Chapter 7 Configuring and Administering Multiplexor Services
This chapter describes the Messaging Multiplexor (MMP) for standard mail protocols (POP, IMAP and SMTP). Previous releases also described the Messenger Express Multiplexor used for the Messenger Express web interface, but this is no longer needed. See 5.7 To Configure HTTP Services.
The following topics are covered in this chapter:
7.1 Multiplexor Services
A multiplexor is necessary to achieve horizontal scalability (the ability to support more users by adding more machines), because it provides a single domain name that can be used to connect indirectly to multiple mail stores. A multiplexor can also provide security benefits.
While MMP is managed separately from Messaging Server, the Messenger Express multiplexing is built-in to the HTTP service (mshttpd) that is included with the Message Store and Message Access installation.
7.1.1 Multiplexor Benefits
Message stores on heavily used messaging servers can grow quite large. Spreading user mailboxes and user connections across multiple servers can therefore improve capacity and performance. In addition, it may be more cost-effective to use several small server machines than one large, high-capacity, multiprocessor machine.
If the size of your mail-server installation requires the use of multiple message stores, your organization can benefit in several ways from using the multiplexor. The indirect connection between users and their message stores, coupled with the ease of reconfiguration of user accounts among messaging servers allows for the following benefits:
-
Simplified User Management
Because all users connect to one server (or more, if you have separate Multiplexor machines for POP, IMAP, SMTP or web access), you can preconfigure email clients and distribute uniform login information to all users. This simplifies your administrative tasks and reduces the possibility of distributing erroneous login information.
For especially high-load situations, you can run multiple Multiplexor servers with identical configurations and manage connections to them by DNS round robin or by using a load-balancing system.
Because the Multiplexors use information stored in the LDAP directory to locate each user’s Messaging Server, moving a user to a new server is simple for the system administrator and transparent to the user. The administrator can move a user’s mailbox from one Messaging Server to another, and then update the user’s entry in the LDAP directory. The user’s mail address, mailbox access, and other client preferences need not change.
-
Improved Performance
If a message store grows prohibitively large for a single machine, you can balance the load by moving some of the message store to another machine.
You can assign different classes of users to different machines. For example, you can choose to locate premium users on a larger and more powerful machine.
The Multiplexors perform some buffering so that slow client connections (through a modem, for example) do not slow down the Messaging Server.
-
Decreased Cost. Because you can efficiently manage multiple Messaging Servers with a Multiplexor, you might be able to decrease overall costs by purchasing several small server machines that together cost less than one very large machine.
-
Better Scalability. With the Multiplexors, your configuration can expand easily. You can incrementally add machines as your performance or storage-capacity needs grow, without replacing your existing investment.
-
Minimum User Downtime. Using the Multiplexors to spread a large user base over many small store machines isolates user downtime. When an individual server fails, only its users are affected.
-
Increased Security. You can use the server machine on which the Multiplexor is installed as a firewall machine. By routing all client connections through this machine, you can restrict access to the internal message store machines by outside computers. The Multiplexors support both unencrypted and encrypted communications with clients.
7.2 About Messaging Multiplexor
The Sun Java System Messaging Multiplexor (MMP) is a specialized messaging server that acts as a single point of connection to multiple back-end messaging servers. With Messaging Multiplexor, large-scale messaging service providers can distribute POP and IMAP user mailboxes across many machines to increase message store capacity. All users connect to the single Multiplexor server, which redirects each connection to the appropriate messaging server.
If you provide electronic mail service to many users, you can install and configure the Messaging Multiplexor so that an entire array of messaging servers will appear to your mail users to be a single host.
The Messaging Multiplexor is provided as part of Messaging Server. You can install the MMP at the same time you install the Messaging Server or other Sun Java System servers, or you can install the MMP separately at a later time. The MMP supports:
-
Both unencrypted and encrypted (SSL) communications with mail clients.
-
Client certificate-based authentication, described in 7.2.3 Certificate-Based Client Authentication
-
User pre-authentication, described in 7.2.4 User Pre-Authentication.
-
Virtual domains that listen on different IP addresses and automatically append domain names to user IDs, described in 7.2.5 MMP Virtual Domains.
-
Multiple installations of the MMP on different servers
-
Enhanced LDAP searching.
