24.4 Getting Started After Installing Messaging Server
This section explains what the S/MIME applet is and provides a basic configuration procedure to set up S/MIME for Communications Express Mail. The configuration process involves setting parameters for the S/MIME applet and options for Messaging Server.
24.4.1 The S/MIME Applet
The process of signing a message, encrypting a message, or decrypting a message, along with the various procedures to verify private and public keys, are handled by a special applet, referred to as the S/MIME applet. The configuration of the S/MIME features is done with parameters in the smime.conf file and options of Messaging Server. Figure 24–1 shows the S/MIME Applet in relation to other system components.
Figure 24–1 S/MIME Applet
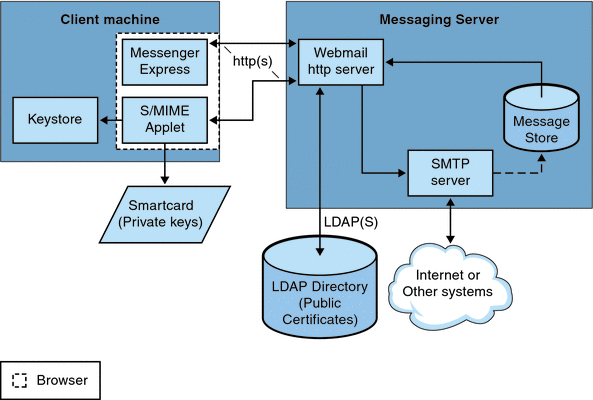
24.4.1.1 Logging In for the First Time
When a Communications Express Mail user who has permission to use S/MIME logs in to the Messaging Server for the first time, a series of special prompts displays about the S/MIME applet. After answering the prompts with Yes or Always, the S/MIME applet is downloaded to their computer. The applet remains on their machine until they log out of Communications Express Mail.
Refer to 24.11 Managing Certificates for more information.
24.4.1.2 Downloading the S/MIME Applet
The S/MIME applet is downloaded each time a user logs in to Communications Express Mail unless caching is enabled for the Java 2 Runtime Environment (JRE) on the user’s machine. When caching is enabled, a copy of the S/MIME applet is saved on the user’s machine after the initial download which prevents downloading the applet every time the user logs in.
Caching can improve performance so you might direct your users to do the following steps to enable caching for Java 2 Runtime Environment, Version 1.4.x:
 To Enable Caching for Java 2 Runtime Environment,
Version 1.4
To Enable Caching for Java 2 Runtime Environment,
Version 1.4
-
Navigate to the Windows Control Panel.
-
Double click the Java Plug-in icon (Java 2 Runtime Environment).
-
Click the Cache tab.
-
Check the Enable Caching checkbox.
-
Click Apply.
After downloading, a user is not aware of the S/MIME applet. It appears that signing, encrypting, or decrypting a message is done by Communications Express Mail. Unless an error message pops up, the user also is unaware of the processes to verify a private or public key. Refer to 24.9 Verifying Private and Public Keys for more information.
24.4.2 A Basic S/MIME Configuration
The configuration file for S/MIME, smime.conf, contains descriptive comments and an example of each S/MIME parameter. The smime.conf file is included with Messaging Server, located in the directory msg-svr-base/config/, where msg-svr-base is the directory where Messaging Server is installed.
The following procedure contains the minimum required steps to configure the S/MIME features:
 To Configure the S/MIME
To Configure the S/MIME
-
Verify that the basic features of Communications Express Mail are working after you install Messaging Server.
-
If you haven’t already, create or obtain private-public key pairs, with certificates in standard X.509 v3 format, for all your mail users who have permission to use the S/MIME features.
-
If smart cards are used for keys and certificates:
-
If local key stores of the browsers are used to store keys and certificates, instruct your mail users how to download their key pairs and certificate to the local key store.
-
Ensure that the correct libraries are on the client machines to support smart cards or local key stores. See 24.8 Key Access Libraries for the Client Machines
-
Set up your LDAP directory to support S/MIME:
-
Store all certificates for the CAs in the LDAP directory, accessible by Directory Server, under the distinguished name for certificate authorities. The LDAP attribute for these certificates is cacertificate;binary. Write down the directory information where you store them. You’ll need this information for a later step.
