Overview of the Access Manager Service Module
The Access Manager service module of the reference configuration's deployment architecture illustrated in Figure 2–2. The module consists of two instances of Sun Java System Access Manager running on two different computers. The module makes use of a hardware load balancer that is configured to provide service failover capability between the two Access Manager instances. All requests for Access Manager services are addressed to the virtual service name and IP address of the load balancer. The load balancer directs each request to one of the two Access Manager instances.
This module implements Access Manager session failover. When a user logs in, the load balancer routes the login request to one of the Access Manager instances, which authenticates the user and creates a session object. Subsequent requests from the user are directed to the same Access Manager instance.
If an Access Manager instance fails, the system recovers as follows:
-
Service Failover. Subsequent requests are routed by the load balancer to the other Access Manager instance.
-
Access Manager Session Failover. The new Access Manager instance retrieves session information from an Access Manager session database, thus making the service failover transparent to the user. The session failover mechanism is designed to revert back to the original Access Manager instance, if that instance subsequently comes back on line.
Access Manager's session failover mechanism is designed to be web container independent. It uses Message Queue and a session database to provide session failover between the two Access Manager instances.
The architecture of the Access Manager service module is shown in the following illustration.
Figure 5–1 Access Manager Service Module
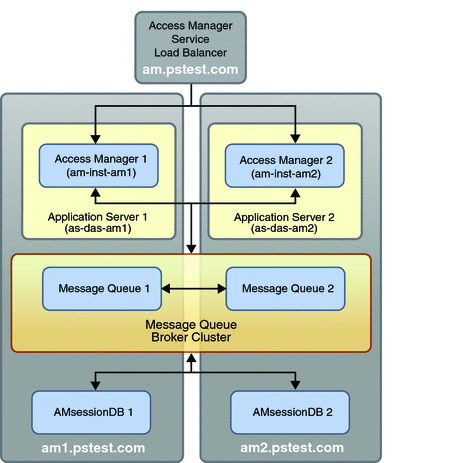
The Access Manager instances run in a web container that is provided by Sun Java System Application Server. Each Access Manager instance runs in the Domain Administration Server (DAS) instance of its respective computer. A Message Queue broker cluster, consisting of one Message Queue broker on each computer, is used by Access Manager to write session information to (and retrieve session information from) an Access Manager session database, which is replicated on each computer. The broker cluster and replicated session database are meant to avoid a single point of failure.
The Message Queue brokers and session database instances can reside on different computers from the Access Manager instances. However, it is simpler to set up the failover mechanism locally.
The general approach to implementing this module is to first set up Access Manager on each computer. In doing so, the Java ES installer is run in Configure Now mode to install and configure Application Server, Message Queue, and Access Manager. Following these procedures, load balancing is implemented to provide Access Manager service failover and then Access Manager session failover is set up.
This module can be scaled horizontally by adding an additional computer like am2 and its respective components, and following the instructions in this chapter that apply to am2. However, the procedures for implementing Access Manager session failover might require some adjustment.
Note –
The procedures in this chapter use the host names, domain name, and IP addresses shown in Figure 3–1 and Figure 5–1. However, you must map these host names, domain name, and IP addresses to equivalent names and addresses in your environment. For this reason, the procedures in this chapter show host names, domain name, and IP addresses as variables.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