-
POP before SMTP service for legacy POP clients. For more information, see 23.8 Enabling POP Before SMTP.
This section consists of the following subsections:
7.2.1 How the Messaging Multiplexor Works
The MMP is a multithreaded server that facilitates distributing mail users across multiple server machines. The MMP handles incoming client connections destined for other server machines (the machines on which user mailboxes reside). Clients connect to the MMP itself, which determines the correct server for the users, connects to that server, and then passes data between the client and server. This capability allows Internet service providers and other large installations to spread message stores across multiple machines (to increase capacity) while providing the appearance of a single mail host for users (to increase efficiency) and for external clients (to increase security). 7.2.1 How the Messaging Multiplexor Works shows how servers and clients relate to each other in an MMP installation.
Figure 7–1 Clients and Servers in an MMP Installation
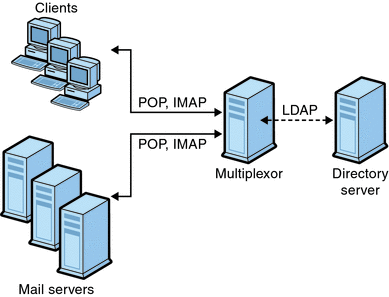
All POP, IMAP, and SMTP clients work with the Messaging Multiplexor. The MMP accepts connections, performs LDAP directory lookups, and routes the connections appropriately. As is typical with other mail server installations, each user is assigned a specific address and mailbox on a specific Messaging Server. However, all connections are routed through the MMP.
In more detail, these are the steps involved in establishing a user connection:
-
A user’s client connects to the MMP, which accepts preliminary authentication information (user name).
-
The MMP queries the Directory Server to determine which Messaging Server contains that user’s mailbox.
-
The MMP connects to the proper Messaging Server, replays authentication, then acts as a pass-through pipe for the duration of the connection.
7.2.2 Encryption (SSL) Option
Messaging Multiplexor supports both unencrypted and encrypted (SSL) communications between the Messaging Server(s) and their mail clients. The current version of Messaging Server supports the new certificate database format (cert8.db).
When SSL is enabled, the MMP supports STARTTLS and the MMP can also be configured to listen on additional ports for SSL IMAP, POP, and SMTP connections.
To enable SSL encryption for your IMAP, POP, and SMTP services, edit the ImapProxyAService.cfg, PopProxyAService.cfg, and SmtpProxyAService.cfg files, respectively. You must also edit the default:ServiceList option in the AService.cfg file to include the list of all IMAP, POP, and SMTP server ports regardless of whether or not they are secure. See 7.4 Configuring MMP with SSL for details.
By default, SSL is not enabled since the SSL configuration parameters are commented out. To enable SSL, you must install an SSL server certificate. Then, you should uncomment and set the SSL parameters. For a list of the SSL parameters, see the Encryption (SSL) Option in Sun Java System Messaging Server 6.3 Administration Reference.
7.2.3 Certificate-Based Client Authentication
The MMP can use a certificate mapping file (certmap.conf) to match a client’s certificate to the correct user in the Users/Groups Directory Server.
In order to use certificate-based client authentication, you must also enable SSL encryption as described in 7.2.2 Encryption (SSL) Option.
You also have to configure a store administrator. You can use the mail administrator, but it is recommended that you create a unique user ID, such as mmpstore for this purpose so that you can set permissions as needed.
Note that the MMP does not support certmap plug-ins. Instead, the MMP accepts enhanced DNComps and FilterComps property value entries in the certmap.conf file. These enhanced format entries use the form:
mapname:DNComps FROMATTR=TOATTRmapname:FilterComps FROMATTR=TOATTR |
So that a FROMATTR value in a certificate’s subjectDN can be used to form an LDAP query with the TOATTR=value element. For example, a certificate with a subjectDN of “cn=Pilar Lorca, ou=pilar, o=siroe.com” could be mapped to an LDAP query of “(uid=pilar)” with the line:
mapname:FilterComps ou=uid
 To Enable Certificate-based Authentication for Your
IMAP or POP Service
To Enable Certificate-based Authentication for Your
IMAP or POP Service
-
Decide on the user ID you intend to use as store administrator.
While you can use the mail administrator for this purpose, it is recommended that you create a unique user ID for store administrator (for example, mmpstore).