See trustedurl in Table 24–3 for an example of specifying LDAP directory information and 24.11 Managing Certificates for information to search an LDAP directory.
-
Store the public keys and certificates in the LDAP directory accessible by Directory Server. The LDAP attribute for public keys and certificates is usercertificate;binary. Write down the directory information where you store them. You’ll need this information for a later step.
See certurl in Table 24–3 for an example of specifying LDAP directory information and 24.11 Managing Certificates for information to search an LDAP directory.
-
Ensure that all users who send or receive S/MIME messages are given permission to use S/MIME with an LDAP filter in their user entries. A filter is defined with the mailAllowedServiceAccess or mailDomainAllowedServiceAccess LDAP attributes.
Note: By default, if you do not use mailAllowedServiceAccess or mailDomainAllowedServiceAccess, all services including smime, are allowed. If you explicitly specify services with these attributes, then the services http and smtp, as well as smime, must be specified to give mail users permission to use the S/MIME features.
See 24.10 Granting Permission to Use S/MIME Features for more information.
-
-
Edit the smime.conf file with any available text editor. See comments at the beginning of the file for parameter syntax.
All text and example parameters in smime.conf are preceded with a comment character (#). You can add the parameters you need to smime.conf or copy a parameter example to another part of the file and change its value. If you copy and edit an example, be sure to remove the # character at the beginning of its line.
Add these parameters to the file, each on its own line:
-
trustedurl (see Table 24–3)-- set to the LDAP directory information to locate the certificates of the CAs. Use the information you saved from Step a.
-
certurl (Table 24–3)-- set to the LDAP directory information to locate the public keys and certificates. Use the information you saved from Step b .
-
usersertfilter (see Table 24–3) -- set to the value of the example in the smime.conf file. The example value is almost always the filter you want. Copy the example and delete the # character at the beginning of the line.
This parameter specifies a filter definition for the primary, alternate, and equivalent email addresses of a Communications Express Mail user to ensure that all of a user’s private-public key pairs are found when the key pairs are assigned to different mail addresses.
-
sslrootcacertsurl (see Table 24–3)-- if you are using SSL for the communications link between the S/MIME applet and Messaging Server, set sslrootcacertsurl with the LDAP directory information to locate the certificates of CAs that are used to verify the Messaging Server’s SSL certificates. See 24.7 Securing Internet Links With SSL for more information.
checkoverssl (see Table 24–3)-- set to 0 if you are not using SSL for the communications link between the S/MIME applet and Messaging Server.
-
crlenable (see Table 24–3)-- set to 0 to disable CRL checking for now because doing CRL checking might require adding other parameters to the smime.conf file.
-
logindn and loginpw (Table 24–3)-- if the LDAP directory that contains the public keys and CA certificates requires authentication to access it, set these parameters to the distinguished name and password of the LDAP entry that has read permission.
Note: The values of logindn and loginpw are used whenever the LDAP directory is accessed with the LDAP information specified by the crlmappingurl, sslrootcacertsurl, or trustedurl parameters. See 24.5 Parameters of the smime.conf File and 24.4.3 Accessing LDAP for Public Keys, CA certificates and CRLs Using Credentials for more information.
Do not set logindn and loginpw if authentication is not required to access the LDAP directory.
-
-
Set the Messaging Server options with configutil:
-
local.webmail.smime.enable -- set to 1.
-
local.webmail.cert.enable -- set to 1 if you want to verify certificates against a CRL.
See 24.6 Messaging Server Options for more information.
-
-
Communications Express Mail is now configured for the S/MIME features. Verify that the S/MIME features are working with the following steps:
-
Restart the Messaging Server.
-
Check the Messaging Server log file, msg-svr-base /log/http, for diagnostic messages relating to S/MIME.
-
If any problems were detected for S/MIME, the diagnostic messages help you determine how to correct the problem with the configuration parameters.
-
Correct the necessary configuration parameters.
-
Repeat Steps a. through d. until there are no more diagnostic messages for S/MIME in the Messaging Server’s log file.
-
Check that the S/MIME features are working with the following steps:
-
Log in to Messaging Server from a client machine. Answer the special prompts for the S/MIME applet with Yes or Always. See 24.11 Managing Certificates
-
Compose a short message, addressed to yourself.
-
Encrypt your message by checking the Encrypt checkbox at the bottom of the Compose window if it is not already checked.
