-
Enables the resource group and moves it to the MANAGED state.
- xserver-rg
-
Specifies the name of the resource group.
Example 7 Configuring a SUNW.sap_xserver Resource
This example shows the sequence of commands that are required to configure an SAP xserver resource. The commands are run on only one cluster node.
-
The following command creates a scalable resource group to contain an SAP xserver resource for a four-node cluster. The resource group is named xsrvrrg. The xsrvrrg resource group can be brought online on all cluster nodes.
# clresourcegroup create \ -p Maximum_primaries=4 \ -p Desired_primaries=4 xsrvrrg
-
The following command adds the HAStoragePlus resource to the SAP xserver resource group. The xserver-storage-resource is called xsstorrs and the mount point, mtp1.
# clresource create -d -g xsrvrrg \ -t SUNW.HAStoragePlus \ -p filesystemmountpoints=mtp1 \ -p affinityon=false xsstorrs
The resource is created in the enabled state.
-
The following command creates an SAP xserver resource that is named xsrvrrs in the xsrvrrg resource group. The SAP xserver resource is an instance of the SUNW.sap_xserver resource type. The xserver-storage-resource is xsstorrs. The registration of this resource type is not shown in this example.
# clresource create -d -g xsrvrrg -t SUNW.sap_xserver \ -p resource_dependencies=xsstorrs xsrvrrs
The resource is created in the enabled state.
-
The following command moves the xsrvrrg resource group to the MANAGED state and brings the resource group online.
# clresourcegroup online -emM xsrvrrg
 How to Register and Configure a MaxDB Resource
How to Register and Configure a MaxDB Resource
-
Register the SUNW.sapdb resource type.
# clresourcetype register SUNW.sapdb
-
Create a MaxDB resource in the MaxDB resource group.
Ensure that the MaxDB resource depends on the following resources:
-
The HAStoragePlus resource for the global device group on which MaxDB is installed.
-
The SAP xserver resource.
When you create this resource, specify the following information about the MaxDB database instance. This information is created when MaxDB is installed and configured as explained in Installing and Configuring MaxDB.
-
The name of the MaxDB database.
-
The UNIX user identity of the OS user who administers the MaxDB database instance. If you are using MaxDB 7.5 or MaxDB 7.6, the UNIX user identity of the OS user who administers the MaxDB database is sdb.
-
The user key of the database user who administers the MaxDB database instance.
# clresource create -d -g sapdb-rg \ -t SUNW.sapdb \ -p DB_Name=db-name \ -p DB_User=os-sapdb-adm-user \ -p User_Key=sapdb-adm-key \ -p resource_dependencies=hsp-resource,xserver-resource sapdb-rs
- -d
-
Specifies that the resource that you are creating is not immediately enabled.
- -g sapdb-rg
-
Specifies that the resource is to be added to the MaxDB resource group.
- -t SUNW.sapdb
-
Specifies that the resource is an instance of the SUNW.sapdb resource type.
- -p DB_Name=db-name
-
Specifies the name of the MaxDB database instance in uppercase.
- -p DB_User=os-sapdb-adm-user
-
Specifies the UNIX user identity of the OS user who administers the MaxDB database. This user's home directory contains the .XUSER.62 file that was created during the installation and configuration of MaxDB. For more information, see Installing and Configuring MaxDB.
- -p User_Key=sapdb-adm-key
-
Specifies the user key of the database user who administers the MaxDB database instance. This user key is created during the installation and configuration of MaxDB. For more information, see Installing and Configuring MaxDB.
- -p resource_dependencies=hsp-resource,xserver-resource
-
Specifies that the MaxDB resource depends on the following resources.
-
The HAStoragePlus resource for the global device group on which MaxDB is installed
-
The SAP xserver resource
-
- sapdb-rs
-
Specifies that the resource that you are creating is named sapdb-rs.
The resource is created in the enabled state.
-
-
Ensure that the MaxDB resource group is brought online only on a node or zone where the SAP xserver resource group is online.
To meet this requirement, create on the MaxDB resource group a strong positive affinity for the SAP xserver resource group.
# clresourcegroup set -p rg_affinities=++xserver-rg sapdb-rg
- -p rg_affinities=++xserver-rg
-
Specifies that the MaxDB resource group declares a strong positive affinity for the SAP xserver resource group.
- sapdb-rg
-
Specifies that theMaxDB resource group is to be modified.
-
Enable the MaxDB resource group.
#clresourcegroup online -emM sapdb-rg
- -emM
-
Enables the MaxDB resource group and moves it to the MANAGED state.
