| Exit Print View | |
Sun OpenDS Standard Edition 2.2 Deployment Planning Guide |

|
1. Overview of Sun OpenDS Standard Edition
2. Overview of the Directory Server
3. Overview of the Proxy Server
4. Building Blocks of the Proxy Server
5. Example Deployments Using the Directory Server
6. Example Deployments Using the Proxy Server
Deciding Your Proxy Deployment Type
Configuration 1: Simple Load Balancing
Configuration 2: Simple Distribution
Configuration 3: Failover Between Data Centers
Configuration 4: Distribution with Load Balancing
7. Simple Proxy Deployments Using the Command Line Interface
In a deployment of Sun OpenDS Standard Edition proxy using distribution with failover load balancing between two data centers, the data is split into partitions, where each partition is managed through a failover load balancing route. As illustrated in Figure 6-5, not only are the remote LDAP servers holding the partitioned data replicated within the data center, but in addition, the data centers are replicated, with one of the two acting as the backup.
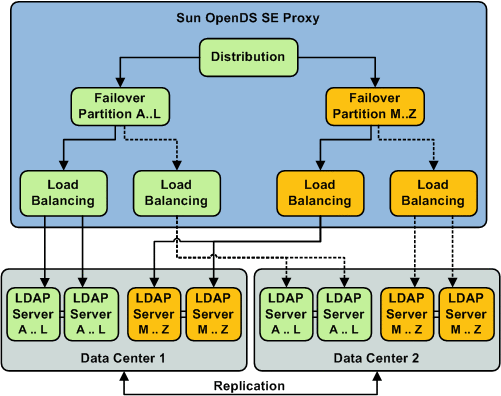
In other words, requests sent to the Sun OpenDS Standard Edition proxy deployed with this configuration are first distributed to the partition in which the data is stored. For example, a request for data Garry would be forwarded to partition 1. The failover load balancer then forwards the request through the main route, depending on the load balancing algorithm set, to one of the one of the remote LDAP servers holding the data for A..L.
In the deployment illustrated in Figure 6-5, Data Center 2 acts as a backup, and is only used on failure of the first data center. However, this same deployment could be configured to use saturation, rather than a failover load balancer. This way, if Data Center 1 in one geographical location (for example in one time-zone) becomes saturated, the other data center can pick up the excess traffic.
The advantages of this deployment are the speed of the reads through the distribution algorithm, and the high availability offered since the remote LDAP servers are replicated, and one data center acts as a backup.
For more information on the different distribution algorithms, see Data Distribution Using the Proxy.
For more information on the different load balancing algorithms, see Load Balancing Using the Proxy.
For details on deploying this configuration, see Configuring Distribution with Failover Between Data Centers.