-
Click Send to send the encrypted message to yourself. This should exercise most of the mechanisms for keys and certificates.
-
If you find problems with the encrypted message, the most likely causes are the values you used for LDAP directory information in the smime.conf file and/or the way keys and certificates are stored in the LDAP directory. Check the Messaging Server log for more diagnostic messages.
The remaining S/MIME parameters, summarized in the table below, provide many options you might want to use to further configure your S/MIME environment. See 24.5 Parameters of the smime.conf File for more information about the parameters.
Required Parameters for S/MIME
Parameters for Smart Cards and Local Key Stores
Parameters for CRL Checking
Parameters for Initial Settings and Secured Links
certurl*
platformwin
checkoverssl
alwaysencrypt
logindn
crlaccessfail
alwayssign
loginpw
crldir
sslrootcacertsurl
trustedurl*
crlenable
usercertfilter*
crlmappingurl
crlurllogindn
crlurlloginpw
crlusepastnextupdate
readsigncert
revocationunknown
sendencryptcert
sendencryptcertrevoked
readsigncert
sendsigncertrevoked
timestampdelta
* You must specify a value for these parameters because they have no default value.
-
-
24.4.3 Accessing LDAP for Public Keys, CA certificates and CRLs Using Credentials
Public keys, CA certificates, and CRLs required for S/MIME may be stored in an LDAP directory (see previous section). The keys, certificates, and CRLs may be accessible from a single URL or multiple URLs in LDAP. For example, CRLs may be stored in one URL and public keys and certificates may be stored in another. Messaging Server allows you to specify which URL contains the desired CRL or certificate information, as well as the DN and password of the entry that has access to these URLs. These DN/password credentials are optional; if none are specified, LDAP access first tries the HTTP server credentials, and if that fails, it tries accessing it as anonymous.
Two pairs of smime.conf credential parameters may be set to access the desired URLs: logindn and loginpw, and crlurllogindn and crlurlloginpw.
logindn and loginpw are the credentials used for all URLs in smime.conf. They specify the DN and password of the LDAP entry that has read permission for the public keys, their certificates, and the CA certificates as specified by the certurl and trustedurl parameters.
crlurllogindn and crlurlloginpw specifies the DN and password of the LDAP entry that has read permission for the resulting URL from the mapping table (see 24.9.3 Accessing a CRL for more information). If these credentials are NOT accepted, LDAP access is denied and no retry with other credentials is attempted. Either both parameters must be specified, or both must be empty. These parameters do not apply to the URLs that come directly from the certificate.
24.4.3.1 Setting Passwords for Specific URLs
Messaging Server allows you to specifically define the DN/password pairs for accessing the following smime.conf URLs: certUrl, trustedUrl, crlmappingUrl, sslrootcacertsUrl.
The syntax is as follows:
url_type URL[|URL_DN | URL_password]
Example:
trustedurl==ldap://mail.siroe.com:389/cn=Directory Manager, ou=people, o=siroe.com,o=ugroot?cacertificate?sub?(objectclass=certificationauthority) | cn=Directory manager | boomshakalaka |
24.4.3.2 Summary of Using LDAP credentials
This section summarizes the use of LDAP credentials.
-
All LDAP credentials are optional; if none are specified, LDAP access first tries the HTTP server credentials, and if that fails, tries anonymous.
Two pairs of smime.conf parameters are used as credentials for the two sets of URLs that may be specified:
logindn & loginpw - all URLs in smime.conf
crlurllogindn & crlurlloginpw - all URLs from mapping table
These are known as the default LDAP credential pair.
-
Any URL specified in smime.conf or via mapping CRL URLs can have an optional local LDAP credential pair specified.
-
Credentials are checked in order in which each is specified:
1) Local LDAP credential pair - if specified, only one tried
2) Default LDAP Credential Pair - if specified, and no Local LDAP credential pair, only one tried
3) Server - if neither Local LDAP credential pair nor default LDAP credential pair specified, first tried
4) anonymous - last tried only if server fails or none specified
-
If a URL has a Local LDAP credential pair specified, it is used first; if the access fails, access is denied.
-
If a URL has no Local LDAP credential pair specified, the corresponding default LDAP credential pair is used; if access fails, then access is denied.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