- sapdb-rg
-
Specifies the name of the MaxDB resource group to be brought online.
-
(Optional) Consider configuring your cluster to prevent noncritical resource groups from being brought online on the same node or zone as the MaxDB resource group.
You might plan to run lower-priority services on a node to which the MaxDB resource can fail over. In this situation, consider using resource group affinities to shut down the noncritical services when the MaxDB resource fails over to the node.
To specify this behavior, declare on the resource group for each noncritical service a strong negative affinity for the MaxDB resource group.
# clresourcegroup set -p rg_affinities=--sapdb-rg noncritical-rg
- -p
-
Sets the resource group property to the specified value.
- noncritical-rg
-
Specifies the name of the noncritical resource group.
Example 8 Creating a SUNW.sapdb Resource
# clresource create -d -g sapdbrg -t SUNW.sapdb \ -p DB_Name=TST -p DB_User=dbadmin \ -p User_Key=DEFAULT -p resource_dependencies=hsprs,xsrvrrs sapdbrs |
The resource is created in the enabled state.
This example shows the creation of a SUNW.sapdb resource that has the following characteristics:
-
The resource is named sapdbrs.
-
The resource is a member of a resource group that is named sapdbrg. The creation of this resource group is shown in Example 5.
-
The resource is an instance of the SUNW.sapdb resource type. The registration of this resource type is not shown in this example.
-
The MaxDB database instance that is associated with this resource is named TST.
-
The UNIX user identity of the OS user who administers the MaxDB database is dbadmin.
-
The user key of the database user who administers the MaxDB database is DEFAULT.
-
The MaxDB resource depends on the following resources:
Tuning the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB Fault Monitors
Fault monitoring for the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB data service is provided by the following fault monitors:
-
The MaxDB fault monitor
-
The SAP xserver fault monitor
Each fault monitor is contained in a resource whose resource type is shown in the following table.
Table 3 Resource Types for Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB Fault Monitors|
Fault Monitor |
Resource Type |
|---|---|
|
MaxDB |
SUNW.sapdb |
|
SAP xserver |
SUNW.sap_xserver |
System properties and extension properties of these resources control the behavior of the fault monitors. The default values of these properties determine the preset behavior of the fault monitors. The preset behavior should be suitable for most Sun Cluster installations. Therefore, you should tune the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB fault monitors only if you need to modify this preset behavior.
Tuning the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB fault monitors involves the following tasks:
-
Setting the interval between fault monitor probes
-
Setting the timeout for fault monitor probes
-
Defining the criteria for persistent faults
-
Specifying the failover behavior of a resource
For more information, see Tuning Fault Monitors for Sun Cluster Data Services in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS. Information about the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB fault monitors that you need to perform these tasks is provided in the subsections that follow.
Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB also enables you to control how the fault monitor responds if the MaxDB parent kernel process is not running. For more information, see Forcing the MaxDB Database Instance to Be Restarted if the Parent Kernel Process Is Terminated.
Tune the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB fault monitors when you register and configure Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB. For more information, see Registering and Configuring Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB.
Factors That Affect the Interval Between Fault Monitor Probes
To determine whether SAP xserver and the MaxDB database instance are operating correctly, the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB fault monitors probe these resources periodically. The optimum interval between fault monitor probes depends on the time that is required to respond to a fault in a resource. This time depends on how the complexity of the resource affects the time that is required for operations such as restarting the resource.
For example, SAP xserver is a much simpler resource and can be restarted much quicker than MaxDB. Therefore, the optimum interval between fault monitor probes of SAP xserver is shorter than the optimum interval between probes of MaxDB.
Operations by the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB Fault Monitors During a Probe
The optimum timeout for fault monitor probes depends on the operations that a fault monitor performs to probe the resource.
Operations by the MaxDB Fault Monitor During a Probe
During a probe, the MaxDB fault monitor performs the following operations:
-
The MaxDB fault monitor determines whether the MaxDB database instance is online.
-
If the MaxDB database instance is online, the MaxDB fault monitor determines whether the parent kernel process of the MaxDB database instance is running. You can control how the fault monitor responds if the parent kernel process is not running. For more information, see Forcing the MaxDB Database Instance to Be Restarted if the Parent Kernel Process Is Terminated.
-
The MaxDB fault monitor determines whether SAP xserver is available. This fault monitoring supplements the fault monitoring that the SAP xserver fault monitor provides.
Operations by the SAP xserver Fault Monitor During a Probe
During a probe, the SAP xserver fault monitor determines whether SAP xserver is available.
