Liberty Identity Federation Framework
The Liberty Identity Federation Framework (Liberty ID-FF) defines a set of protocols, bindings, and profiles that provides a solution for identity federation, cross-domain authentication, and session management. This framework can be used to create a new identity management system or to develop one in conjunction with legacy systems. The Liberty ID-FF is designed to work with heterogeneous platforms, various networking devices (including personal computers, mobile phones, and personal digital assistants), and emerging technologies. The following figure shows the subjects involved in a Liberty ID-FF implementation.
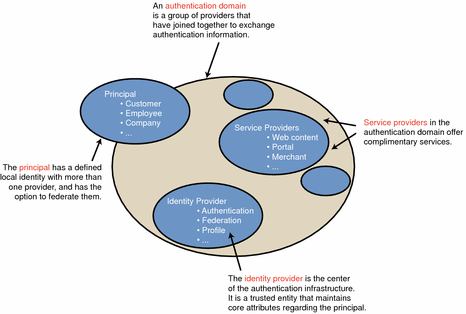
Figure 1–1 Subjects Involved in a Liberty ID-FF Implementation
-
A principal can have a defined local identity with more than one provider, and it has the option to federate the identities. The principal might be an individual user, a group of individuals, a corporation, or a component of the Liberty architecture.
-
A service provider is a commercial or not-for-profit organization that offers a web-based service such as a news portal, a financial repository, or retail outlet.
-
An identity provider is a service provider that stores identity profiles and offers incentives to other service providers for the prerogative of federating their user identities. Identity providers might also offer services above and beyond those related to identity profile storage.
-
To support identity federation, both service and identity providers must join together into an authentication domain. An authentication domain must contain at least one identity provider and at least two service providers. One organization may be both an identity provider and a service provider.
Organizations in an authentication domain must first write operational agreements to define their relationships in a circle of trust. An operational agreement is a contract between organizations that defines how the circle will work. For more information, see Authentication Domain and Provider Federation.
Liberty ID-FF Protocols and Schema
The Liberty ID-FF Protocols and Schema Specifications defines these abstract protocols:
Following are short explanations of each protocol. More detailed information can be found in the Liberty ID-FF Protocols and Schema Specifications.
Single Sign-On and Federation Protocol
The Single Sign-On and Federation Protocol defines a request and response protocol by which a principal is able to authenticate to one or more service providers and federate (or link) configured identities. A service provider issues a request for authentication to an identity provider. The identity provider responds with a message that contains authentication information, or an artifact that points to authentication information. The identity provider can also federate the principal’s identity (configured at the identity provider level) with the principal’s identity (configured at the service provider level).
Note –
Under certain conditions, an identity provider may issue an authentication response to a service provider without having received an authentication request.
The Single Sign-On and Federation Protocol also defines controls that allow for the following behaviors:
-
Account federation. A principal can choose to federate a configured identity at the identity provider site with a configured identity at the service provider site.
-
Account handle. An identity provider can issue an anonymous, temporary identifier to refer to a particular principal during communication with a service provider. This identifier is used to obtain information for or about the principal during federation (with the principal's consent). The account handle is generated by the identity provider during federation. This account handle is not to be confused with the handle that can be generated by the service provider after federation using the Name Registration Protocol as discussed in Name Registration Protocol.
-
Affiliation federation. Federation based on group affiliation can be enabled in an authentication request. If enabled, it indicates that the requester is acting as a member of the specified affiliation group. Federations are then established and resolved based on the affiliation, not the requesting provider. The process allows for a unique identifier that represents the affiliation.
-
Authentication context. A service provider can choose the type and level of authentication that should be used when a principal logs in.
-
Authentication credentials. A principal can be prompted to authenticate with a user name and password, for example, at the behest of the service provider.
