The Java ES Release Model
A key consideration in planning an upgrade is whether the objective of the upgrade is to achieve major functional enhancements or to apply bug fixes (or minor functional updates) to existing software.
The Java ES release model is a categorization scheme for Java ES releases that clarifies the nature of the releases, their relationships to one another, and the risks and planning required to upgrade from one to another.
Component Release Levels
The Java ES release model is based on a set of release levels that define the characteristics of individual Java ES component releases:
-
Major release. The purpose of a major release is to introduce or change significant software functionality and architectural features. As such, it can introduce incompatibilities with previous versions, and operating system support may be dropped. As a result, users may be required to take specific actions in order for their applications to integrate with a major release. As part of upgrading to a new major release, users might have to perform migrations, redeployments, and possibly redesign their solutions to utilize new features or respond to the removal of old features.
-
Minor release. The purpose of a minor release is to introduce new, non-interfering features without introducing incompatibilities. New prerequisites or dependencies can be established and previous features can be deprecated in a minor release. As compared to upgrading to a major release, users might have to perform migrations and redeployments, but a redesign of their existing solution should not be necessary.
-
Update release. The purpose of an update release is to provide fixes to an existing component implementation so that it more accurately implements a prior release's functional specification. The update release provides for the delivery of bug fixes and a constrained set of feature enhancements such that the release remains suitable for adoption by the majority of existing users. When compared to a major or minor release an update release contains fewer, smaller and/or lower risk features. Other than in rare exceptions, an update release is 100% backwardly compatible with the prior release. Upgrading to an update release from the prior release should require minimal planning and investment.
-
Point-fix release. The purpose of a point-fix release is to address critical customer issues quickly. Like an update release, it supports existing users, but is generally more limited or focused, typically containing only a few bug fixes. Feature enhancements or new feature additions are not allowed in a point-fix release. Upgrading to a point-fix release from the prior release should be simple an low risk.
Java ES System Release Types
A Java ES release is a consolidation of individual Java ES component releases that are synchronized and collected in a single distribution that can be used for initial installation and upgrade.
The Java ES release model specifies two general types of Java ES releases: feature releases, which can include all levels of component releases, including major and minor releases, and maintenance releases, which can include only update and point-fix releases.
The two types of Java ES releases have the characteristics described below:
Feature Release
The primary purpose of a feature release is to deliver new features and functional capabilities. While specific components within a Java ES feature release might be only update or point-fix releases, the purpose of the release is to deliver major or minor component releases. A Java ES feature release has the following general characteristics:
-
The release can introduce significant interface changes, new dependencies, and/or incompatibilities with respect to Java ES components
-
The release requires a longer planning cycle prior to adoption
-
Upgrade to the release generally requires reconfiguration and/or migration of component data
-
The release can involve significant impact or risk
Maintenance Release
The primary purpose of a maintenance release is to fix bugs in the software, so that components work as originally documented. New features are limited in number and highly constrained. A Java ES maintenance release cannot include major or minor component releases, only update and point-fix releases. A Java ES maintenance release has the following general characteristics:
-
The release cannot introduce significant interface changes, new dependencies, or incompatibilities with respect to Java ES components
-
The release allows for quick adoption
-
Upgrade to the release requires no reconfiguration or migration of component data
-
The release involves minimal impact or risk
Java ES Release Families
A Java ES release family consists of a feature release and its associated maintenance release as illustrated in the following figure.
Figure 1–1 Java ES Release Family
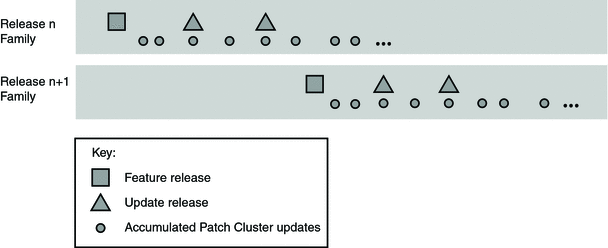
A Java ES feature release initiates a release family, and a number of subsequent maintenance releases (called Java ES update releases) provide distributions that periodically consolidate intervening component update and point-fix releases. These individual component maintenance releases are independently collected in a Java ES accumulated patch cluster.
The maintenance aspect of the Java ES release model is represented by both the Java ES update release and the Java ES accumulated patch cluster, described as follows:
-
Java ES Update release. The maintenance aspect of the Java ES release model is represented by both the Java ES update release and the Java ES accumulated patch cluster, described as follows:
As compared to a feature release, an update release contains fewer, smaller, and/or lower risk features. Other than in rare exceptions, an update release is 100% backwardly compatible with the release family with which it is associated.
Note –Java ES 5 Update 1 is a Java ES update release.
-
Accumulated patch cluster. The accumulated patch cluster contains the latest set of individual component point-fix and update releases for the components in a release family. It facilitates upgrade to the most recent versions of all Java ES components.
The accumulated patch cluster is established at the onset of a release family and has a life cycle corresponding to the support life of the release family. It is updated whenever a new component point fix or update release is made available. Other than in rare exceptions, the accumulated patch cluster is 100% backwardly compatible with earlier releases in its release family.
The significance of the Java ES release model, from an upgrade point of view, is that an upgrade from one Java ES release family to another (a feature upgrade) involves significant impact and risk, and requires a more complex upgrade plan, as compared to an upgrade within a release family (a maintenance upgrade).
Release Delivery Formats
The following table shows the delivery formats of the releases within the Java ES release model shown in Figure 1–1.
Table 1–3 Characteristics of Java ES Release Types|
Release Type |
Delivery Format |
Suitable For |
|---|---|---|
|
Feature Release |
Available as a full distribution that contains new component packages that are generally installed using the Java ES installer. |
Installation by new Java ES users and feature upgrades from previous release families. |
|
Update Release |
Available as a full distribution and also as a corresponding accumulated patch cluster. (The accumulated patch cluster supports in-place maintenance upgrades within the current release family.) |
Installation by new Java ES users, feature upgrades from previous release families, and maintenance upgrades from within the current release family. |
|
Accumulated Patch Cluster |
Available as a set of individual component patches, each of which accumulates previous sustaining patches. Patches can be applied in-place without requiring reconfiguration or migration of component data. |
Maintenance upgrades from a feature release, update release, or previous individual component release within the current release family. |
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
