Access Manager Session Failover Deployment
Access Manager provides a web container independent session failover implementation using Sun Java System Message Queue (Message Queue) as the communications broker and the Berkeley DB as the default session store database. Access Manager session failover retains a user’s authenticated session state in the event of a single hardware or software failure, which allows the user’s session to fail over to a secondary Access Manager instance without losing any session information or requiring the user to login again.
Overview of Access Manager Session Failover
Access Manager 7.1 session failover includes these components:
-
Two or more instances of Access Manager 7.1, with each instance running on a supported web container on two or more host servers.
-
Message Queue broker cluster, which manages the session messages between the Access Manager instances and the session store database.
-
Berkeley DB (http://www.oracle.com/database/berkeley-db.html), as the session store database. The Berkeley DB client daemon is amsessiondb.
Access Manager session failover follows the Message Queue publish/subscribe (topic destinations) delivery model:
-
When a user initiates, updates, or ends a session, Access Manager publishes a session creation, update, or deletion message to the Message Queue broker cluster.
-
The Berkeley DB client (amsessiondb) subscribes to the Message Queue broker cluster, reads the session messages, and stores the session operations in the database.
If an Access Manager instance fails due to a single hardware or software problem, a user’s session associated with that instance fails over to a secondary Access Manager instance, as follows:
-
The secondary Access Manager instance publishes a query request to the Message Queue broker cluster for the user’s session information.
-
The Berkeley DB clients (amsessiondb) subscribing to the same session request topic on the Message Queue broker cluster receive the query request retrieve the corresponding entry from the session database, and then publish the user’s session information to the Message Queue broker cluster with the session response topic.
-
The secondary Access Manager instance subscribing to the session response topic receives the response with the user’s session and continues without losing any session information or the user having to login again.
If a Message Queue broker fails, Access Manager continues to operate in non-session failover mode. When the Message Queue broker is later restarted, Access Manager returns to session failover mode.
For more information about the Message Queue components and the publish/subscribe delivery model, see the Sun Java System Message Queue 3.7 UR1 Technical Overview.
Session Failover Deployment Scenario
The following figure shows a basic scenario with two host servers, each running an Access Manager instance on a web container, the Message Queue broker cluster, and the Berkeley DB client (amsessiondb). The load balancer distributes client requests to the Access Manager instances. Both Access Manager instances access the same Directory Server (not shown in the figure).
Figure 4–4 Access Manager Session Failover Basic Deployment Scenario
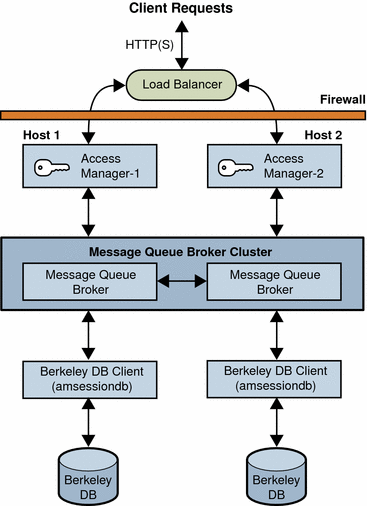
You can add additional sites similar to the one shown in the figure, with each site accessing the same Directory Server. Session failover, however, occurs only for the Access Manager instances within a site; cross-site session failover is not supported in the current release.
For more information, see Chapter 6, Implementing Session Failover, in Sun Java System Access Manager 7.1 Postinstallation Guide.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