-
Make sure that SSL encryption is (or will be) enabled as described in 7.2.2 Encryption (SSL) Option.
-
Configure the MMP to use certificate-based client authentication by specifying the location of the certmap.conf file in your configuration files.
-
Install at least one trusted CA certificate, as described in 23.5.1.6 To Install Certificates of Trusted CAs
7.2.4 User Pre-Authentication
The MMP provides you with the option of pre-authenticating users by binding to the directory as the incoming user and logging the result.
Note –
Enabling user pre-authentication will reduce server performance
The log entries are in the format:
date time (sid 0xhex) user name pre-authenticated - client IP address, server IP address |
Where date is in the format yyyymmdd, time is in the time configured on the server in the format hhmmss, hex is the session identifier (sid) represented as a hexidecimal number, the user name includes the virtual domain (if any), and the IP address is in dot-quad format.
7.2.5 MMP Virtual Domains
An MMP virtual domain is a set of configuration settings associated with a server IP address. The primary use of this feature is to provide different default domains for each server IP address.
A user can authenticate to MMP with either a short-form userID or a fully qualified userID in the form user@domain. When a short-form userID is supplied, the MMP will append the DefaultDomain setting, if specified. Consequently, a site which supports multiple hosted domains can permit the use of short-form user IDs simply by associating a server IP address and MMP virtual domain with each hosted domain.
The recommended method for locating the user subtree for a given hosted domain is via the inetDomainBaseDN attribute in the LDAP domain tree entry for that domain. The MMP’s LdapUrl setting is not suitable for this purpose since the back-end mail store servers will also need to look up the user in LDAP and do not support virtual domains.
When Sun LDAP Schema 2 is enabled (see the Sun Java Enterprise System 5 Installation Guide for UNIX and Sun Java Communications Suite 5 Schema Reference), the user subtree for the specified domain will be all the users in the subtree below the organization node for that domain.
To enable virtual domains, edit the ImapProxyAService.cfg, PopProxyAService.cfg, or SmtpProxyAService.cfg file(s) in the instance directory such that the VirtualDomainFile setting specifies the full path to the virtual domain mapping file.
Each entry of a virtual domain file has the following syntax:
vdmap name IPaddr name:parameter value
Where name is simply used to associate the IP address with the configuration parameters and can be any name you choose to use, IPaddr is in dot-quad format, and parameter and value pairs configure the virtual domain. When set, virtual domain configuration parameter values override global configuration parameter values.
Listed below are the configuration parameters you can specify for a virtual domain:
AuthCacheSize and AuthCacheSizeTTL AuthService BindDN and BindPass CertMap ClientLookup CRAMs DefaultDomain DomainDelim HostedDomains LdapCacheSize and LdapCacheTTL LdapURL MailHostAttrs PreAuth ReplayFormat RestrictPlainPasswords StoreAdmin and StoreAdminPass SearchFormat TCPAccess TCPAccessAttr |
Note –
Unless the LdapURL is correctly set, the BindDN, BindPass, LdapCacheSize and LdapCacheTTL settings will be ignored.
For detailed descriptions of these configuration parameters, see the Sun Java System Messaging Server 6.3 Administration Reference
7.2.6 About SMTP Proxy
The MMP includes an SMTP proxy which is disabled by default. Most sites do not need the SMTP proxy because Internet Mail standards already provide an adequate mechanism for horizontal scalability of SMTP (DNS MX records).
The SMTP proxy is useful for the security features it provides. First, the SMTP proxy is integrated with the POP proxy to implement the POP before SMTP authorization facility required by some legacy POP clients. For more information, see Using the MMP SMTP Proxy in Sun Java Communications Suite 5 Deployment Planning Guide and 23.8 Enabling POP Before SMTP. In addition, an investment in SSL acceleration hardware can be maximized by using the SMTP proxy. See 23.5.4 How to Optimize SSL Performance Using the SMTP Proxy.
7.3 Setting Up the Messaging Multiplexor
During the initial runtime configuration of Messaging Server, you determined if you wanted to configure the MMP on a machine. You could either set it up on the same machine as your Messaging Server or set it up on a separate machine.
Note –
MMP does not cache DNS results. A high quality caching DNS server on the local network is a requirement for a production deployment of Messaging Server.