-
Dynamic identity provider proxying. One identity provider might be asked to authenticate a principal that has already been authenticated by a second identity provider. In this case, the first identity provider may request authentication information from the second identity provider on behalf of the service provider. Proxy behavior can be controlled by indicating a list of preferred identity providers, and a value that defines the maximum number of proxy steps that can be taken. Proxy behavior is defined locally by the proxying identity provider, although a service provider controls whether or not to proxy. For more information, see Dynamic Identity Provider Proxying.
-
Identity provider introduction. When an authentication domain has more than one identity provider, a service provider can use this feature to determine which identity provider a principal is using.
-
Message exchange profiles. The authentication request defines how messages are exchanged between identity providers and service providers. The particular transfer and messaging protocol used in the exchange (such as HTTP or SOAP) are specified in profiles. Two of these profiles are:
-
The Liberty Artifact profile relies on Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) artifacts and assertions to relay authentication information.
-
The Liberty Browser POST profile relies on an HTML form to communicate authentication information between providers.
-
-
One-time federation. The ability to federate for one session only can be enabled in an authentication request. This feature is useful for service providers with no user accounts, for principals who want to act anonymously, or for dynamically created user accounts. It allows for one-time federation, rather than a one-time name identifier for a session.
Name Registration Protocol
The optional Name Registration Protocol is used by the service provider to create its own opaque handle to identify a principal when communicating with the identity provider.
Note –
The handle discussed in this section is not related to the opaque handle that is generated by the identity provider during federation as defined in Single Sign-On and Federation Protocol. The Name Registration Protocol can, however, be used by the identity provider to change the opaque handle that it registered with the service provider during initial federation.
Federation Termination Notification Protocol
The Federation Termination Notification Protocol defines how the identity provider or the service provider notifies the other provider when a principal has terminated identity federation. The notification is a one-way, asynchronous message which states one of the following:
-
The service provider will no longer accept authentication information regarding the particular user.
-
The identity provider will no longer provide authentication information regarding the particular user.
Single Logout Protocol
The Single Logout Protocol defines how providers notify each other of logout events. This message exchange protocol is used to terminate all sessions when a logout occurs at the service provider or identity provider. The particular transfer and messaging protocol used in the exchange (such as HTTP or SOAP) are specified in profiles. Two of these profiles are:
-
The SOAP/HTTP-based profile relies on asynchronous SOAP over HTTP messaging calls between providers.
-
The HTTP Redirect-based profile relies on HTTP redirects between providers.
Name Identifier Mapping Protocol
The Name Identifier Mapping Protocol defines how service providers can obtain name identifiers that are assigned to a principal that has federated in the name space of a different service provider. When a principal authenticated to one service provider requests access to a second service provider site, the second service provider can use this protocol to obtain the name identifier. The protocol allows the second service provider to communicate with the first service provider about the principal even though no identity federation for the principal exists between them.
Liberty ID-FF Bindings and Profiles
The Liberty ID-FF Bindings and Profiles Specification defines the bindings and profiles for the Liberty protocols and messages sent to HTTP-based communication frameworks. This specification relies on the core SAML framework. For example, the Name Identifier Encryption Profile permits a principal’s name identifier to be encrypted so that only the provider possessing the decryption key can realize the identity. The encrypted identifier is a different value when requested by different providers. Using different values reduces the chance for correlation of the encrypted value across multiple logical transactions. For more information about the Name Identifier Encryption Profile and the specification in general, see the Liberty ID-FF Bindings and Profiles Specification.
Additional Liberty ID-FF Documents
For additional information about the Liberty ID-FF specifications, see the following documents.
-
Liberty ID-FF 1.2 Architecture Overview
Provides an architectural description of the Liberty ID-FF framework as well as policy, security, and technical notes.
-
Liberty ID-FF 1.2 Implementation Guidelines
Provides guidance and checklists for implementing a Liberty-enabled environment using the Liberty ID-FF specifications.
-
Liberty ID-FF 1.2 Static Conformance Requirements
Defines what features are mandatory and optional for implementations conforming to this version of the Liberty ID-FF specifications.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