Faults Detected by the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB Fault Monitors
Faults that each Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB fault monitor detects are described in the subsections that follow.
Faults Detected by the MaxDB Fault Monitor
The MaxDB fault monitor detects the following faults in MaxDB:
-
A status of the MaxDB database instance that is not ONLINE, for example, OFFLINE or ADMIN
-
Unexpected termination of the parent kernel process of the MaxDB database instance
The MaxDB fault monitor also detects the unavailability of SAP xserver. This fault monitoring supplements the fault monitoring that the SAP xserver fault monitor provides.
Note –
If the MaxDB fault monitor detects that SAP xserver is unavailable twice within the retry interval, the MaxDB fault monitor restarts MaxDB. By restarting MaxDB, the fault monitor ensures that the MaxDB database fails over to another node when SAP xserver is persistently unavailable.
Faults Detected by the SAP xserver Fault Monitor
The SAP xserver fault monitor detects following faults:
-
Unavailability of SAP xserver. Unavailability of SAP xserver is also detected by the MaxDB fault monitor.
-
Persistent system errors. A persistent system error is a system error that occurs four times within the retry interval. If a persistent system error occurs, the fault monitor restarts SAP xserver.
Recovery Actions in Response to Detected Faults
To minimize the disruption that transient faults in a resource cause, a fault monitor restarts the resource in response to such faults. For persistent faults, more disruptive action than restarting the resource is required:
-
For the MaxDB resource, the fault monitor fails over the resource to another node. The MaxDB resource is a failover resource.
-
For the SAP xserver resource, the fault monitor takes the resource offline. The SAP xserver is a scalable resource.
Forcing the MaxDB Database Instance to Be Restarted if the Parent Kernel Process Is Terminated
By default, unexpected termination of the parent kernel process does not cause the MaxDB fault monitor to restart the MaxDB database instance. The MaxDB database instance can continue to function without the parent kernel process. Restarting the MaxDB database instance in this situation might cause unnecessary unavailability of the MaxDB database instance. Therefore, you should force the MaxDB database instance to be restarted only if you require a feature that the parent kernel process provides. An example of such a feature is maintaining the integrity of the log history.
To force the MaxDB database instance to be restarted if the parent kernel process is terminated, set the Restart_if_Parent_Terminated extension property of the SUNW.sapdb resource to True.
Verifying the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB Installation and Configuration
After you install, register, and configure Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB, verify the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB installation and configuration. Verifying the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB installation and configuration determines if the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB data service makes the MaxDB application highly available.
Verifying the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB installation involves verifying the operation of the following fault monitors:
-
The MaxDB fault monitor
-
The SAP xserver fault monitor
 How to Verify the Operation of the MaxDB Fault
Monitor
How to Verify the Operation of the MaxDB Fault
Monitor
Perform this procedure on each node where MaxDB can run.
-
Log in as superuser to a node or zone that can master the MaxDB resource group.
-
Switch the MaxDB resource group to the node or zone that you logged in to in Step 1.
# clresourcegroup switch -n node sapdb-rg
- node
-
Specifies the node to which the MaxDB resource group is to be switched
- sapdb-rg
-
Specifies the name of the MaxDB resource group is to be switched to another node
-
Abnormally terminate MaxDB.
-
Determine the process identities of all kernel processes for the MaxDB database instance that you are running.
# ps -ef | grep kernel | grep db-name
- db-name
-
Specifies the name of the MaxDB database instance in uppercase
-
Kill all kernel processes for the MaxDB database instance that you are running.
# kill -9 sapdb-kernel-pid
- sapdb-kernel-pid
-
Specifies the process identities of the MaxDB kernel processes that you determined in Step a
-
-
Confirm that the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB fault monitor performs the appropriate operation from the following list:
-
Restarting the MaxDB resource
-
Failing over the MaxDB resource to another node
The expected behavior of the fault monitor depends on the failure history of the resource and the value of the Failover_enabled extension property. For more information, see the following sections:
-
-
Terminate MaxDB normally.
-
Become the OS user who administers the MaxDB database.
# su - os-sapdb-adm-user
- os-sapdb-adm-user
-
Specifies the UNIX user identity of the OS user who administers the MaxDB database. This user's home directory contains the .XUSER.62 file that was created during the installation and configuration of MaxDB. For more information, see Installing and Configuring MaxDB. You specify this user when you set the DB_User extension property as explained in How to Register and Configure a MaxDB Resource. If you are using MaxDB 7.5 or MaxDB 7.6, the UNIX user identity of the OS user who administers the MaxDB database is sdb.