The following sections describe how to set up the MMP:
More information about the MMP can be found in the following:
7.3.1 Before You Configure MMP
-
Choose the machine on which you will configure the MMP. It is best to use a dedicated machine set aside for the MMP.
Note –It is recommended that the MMP not be enabled on a machine that is also running either the POP or IMAP servers.
If you install MMP on the same machine as Messaging Server, you must make sure that the POP and IMAP servers are set to non-standard ports. That way, the MMP and Messaging Server ports will not conflict with one another.
-
On the machine that the MMP is to be configured, create a UNIX system user to be used by the MMP. This new user must belong to a UNIX system group. See 1.1 Creating UNIX System Users and Groups
-
Set up the Directory Server and its host machine for use with Messaging Server, if they are not already set up. See 1.2 To Prepare Directory Server for Messaging Server Configuration
-
If the MMP is upgraded before the backend servers, customers should set the Capability option in ImapProxyAService.cfg to match the response to the capability command from the older backend. This would be:
IMAP4 IMAP4rev1 ACL QUOTA LITERAL+ NAMESPACE UIDPLUS CHILDREN LANGUAGE XSENDER X-NETSCAPE XSERVERINFO
Note that line break is for editorial clarity, and that the configuration value must be on one line.
7.3.2 Multiplexor Configuration
To configure the MMP, you must use the Messaging Server configure program, which gives you the option of enabling the Messaging Multiplexor. For detailed information about the configure program see 1.3 Creating the Initial Messaging Server Runtime Configuration
 To Configure the MMP
To Configure the MMP
-
Put Sun Java System Messaging Server on the machine where you are installing and configuring the MMP.
-
Configure the MMP by creating the Messaging Server Initial Runtime Configuration. See 1.3 Creating the Initial Messaging Server Runtime Configuration
Note the following exception: when installing Messaging Server, check only the Messaging Multiplexor option.
7.3.3 Multiplexor Files
The Messaging Multiplexor files are stored in the msg-svr-base/config configuration file directory. You must manually edit the configuration parameters in the Messaging Multiplexor configuration files listed in Table 7–1. For a complete description of all MMP configuration parameters, see the Multiplexor Configuration Parameters in Sun Java System Messaging Server 6.3 Administration Reference.
Table 7–1 Messaging Multiplexor Configuration Files|
File |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Configuration file specifying configuration variables used for POP services. |
|
|
POP services configuration template. File comes into existence only after initial MMP start with start-msg mmp |
|
|
Configuration file specifying configuration variables used for IMAP services. |
|
|
IMAP services configuration template. File comes into existence only after initial MMP start with start-msg mmp |
|
|
Configuration file specifying which services to start and a few options shared by both POP and IMAP services. |
|
|
Configuration template specifying which services to start and a few options shared by both POP and IMAP services. File comes into existence only after initial MMP start with start-msg mmp |
|
|
Optional configuration file specifying configuration variables used for SMTP Proxy services. Required if you enable POP before SMTP; useful for maximizing support for SSL hardware even if POP before SMTP is not enabled. For more information on POP before SMTP, see 23.8 Enabling POP Before SMTP |
|
|
Configuration template specifying configuration variables used for SMTP Proxy services. File comes into existence only after initial MMP start with start-msg mmp |
As an example, the LogDir and LogLevel parameters can be found in all configuration files. In ImapProxyAService.cfg, they are used to specify logging parameters for IMAP-related events; similarly, these parameters in PopProxyAService.cfg are used to configure logging parameters for POP-related events. In SmtpProxyAService.cfg, they are used to specify logging for SMTP Proxy-related events.
In AService.cfg, however, LogDir and LogLevel are used for logging MMP-wide failures, such as the failure to start a POP, IMAP, or SMTP service.
Note –
When the MMP is configured or upgraded, the configuration template files will be overwritten.
7.3.4 Starting the Multiplexor
To start, stop, or refresh an instance of the Messaging Multiplexor, use the one of the following commands in Table 7–2 located in the msg-svr-base/sbin directory:
Table 7–2 MMP Commands|
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
start-msg mmp |
Starts the MMP (even if one is already running). |
|
stop-msg mmp |
Stops the most recently started MMP. |
|
refresh mmp |
Causes an MMP that is already running to refresh its configuration without disrupting any active connections. |
7.3.5 Modifying an Existing MMP
To modify an existing instance of the MMP, edit the ImapProxyAService.cfg and/or PopProxyAService.cfg configuration files as necessary. These configuration files are located in the msg-svr-base/config subdirectory.
