Administrator Roles and the Directory Hierarchy
This section shows sample Directory Information Trees that implement one- and two-tiered hierarchies. It then describes the tasks that can be performed by the Top-Level Administrator and Organization Administrator.
Directory Structure Supporting a One-Tiered Hierarchy
When you configure Delegated Administrator by running the configuration program, config-commda, you create a Top-Level Administrator (TLA) and a default organization.
One-Tiered Hierarchy: Default Organization Under the Root Suffix
By default, the configuration program places the default organization under the root suffix.
The Directory Information Tree will look similar to the one shown in Figure 1–4.
Figure 1–4 shows a sample Directory Information Tree organized in a one-tiered hierarchy (default configuration).
Figure 1–4 One-Tiered Hierarchy: Sample Directory Information Tree (default)
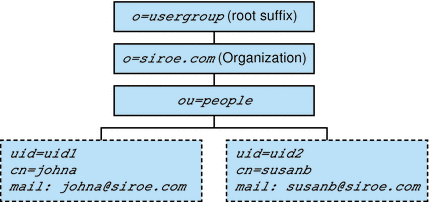
One-Tiered Hierarchy: Default Organization at the Root Suffix
When you run the configuration program, config-commda, you can choose to create the default organization at the root suffix instead of under it. For configuration details, see Configuring the Delegated Administrator Server in Chapter 3, Configuring Delegated Administrator.
In this situation, the Directory Information Tree will look similar to the one shown in Figure 1–5.
However, if you create the default organization at the root suffix, this configuration of the LDAP directory cannot support multiple hosted domains. To support hosted domains, the default organization must be under the root suffix.
Figure 1–5 shows a sample one-tiered hierarchy in which the default organization is created at the root suffix.
Figure 1–5 One-Tiered Hierarchy: Default Organization at Root Suffix
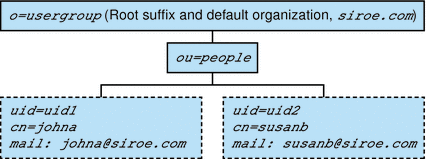
Directory Structure Supporting a Two-Tiered Hierarchy
After Delegated Administrator has been configured with the config-commda program, the TLA can create additional organizations, as shown in Figure 1–6.
Figure 1–6 shows a sample Directory Information Tree organized in a two-tiered hierarchy.
Figure 1–6 Two-Tiered Hierarchy: Sample Directory Information Tree
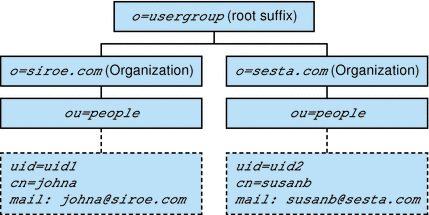
Top-Level Administrator Role
The TLA has the authority to perform the following tasks:
-
Create, delete, and modify organizations.
In the example shown in Figure 1–6, the TLA can modify or delete siroe.com or sesta.com and can create additional organizations.
Note that in this example, the two organizations are also unique (hosted) domains.
-
Create, delete, and modify users.
-
Create, delete, and modify groups.
-
Create, delete, and modify Calendar resources.
-
Assign OA roles to users. For example, the TLA could assign an OA role to the user johna in the siroe.com organization.
The TLA also can remove the OA role from a user.
-
Assign TLA roles to other users. The TLA also can remove the TLA role from a user.
-
Assign service packages to organizations.
For information about service packages, see Service Packages, later in this overview.
The TLA can assign specified types of service packages to an organization and determine the maximum number of each package that can be used in that organization.
For example, the TLA could assign the following service packages:
-
In the siroe.com organization:
1,000 gold packages
500 platinum packages
-
In the sesta.com organization:
2,000 silver packages
1,500 gold packages
100 platinum packages
The TLA can perform the preceding tasks by using the Delegated Administrator console or by executing Delegated Administrator utility (commadmin) commands.
For a description of the commadmin commands, see Table 5–1 in Chapter 5, Command Line Utilities.
-
Organization Administrator Role
The OA has the authority to perform the following tasks within the OA’s organization:
-
Create, delete, and modify users.
In the example shown in Figure 1–6, if the user johna is assigned the OA role in the siroe.com organization, johna can manage users in siroe.com.
-
Create, delete, and modify groups.
-
Create, delete, and modify Calendar resources.
-
Assign the OA role to other users.
-
Assign and remove service packages for users.
The OA cannot perform any of these tasks for users, groups, or resources outside the OA’s organization.
For example, if johna is the OA for siroe.com in Figure 1–6, johna cannot manage users, groups, or resources in sesta.com.
The OA can perform the preceding tasks by using the Delegated Administrator console or by executing Delegated Administrator utility (commadmin) commands.
For a description of the commadmin commands available to the OA, see Table 5–1 in Chapter 5, Command Line Utilities.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