-
Manually stop the MaxDB database instance.
# dbmcli -U sapdb-adm-key db_offline
- -U sapdb-adm-key
-
Specifies that the dbmcli command is run with the user key of the database user who administers the MaxDB database. This user key is created during the installation and configuration of MaxDB. For more information, see Installing and Configuring MaxDB. You specify this user key when you set the User_Key extension property as explained in How to Register and Configure a MaxDB Resource.
-
-
Confirm that the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB fault monitor performs the appropriate operation from the following list:
-
Restarting the MaxDB resource
-
Failing over the MaxDB resource to another node
The expected behavior of the fault monitor depends on the failure history of the resource and the value of the Failover_enabled extension property. For more information, see the following sections:
-
 How to Verify the Operation of the SAP xserver Fault
Monitor
How to Verify the Operation of the SAP xserver Fault
Monitor
Perform this procedure on each node that can master SAP xserver.
-
Log in to a node or zone that can master SAP xserver.
-
Abnormally terminate SAP xserver.
-
Determine the process identities of all SAP xserver processes.
# ps -ef | grep vserver
-
Kill all SAP xserver processes.
# kill -9 xserver-pid
- xserver-pid
-
Specifies the process identities of the SAP xserver processes that you determined in Step a
-
-
Confirm that the SAP xserver fault monitor restarts the SAP xserver resource.
-
Terminate SAP xserver normally.
-
Become the OS user who administers SAP xserver.
# su - os-sapxsrvr-adm-user
- os-sapxsrvr-adm-user
-
Specifies the UNIX user identity of the OS user who administers SAP xserver. By default, this user is root. You can specify this user by setting the Xserver_User extension property. For more information, see SUNW.sap_xserver Extension Properties.
-
Manually stop the SAP xserver.
# x_server stop
-
-
Confirm that the SAP xserver fault monitor restarts the SAP xserver resource.
Upgrading the SUNW.sap_xserver Resource Type
The SUNW.sap_xserver resource type is supplied with the Sun Cluster HA for SAP liveCache data service. The Sun Cluster HA for SAP liveCache data service is installed when you install Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB data service. Upgrade the SUNW.sap_xserver resource type if all conditions in the following list apply:
-
You are using version 3.0 5/02 asynchronous release, version 3.1 5/03, version 3.1 10/03, or 3.1 4/04 of the Sun Cluster HA for SAP liveCache data service.
-
You plan to use the Sun Cluster HA for MaxDB data service with your existing version of the Sun Cluster HA for SAP liveCache data service.
-
You need to use the new features of the SUNW.sap_xserver resource type.
For general instructions that explain how to upgrade a resource type, see Upgrading a Resource Type in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS. The information that you need to complete the upgrade of the SUNW.sap_xserver resource type is provided in the subsections that follow.
Information for Registering the New Resource Type Version
The relationship between a resource type version and the release of Sun Cluster data services is shown in the following table. The release of Sun Cluster data services indicates the release in which the version of the resource type was introduced.
|
Resource Type Version |
Sun ClusterData Services Release |
|---|---|
|
1.0 |
3.0 5/02 asynchronous release |
|
2 |
3.1 4/04 |
|
3.1 |
3.2 |
To determine the version of the resource type that is registered, use the clresource list command.
The resource type registration (RTR) file for this resource type is /opt/SUNWsclc/xserver/etc/SUNW.sap_xserver.
Information for Migrating Existing Instances of the Resource Type
The information that you need to migrate instances of the SUNW.sap_xserver resource type is as follows:
-
You can perform the migration only when the resource is unmonitored.
-
If you need to use the new features of the SUNW.sap_xserver resource type, the required value of the Type_version property is 2.
-
If you need to specify the directory that contains programs and libraries for the SAP xserver runtime environment, set the Independent_Program_Path extension property. For more information, see SUNW.sap_xserver Extension Properties.
The following example shows a command for editing an instance of the SUNW.sap_xserver resource type.
Example 9 Editing an Instance of the SUNW.sap_xserver Resource Type During Upgrade
# clresource set -p Independent_Program_Path=/sapdb/indep_prog \ -p Type_version=2 sapxserver-rs |
This command edits a SUNW.sap_xserver resource as follows:
-
The SUNW.sap_xserver resource is named sapxserver-rs.
-
The Type_version property of this resource is set to 2.
-
The independent program path is /sapdb/indep_prog.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