7.4 Configuring MMP with SSL
To configure the MMP to use SSL, do the following:
Note –
It is assumed that the MMP is installed on a machine that does not have a Message Store or MTA.
 To Configure MMP with SSL
To Configure MMP with SSL
-
Install an SSL server certificate (see 23.5 Configuring Encryption and Certificate-Based Authentication.
-
Edit the ImapProxyAService.cfg file and uncomment the relevant SSL settings.
-
If you want SSL and POP, edit the PopProxyAService.cfg file and uncomment the relevant SSL settings.
Additionally, you must edit the AService.cfg file and add |995 after the 110 in the ServiceList setting.
-
Make sure that the BindDN and BindPass options are set in the ImapProxyAService.cfg and PopProxyAService.cfg files.
You should also set the DefaultDomain option to your default domain (the domain to use for unqualified user names).
If you just want server-side SSL support, you are finished. Start the MMP with the following command in the msg-svr-base/sbin directory:
start-msg mmp
-
If you do not want to use SSL between the MMP and the backend server, then set the SSLBacksidePort option to 0 in the ImapProxyAService.cfg or PopProxyAService.cfg MMP configuration files.
 To Configure MMP with Client Certificate-based Login
To Configure MMP with Client Certificate-based Login
If you want client certificate based login, do the following:
-
Get a copy of a client certificate and the CA certificate which signed it.
-
Import the CA certificate as a Trusted Certificate Authority (see 23.5.1 Obtaining Certificates).
-
Use the Store Administrator you created during your Messaging Server installation.
For more information, see the 20.4 Specifying Administrator Access to the Store
-
Create a certmap.conf file for the MMP. For example:
certmap default default default:DNComps default:FilterComps e=mail
This means to search for a match with the e field in the certificate DN by looking at the mail attribute in the LDAP server.
-
Edit your ImapProxyAService.cfg file and do the following:
-
If you want client certificates with POP3, repeat Step 5 for the PopProxyAService.cfg file.
-
If the MMP is not already running, start it with the following command in the msg-svr-base/sbin directory:
start-msg mmp
-
Import the client certificate into your client. In NetscapeTM Communicator, click on the padlock (Security) icon, then select Yours under Certificates, then select Import a Certificate... and follow the instructions.
Note –All your users will have to perform this step if you want to use client certificates everywhere.
7.4.1 A Sample Topology
The fictional Siroe Corporation has two Messaging Multiplexors on separate machines, each supporting several Messaging Servers. POP and IMAP user mailboxes are split across the Messaging Server machines, with each server dedicated exclusively to POP or exclusively to IMAP (You can restrict client access to POP services alone by removing the ImapProxyAService entry from the ServiceList setting; likewise, you can restrict client access to IMAP services alone by removing the PopProxyAService entry from the ServiceList setting.). Each Messaging Multiplexor also supports only POP or only IMAP. The LDAP directory service is on a separate, dedicated machine.
This topology is illustrated below in Figure 7–2.
Figure 7–2 Multiple MMPs Supporting Multiple Messaging Servers
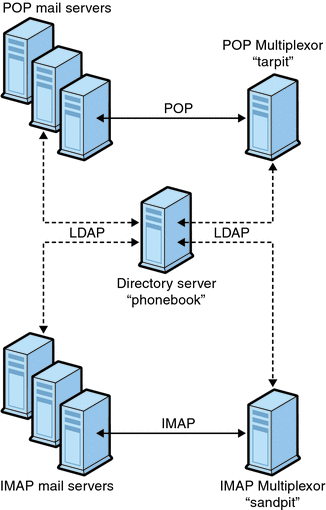
7.4.1.1 IMAP Configuration Example
The IMAP Messaging Multiplexor in Figure 7–2 is installed on sandpit, a machine with two processors. This Messaging Multiplexor is listening to the standard port for IMAP connections (143). Messaging Multiplexor communicates with the LDAP server on the host phonebook for user mailbox information, and it routes the connection to the appropriate IMAP server. It overrides the IMAP capability string, provides a virtual domain file, and supports SSL communications.
This is its ImapProxyAService.cfg configuration file:
default:LdapUrl ldap://phonebook.siroe.com/o=internet default:LogDir /opt/SUNWmsgsr/config/log default:LogLevel 5 default:BindDN "cn=Directory Manager" default:BindPass secret default:BacksidePort 143 default:Timeout 1800 default:Capability "IMAP4 IMAP4rev1 ACL QUOTA LITERAL+ NAMESPACE UIDPLUS CHILDREN BINARY LANGUAGE XSENDER X-NETSCAPE XSERVERINFO" default:SearchFormat (uid=%s) default:SSLEnable yes default:SSLPorts 993 default:SSLSecmodFile /opt/SUNWmsgsr/config/secmod.db default:SSLCertFile /opt/SUNWmsgsr/config/cert8.db default:SSLKeyFile /opt/SUNWmsgsr/config/key3.db default:SSLKeyPasswdFile /opt/SUNWmsgsr/config/sslpassword.conf default:SSLCipherSpecs all default:SSLCertNicknames Siroe.com Server-Cert default:SSLCacheDir /opt/SUNWmsgsr/config default:SSLBacksidePort 993 default:VirtualDomainFile /opt/SUNWmsgsr/config/vdmap.cfg default:VirtualDomainDelim @ default:ServerDownAlert "your IMAP server appears to be temporarily out of service" default:MailHostAttrs mailHost default:PreAuth no default:CRAMs no default:AuthCacheSize 10000 default:AuthCacheTTL 900 default:AuthService no default:AuthServiceTTL 0 default:BGMax 10000 default:BGPenalty 2 default:BGMaxBadness 60 default:BGDecay 900 default:BGLinear no default:BGExcluded /opt/SUNWmsgsr/config/bgexcl.cfg default:ConnLimits 0.0.0.0|0.0.0.0:20 default:LdapCacheSize 10000 default:LdapCacheTTL 900 default:HostedDomains yes default:DefaultDomain Siroe.com |
7.4.1.2 POP Configuration Example
The POP Messaging Multiplexor example in 7.4.1 A Sample Topology is installed on tarpit, a machine with four processors. This Messaging Multiplexor is listening to the standard port for POP connections (110). Messaging Multiplexor communicates with the LDAP server on the host phonebook for user mailbox information, and it routes the connection to the appropriate POP server.
This is its PopProxyAService.cfg configuration file:
default:LdapUrl ldap://phonebook.siroe.com/o=internet default:LogDir /opt/SUNWmsgsr/config/log default:LogLevel 5 default:BindDN "cn=Directory Manager" default:BindPass password default:BacksidePort 110 default:Timeout 1800 default:SearchFormat (uid=%s) default:SSLEnable no default:VirtualDomainFile /opt/SUNWmsgsr/config/vdmap.cfg default:VirtualDomainDelim @ default:MailHostAttrs mailHost default:PreAuth no default:CRAMs no default:AuthCacheSize 10000 default:AuthCacheTTL 900 default:AuthService no default:AuthServiceTTL 0 default:BGMax 10000 default:BGPenalty 2 default:BGMaxBadness 60 default:BGDecay 900 default:BGLinear no default:BGExcluded /opt/SUNWmsgsr/config/bgexcl.cfg default:ConnLimits 0.0.0.0|0.0.0.0:20 default:LdapCacheSize 10000 default:LdapCacheTTL 900 default:HostedDomains yes default:DefaultDomain Siroe.com |
7.5 MMP Tasks
This section describes miscellaneous MMP configuration tasks. These include:
7.5.1 To Configure Mail Access with MMP
The MMP does not make use of the PORT_ACCESS mapping table. If you wish to reject SMTP connections from certain IP addresses and you are using the MMP, you must use the TCPAccess option. The syntax of this option is the same as mailDomainAllowedServiceAccess (see Sun Java Communications Suite 5 Schema Reference). It is also described at 23.7.2 Filter Syntax.
7.5.2 To Set a Failover MMP LDAP Server
It is possible to specify more than one LDAP server for the MMP so that if one fails another takes over. Modify your PopProxyAservice.cfg or ImapProxyAservice.cfg to the following:
default:LdapUrl "ldap://ldap01.yourdomain ldap02.yourdomain/o=internet"
Note –
Make sure there is a space between the host names in the above configuration.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
